Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Hosted at http://www.allbest.ru/
VOLGOGRAD STATE TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
KAMYSHINSKY TECHNOLOGICAL INSTITUTE
DEPARTMENT OF MANAGEMENT AND BUSINESS
Course work
by subject:
Creating your own business
For example " LLC "Hotel" Favorite Territory »
Is done by a student
faculty
Economics and management
Usanova L.M.
Work checked
head of department
Kartashov B.A.
Kamyshin 2009
3. Choice of organizational and legal form of entrepreneurship
5. Business plan for a small business (firm)
7. Production plan
8. Market characteristics
9. Characteristics of competitiveness in the market
10. Marketing strategy
11. Guide
12. Risks and their accounting
13. Financial plan
Bibliography
Appendix
1. Importance of small business in Russia
After analyzing the state of small business and the scope of its development at the moment, we can conclude that our state and local authorities are extremely unfriendly to small business. As a result, the question arises - does modern Russian society need it? Maybe big business will provide Russia with everything it needs at the expense of its foreign e economic activity? This position reflects Soviet economic practice, the so-called. “gas - and not f tedollars." Of course, if Russia wants to remain a raw material about dynamics of developed countries, then small business can continue to be ignored. However, I think that such a state of affairs cannot suit Russia, about which was a great power, strives to remain one, and hopes in the future not to give up its positions, but, on the contrary, to increase them. In this case, small business is vital our country.
For the effective functioning of a market economy, it is necessary for The condition is the formation of a competitive environment through the development of entrepreneurship, including small business. This form of entrepreneurship has certain advantages: it is flexibility and instant adaptability to market conditions, the ability to quickly change the structure of production, quickly create and quickly apply new technologies and scientific developments; it is also the spirit of initiative, enterprise and dynamism.
Currently, small businesses have become essentially the backbone of the economy of the most developed countries. A striking example of this is the United States, the EU countries and Japan, in which small and medium-sized businesses account for 50-70% of GDP and 50-70% of the total number of employees.
The social significance of small business is determined by the mass character of a group of small owners - owners of small enterprises and their employees, the total number of which is one of the most significant qualitative characteristics of any country with a developed market economy. It is this group of the active population that serves the bulk of consumers, producing a range of products and services in accordance with rapidly changing market requirements.
The development of small business contributes to the gradual creation of a wide layer of small owners (middle class), who independently ensure their own well-being and a decent standard of living, which are the basis of socio-economic reforms, the guarantor of political stability and the democratic development of society.
It should also be noted that small business is not only a source of livelihood, but also a way to unlock the inner potential of the individual. The objectively inevitable restructuring of the economy is forcing an increasing number of citizens to engage in self-employment.
The small business sector is able to create new jobs, and, therefore, can reduce unemployment and social tension in the country. The mass development of small enterprises contributes to a change in the social psychology and life orientations of the bulk of the population, and is the only alternative to social dependency.
The political influence of small business in various countries is quite large, since this social group has long become the basis of the formed middle class, the most representative in terms of its size and which is the spokesman for the political preferences of a significant part of the population. In the conditions of sustainable socio-economic and political development of society, small entrepreneurs are most committed to the principles of democracy, political stability and economic freedom. The layer of small owners is most active, and even aggressive when there is a threat to property, since, unlike large and medium-sized owners, for small business owners their property is often the only means of subsistence and the most important way of self-expression. The middle class either forms its own political movements, or becomes the object of the struggle of various political forces for votes.
This factor determines the inseparability of the connection between small business and the interests of local and regional communities, which makes it dependent on the national basis and constitutes a breeding ground for its patriotic sentiments. At the same time, as the historical experience of Russia and a number of other countries testifies, patriotic sentiments among small owners in the conditions of economic recession and political instability can take extreme forms and push them to support the most extremist political forces.
The significant role of small business in the economic life of countries with a market economy is determined by the fact that the vast majority of enterprises operate in this sector of the economy, most of the economically active population is concentrated, and about half of the gross domestic product is produced.
The small business sector is most dynamically developing new types of products and economic niches, developing in industries that are unattractive to large businesses, and so on. The most important features of small enterprises are the ability to accelerate the development of investments and the high turnover of working capital. Another characteristic feature of this sector is active innovation, which contributes to the accelerated development of various sectors of the economy in all sectors of the economy.
The flexibility and high adaptability to the volatility of market conditions inherent in small business contribute to the stabilization of macroeconomic processes in the country. However, this sector is characterized by relatively low profitability, high labor intensity, difficulties with the introduction of new technologies, limited own resources and increased risk in intense competition. This leads to constant renewal in the SE sector due to massive bankruptcies or re-specialization of activities.
With all this, I would like to note the great potential for the development of small businesses in such sectors as agriculture and the industry involved in the processing of agricultural products. This direction is considered the most promising, therefore, work to stimulate the growth of small firms in these areas should be carried out now. The need for this step has long come, and if the Russian leadership continues to delay the development of a program to support and develop the domestic agro-industrial complex, then our country risks losing a lot of time and making life very difficult for itself, which happens in Russia quite often and regularly. This must not be allowed under any circumstances!
2. Brief description of the current state of small business in Kamyshin
The state of small business is clearly reflected in the economic and social development of the city. Since basically all consumer goods and services are the result of the activities of small businesses. Whichever way you turn, today it is the most dynamically developing sector of the city's economy.
As of January 1, 2008, 4,466 individuals and 568 legal entities engaged in entrepreneurial activities, which are payers of local taxes, are registered in Kamyshin. In the field of small and medium business in 2007. 14,051 people were employed (28.9% of the total number of employees). Key performance indicators of small enterprises in 2007-2008. are presented in table 1.
The volume of production of small enterprises is more than 40% of the total production in the city. Their profitability is on average higher than in other enterprises, and ranges from 15-25 percent. And the profit received by them, in certain industries, even reaches 45 - 50%. Tax revenues in the budgets of different levels from small enterprises average 25% or more.
Table 1. Key performance indicators of small businesses in Kamyshin for 2007-2008
|
Indicators |
|||||||
|
including small businesses |
Specific weight, % |
Total legal entities in the city |
including small businesses |
Specific weight, % |
|||
|
Number of enterprises in total |
|||||||
|
Including: |
|||||||
|
industry |
|||||||
|
construction |
|||||||
|
transport |
|||||||
|
wholesale |
|||||||
|
household service |
|||||||
As can be seen from the table (Appendix A), in 2008 the main part of enterprises operated in the sectors of construction, wholesale and retail trade. Small businesses are more prone to trading and purchasing activities, where the time between investing capital and making a profit was much shorter than in the production of products. The share of small businesses in the total number of legal entities in the city amounted to 37.6%.
The share of the working population employed at small enterprises of the city in 2007 was 28.9%, and at the beginning of 2008 it was 30.2% (Table 2).
Table 2. The share of the working population at small enterprises of the city.
|
Indicators |
|||||||
|
Total population |
Specific weight, % |
Total population |
including small businesses |
Specific weight, % |
|||
|
Number of employees, total |
|||||||
|
including: |
|||||||
|
industry |
|||||||
|
construction |
|||||||
|
transport |
|||||||
|
retail and catering |
|||||||
|
household service |
|||||||
|
other industries |
As of July 1, 2008, 4,569 individuals and 595 legal entities engaged in entrepreneurial activities are registered in the city. In the revenue side of the city budget, the share of receipts from the small business sector amounted to 100,000 rubles in the first half of 2003. - 10.8%.
As of January 1, 2008 according to the State Register of Enterprises, 1,273 legal entities are registered with the tax inspectorate, of which 48 are state and 82 are municipal; with private administrative property - 1132, 7 banks, 4 insurance organizations.
Out of 4,999 entrepreneurs registered as of January 1, 2008, 4,292 were engaged in trade and purchasing activities, 31 - in consumer services; 29 people were employed in the socio-cultural sphere, 262 - in intermediary activities; 15 - fishing; 370 - other.
As a result of the analysis of the development of entrepreneurship in the city of Kamyshin, it can be concluded that the number of legal entities in 2007-2008. increased by 2.24 times, and physical - by 1.12 times.
3. Choice of organizational - legal form of entrepreneurship
From the whole variety of organizational and legal forms operating on the territory of the Russian Federation for a newly created new enterprise, we will choose such an organizational and legal form as a limited liability company. Moreover, this legal form is most common among small and medium-sized enterprises.
A limited liability company (LLC) is a company established by one or more persons, the authorized capital of which is divided into shares determined by the constituent documents of the size. The participants in this company are not liable for its debts and only bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company, within the value of their contributions.
Even participants who have not made their contributions in full are liable for the obligations of a limited liability company only with that part of their personal property that corresponds to the value of the unpaid part of the contribution (clause 1, article 87 of the Civil Code).
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 89 of the Civil Code, it is provided that the number of participants in a limited liability company should not exceed the limit established by the law on these companies. Otherwise, it is subject to transformation into a joint-stock company within a year, and after the expiration of this period - to liquidation by judicial procedure, if the number of its participants does not decrease to the limit established by law. It should be noted that the federal law on limited liability companies has not yet been adopted.
The trade name of a limited liability company must contain the name of the company and the words "limited liability" (clause 2, article 87 of the Civil Code).
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 89 of the Civil Code, a limited liability company must have two constituent documents: a constituent agreement signed by its founders and a charter approved by them.
In addition to the information specified in paragraph 1 of Article 52 of the Civil Code, the constituent documents of a limited liability company must contain the mandatory information required for the documents of this company. These include conditions on the size of the authorized capital of a limited liability company, on the size of the shares of each of the participants, on the amount, composition, timing and procedure for making contributions by them, on the liability of participants for violation of obligations to make contributions, on the composition and competence of the company's management bodies and the procedure for making decisions by them, including on issues, decisions on which are taken unanimously or by a qualified majority of votes, as well as other information provided for by the law on limited liability companies (clause 2 of article 89 of the Civil Code).
A limited liability company is reorganized or liquidated voluntarily by a unanimous decision of its participants. It can also be liquidated on the general grounds specified in Article 61 of the Civil Code.
A limited liability company can be reorganized in the form of transformation into a joint-stock company or a production cooperative (clause 2, article 91 of the Civil Code).
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for a two-tier management system in a limited liability company (Article 91 of the Civil Code)
The supreme body of this society is the general meeting of its members. The following issues fall within the exclusive competence of the general meeting:
1. Change of the charter of the company, including the amount of its authorized capital.
2. Formation of the executive bodies of the company and early termination of their powers.
3. Approval of the company's annual reports and balance sheets and distribution of its profits and losses.
4. Decision on reorganization or liquidation of the company.
5. Election of the audit commission (auditor) of the company.
The competence of the general meeting cannot be reduced, but it can be expanded by the law on limited liability companies or the charter of the company. Issues not referred to the exclusive competence of the general meeting are within the competence of the executive (collegiate and (or) sole) accountable to it. The sole management body may also be elected from among the members of a limited liability company.
The general meeting of a limited liability company elects an audit commission or an auditor.
An external audit may be used to verify and confirm the correctness of the annual financial statements. An audit can be carried out at the request of both the general meeting and any of the company's participants. The procedure for conducting audits is determined by law and the charter of the company (clause 4 of article 91 of the Civil Code). Publication by the company of information on the results of the conduct of its affairs (public reporting) is not required (clause 5 of article 91).
The basis of the property isolation of a limited liability company is its authorized capital, which is made up of the value of the contributions of the participants in the company. In accordance with paragraph 1 of article 90 of the Civil Code, the authorized capital determines the minimum amount of the company's property that guarantees the interests of its creditors. The size of the authorized capital cannot be less than the amount established by law. Since the law on limited liability companies has not yet been adopted, the Regulation on the procedure for registering business entities, approved by Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of July 8, 1994 N 1482, is in force. be less than the amount equal to 100 times the minimum wage per month, established by law on the date of submission for registration of the constituent documents of a limited liability company.
The Civil Code provides that all members of a limited liability company must participate in the formation of the authorized capital of the company by paying contributions. The release of a member of the company from this obligation is not allowed (clause 2, article 90 of the Civil Code). However, it provides for the possibility of paying the authorized capital in installments, and at the time of registration of the company, its authorized capital must be paid in at least half. The remaining unpaid part of the authorized capital of the company must be paid by its participants during the first year of the company's activity (clause 3, article 90 of the Civil Code).
It should be noted that a decrease in the authorized capital of a limited liability company leads to a weakening of the guarantees of its creditors. In order to avoid such situations, the Civil Code introduces the concept of a company's net assets. They should be understood as the actual value of all property of a limited liability company without the value of existing debts.
If the net assets of a limited liability company at the end of the second and each subsequent financial year turn out to be less than the authorized capital, the company is obliged to announce this decrease and register the decrease in the prescribed manner or terminate its activities through liquidation (paragraph 4 of article 90 of the Civil Code). The reduction of the authorized capital is allowed after notification of all creditors of the company. Creditors in this case may demand early termination or performance of the relevant obligations with the obligation to compensate for losses on the company (clause 5 of article 90 of the Civil Code).
An increase in the authorized capital of a limited liability company is allowed after all its participants have made contributions in full, i.e. after full payment of the entire declared capital (clause 6 of article 90 of the Civil Code).
Clause 1 of Article 93 of the Civil Code provides that a participant in a limited liability company has the right to transfer his share or part of it in the authorized capital of the company to one or more of its participants.
Alienation by a company participant of his share or part of it to third parties is allowed, unless otherwise provided by the company's charter (clause 2, article 93 of the Civil Code).
The Civil Code (clause 4, article 93 of the Civil Code) does not allow the alienation of the unpaid part of the debt in the authorized capital.
Members of the company enjoy the pre-emptive right to purchase a share (or part thereof) of a withdrawing member. This right belongs to all participants in the company in proportion to the size of their shares in the authorized capital, unless the company's charter or agreement of its participants provides for a different procedure for exercising this right. If the participants in the company do not use their pre-emptive right within a month from the date of notification or within another period provided for by the charter of the company or agreement of its participants, the share of the retired participant may be alienated to a third party (clause 2 of article 93 of the Civil Code). If the participants in the company refuse to purchase a share, and the charter of a limited liability company does not provide for its alienation to third parties, the company itself must acquire this share from the alienator by paying him the actual value of the share, or give in kind property corresponding to such a value (clause 3 of Art. .93 GK).
In accordance with paragraph 5 of article 93 of the Civil Code, a limited liability company is obliged to sell the acquired share of a participant to other participants or reduce its authorized capital by this share.
Clause 6 of Article 93 of the Civil Code provides that the heirs of citizens and the legal successors of legal entities that are participants in a limited liability company are transferred their debts in the authorized capital of the company. However, the constituent documents of the company may provide that such a transfer is allowed only with the consent of the other participants in the company. In this case, the company is obliged to pay to the heirs or successors the actual value of the share or to give them property in kind for such a value. The procedure and conditions for such compensation are provided for by the founding documents of a limited liability company.
A participant in a limited liability company has the right to leave the company at any time without the consent of other participants (Article 94 of the Civil Code). At the same time, he must be paid the value of the part of the property corresponding to his share in the authorized capital. The procedure, method and terms for issuing or paying the value of property to a withdrawing participant must be regulated by the constituent documents of a limited liability company, tk. there is no law on these companies.
4. State registration of entrepreneurial activity
The procedure for state registration of individual entrepreneurs is established by the Regulations on the procedure for state registration of business entities, determined by the Federal Law of August 8, 2001 No. 129-FZ “On State Registration of Legal Entities”. The documents specified in the law are submitted to the tax office, and after 5 days a certificate of state registration of a legal entity is issued. In turn, the tax inspectorate assigns a TIN, sends the necessary documents to the State Statistics Committee for assigning codes, notifies non-budgetary funds that the organization is registered on such and such a date, the state number is such and such.
Registration of an enterprise takes place according to the following scheme:
1. For state registration of an enterprise, the following documents must be submitted:
An application for registration of an enterprise, drawn up in any form and signed by the founder (founders) of the enterprise;
The charter of the enterprise approved by the founder (founders);
Decision on the establishment of an enterprise or an agreement of founders;
Documents confirming the payment of at least 50 percent of the authorized capital (fund) of the enterprise specified in the decision on the establishment of the enterprise or the agreement of founders;
Certificate of payment of the state fee.
The state registration of general partnerships does not require the submission of a charter, and the state registration of non-profit organizations with the right to conduct entrepreneurial activities does not require the submission of a decision on the establishment of an enterprise or an agreement of founders.
In cases of establishment of an enterprise by one founder, the decision on the establishment of the enterprise shall be considered the charter of the enterprise approved by him.
2. The founding documents of an enterprise are submitted to the registering body by its founder (founders) or representatives of the founder (founders) or sent to the registering body by valuable mail with notification and description of the attachment.
The date of submission of constituent documents for registration of an enterprise is, respectively, the date of their actual submission to the registering authority or the date of posting indicated in the receipt of the postal item with a description of the sent constituent documents. In the latter case, the receipt certifies the fact that these documents have been submitted for registration.
3. When registering an enterprise, the following requirements are imposed on the constituent documents in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation:
a) the charter must contain information about the organizational and legal form, name, location of the enterprise, the amount of its authorized capital (fund), the composition, procedure for the formation and competence of its management and control bodies, the procedure for distributing profits and forming funds of the enterprise, the procedure and conditions for reorganization and liquidation of the enterprise;
b) for state and municipal enterprises, as well as non-profit organizations that have the right to conduct entrepreneurial activities, it is mandatory to indicate in their charters the types of activities carried out by enterprises;
c) the agreement of the founders must contain information about the name (name) and legal status of the founders, their location (residence), state registration (for legal entities) or identity (passport data - for individuals), the amount of the authorized capital of the newly created enterprise, participation shares ( shares, the number of shares) owned by each founder, the size, procedure and methods of making contributions (payment for shares).
The agreement of the founders of a full or mixed partnership also indicates the numbers of certificates of registration as entrepreneurs of citizens who are its full members;
d) the size of the authorized capital (fund) of a joint-stock company, an enterprise with a share of foreign investment (a joint venture, regardless of its organizational and legal form), a state or municipal enterprise must not be less than an amount equal to 1,000 times the minimum wage per month, established by the legislation of the Russian Federation as of the date of submission of constituent documents for registration;
e) The size of the authorized capital (fund) of enterprises of other organizational and legal forms should not be less than the amount equal to 100 times the minimum wage per month established by the legislation of the Russian Federation as of the date of submission of constituent documents for registration;
f) when submitting documents for registration of an enterprise, the size of the authorized capital (fund) of which exceeds the amount established by the antimonopoly legislation of the Russian Federation, the founder (founders) is obliged to submit a document confirming the consent of the relevant antimonopoly body to the establishment of the enterprise;
g) when submitting documents for registration of an enterprise whose founders include state and (or) municipal enterprises, it is necessary to submit documents confirming the approval by the relevant property management committee or other authorized body of the amount and method of payment of contributions by state and (or) municipal enterprises in the authorized capital (fund) of the registered enterprise, except for the cases when the said contributions are made in monetary form at the expense of the profits of the founding enterprises;
h) the decision to create an individual private enterprise is drawn up in an arbitrary form without mandatory notarization (in the case of presentation of documents proving the identity of the founder).
4. During the state registration of an enterprise, it is not allowed to require letters of guarantee and other documents confirming its location, specified in the constituent documents (charter) of the enterprise. Responsibility for damage that may be caused to third parties due to the unreliability of the location of the enterprise indicated in the constituent documents (charter) shall be borne by its founder (founders).
Presentation by registering and other state bodies of other requirements for applicants and constituent documents submitted by them for registration, except for those provided for by this Regulation, is not allowed.
5. Registration of enterprises is carried out by the registering authority no later than three days from the date of submission of the necessary documents or within 30 calendar days from the date of posting indicated in the receipt for sending the constituent documents listed in paragraph 2 of this Regulation.
Registration is carried out by assigning to the enterprise the next number in the register of incoming documents and affixing a special inscription (stamp) with the name of the registering authority, number and date on the first page (title page) of the enterprise charter, sealed with the signature of the official responsible for registration.
5. Business plan for a small business (firm)
Planning is an essential part of any business venture, no matter how big or small. A business plan is a planning document that summarizes the analysis of opportunities for starting or expanding a business in a particular situation and gives a clear idea of how the management staff of a given company intends to use these opportunities.
Most small businesses resort to drawing up business plans mainly to obtain loans, search for investors, participate in investment competitions and privatization projects.
A business plan is a detailed, clearly structured, and carefully prepared document that describes what the firm is aiming for, how it intends to achieve its goals, and what it will look like once it has been achieved. This is a convenient, generally accepted form of familiarization of potential investors with the project in which they are invited to participate.
The need for business planning is as follows: taking the first steps, small businesses are faced, firstly, with a lack of financial resources, and secondly, with many unforeseen circumstances that can lead your business away from the chosen course. To avoid this, you must first set out your goals, estimates and forecasts on paper, that is, draw up a business plan.
There are two main reasons for preparing a business plan:
to convince outside investors of the expediency of investing money in your business or providing a loan;
help you stay on course and not let random circumstances deviate you from your chosen goal.
However, this does not mean that everything outlined in the plan will certainly be fulfilled: the goals and objectives will be adjusted as additional information becomes available and practical experience is gained. A business plan does not guarantee getting rid of problems, but it increases the efficiency of managing a company.
The main goal of a business plan is to reach a reasonable and feasible compromise between what the firm wants and what it can achieve.
Picture. 1. Outlines of the business plan.
Business analysis of the external environment and the current state of the enterprise is a necessary prerequisite for the development of an effective plan. It is aimed at obtaining and summarizing objective information about the state of the enterprise, its compliance with the requirements of the external environment and internal organization. The structure of business analysis is presented in table 3.
Table 3. The structure of business analysis.
Environmental analysis is a process by which an entrepreneur or manager assesses external dangers and opportunities that may hinder or help achieve their goals.
Self-analysis is a methodical assessment of all areas of the enterprise. It is aimed at identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise, designed to help identify those areas that require more detailed consideration or improvement, and at the same time see what tasks were set in the previous period of time and whether they were completed, what were the reasons for the failures.
Analysis is necessary not only when drawing up a business plan, it is also useful in current activities.
For an early-stage firm, the business plan is in many ways the first attempt at strategic planning. The plan is used to set development guidelines for the next few years. The intended direction of development should be clear and precise, understandable to the company's employees and potential creditors and investors.
The period of time for which a business plan is developed can be very different, it depends on the specifics of the business and product. Experience shows that too long a planning horizon only leads to the meaninglessness of all calculations. Usually the plan is drawn up for two or three years with a detailed study of the first year and an enlarged forecast for the next period. Although the plan can be drawn up for five years, and for one year.
A business plan is a general strategy for the company's activities in a particular product market.
Most managers consider a business plan as a necessary document to receive money from a bank or another investor, lender. For this reason, businesses that do not require additional capital do not write a business plan without fully understanding the business planning process, its benefits and benefits.
A business plan allows you to solve a number of tasks, but the main ones are the following:
substantiation of the economic feasibility of the company's development directions;
calculation of expected financial performance, primarily sales volumes, profits, capital gains;
determination of the planned source of financing for the implementation of the chosen strategy, i.e. ways of concentrating financial resources;
selection of employees who are able to implement this plan.
A business plan can be used in various situations and to the benefit of various people - managers, owners, investors.
So, a business plan is needed in the following situations:
The company needs capital for further development. Forms of raising capital can be different. Most often, this is the main argument for drawing up a business plan.
a new company is created or the owner changes, so a development strategy is being developed.
a business plan is being developed at a time of significant change
(reconstruction, purchase of equipment, transition to the production of new products, etc.).
In order to achieve your goals and obtain funds, you need to communicate something intriguing about the prospects of this business, combined with a well-prepared presentation of numbers and research. The idea should be not only good in itself, but also well presented.
Three types of people are interested in a business plan: managers, owners, creditors. Managers are usually the creators and executors of the business plan. It is often forgotten that managers can gain important benefits from the planning process itself, not just from the plan. The owners are interested in drawing up a business plan in terms of the prospects for the development of the company. In small firms, the manager can be the owner at the same time, that is, he can act in different roles: as the creator of the plan, its executor, and the controlling body.
This project is the creation of a new enterprise by establishing a limited liability company Hotel Lyubimy Krai LLC - a private hotel close to a three-star hotel in accordance with the requirements for the hotel and its number of rooms listed in Annexes A1, A2. Dedicated to substantiating the efficiency of construction and commissioning of a private hotel.
The objectives of the business plan are:
1. Justification of the profitability of the construction and commissioning of a private hotel designed for guests of the city of Kamyshin, who come from various cities of Russia for various purposes (business trip, tourism, sports, transit, etc.)
2. Evaluation of the expected financial results of the business.
The private hotel "Lubimiy Krai" is a five-story building located on the picturesque bank of the Volga River and has convenient transportation. The hotel "Lyubimy Krai" is a private hotel, the services provided by which at the new stage of development are planned to be as close as possible to world standards.
On the ground floor of the hotel are planned: a bar-restaurant, a billiard room, a sauna, a SPA-salon, cosmetic and hairdressing services, a gym, medical services. The hotel lobby will be equipped with a reception and accommodation service with a seating and waiting area with appropriate furniture (armchairs, a sofa, chairs, coffee tables with newspapers and magazines), individual safe boxes for storing guests' valuables, terminals, ATMs, taxi call services will be provided. , long-distance and international communication.
It is planned to put into operation the number of rooms on 4 floors (second, third, fourth, fifth), equip the rooms with good furniture, maximizing the comfort of residents (number of rooms - 102, number of seats - 192).
Total in the Hotel:
Single three-room apartments (Apartments) - 2
single two-room (Lux) - 18
single one-room apartments (improved category 1) - 38
One of the most important factors influencing the successful implementation and ensuring the planned return on investment is the predicted stable attendance of the hotel. The competitiveness of the company is ensured by the variety of hotel services offered, the favorable location of the construction site.
The main risks of the project are:
Reduction of tourism business in the country and region;
Unfavorable factors classified as "force majeure".
The main strategy of the company is to attract customers with high quality and service.
The payback period of investments is 5 years.
The calculations given in the business plan give reason to believe that the Lyubimy Kray Hotel LLC will complete the construction process and will be put into operation as scheduled.
The projected profitability of activities assumes a short period of accumulation of net profit sufficient to make a profit and, at the same time, a large margin of financial stability.
7. Production plan
This section is one of the most important sections in planning the construction process. Drawing up a production plan is necessary in order to assess the feasibility of the planned construction process, taking into account the size of the investment, as well as the qualifications of the company's management and the validity of its plans.
The production plan for the construction of the hotel is designed for two years.
The program is calculated on the basis of the available capacities of the enterprise, in this case contractors and the necessary rental construction equipment. The production plan takes into account the list for the purchase of the necessary raw materials and equipment and the types of work performed in the construction process. The section provides an organizational chart of the company, as it is necessary to coordinate the planned actions and control. It is also necessary to highlight the issues of remuneration of administrative and managerial and production personnel.
Thus, the development of this section consists of the following steps:
I stage. Composition and cost of works:
1. Types of work performed during the construction of a private hotel.
2. Construction costs.
Stage II. Subcontracts:
1. Availability of contractors.
2. Distribution of construction work.
Stage III. Construction equipment:
1. Provision of contractors with construction equipment.
2. The cost of operating construction equipment.
IV stage. Hotel equipment:
1. List of required equipment.
2. The cost of purchasing equipment.
V stage. Raw materials and supplies:
1. List of materials
2. Purchase costs.
VI stage. Human Resources:
1. Availability of a workforce of the necessary qualifications.
2. Labor costs.
The construction process used in the implementation of the project is of the type of single construction, which is characterized by the uniqueness of the project, the construction of the first three-star hotel in Kamyshin. At the same time, the construction process is carried out on various equipment, including foreign ones, as well as the latest technologies used in the West in the construction of private hotels. This entails the involvement of Western specialists, which explains the high level of wages.
The construction process consists of four main stages: preparatory work, main work, finishing work, installation and adjustment of equipment.
During the preparatory work, a site for the construction of a hotel is prepared, a foundation pit is dug, according to the project for the production of works, equipment and machinery necessary for construction are imported and installed, a temporary fence and housing are erected.
At the main stage, the foundation is poured, floors are erected, equipment is installed, rooms are equipped.
The final stage involves the final check of the quality of construction, cleaning the territory, inspecting hotel rooms, preparing them for work.
The composition and cost of work is indicated in table 4.
Table 4. Composition and cost of work.
|
Name of works |
Name of contractor organization |
Total, thousand rubles |
||
|
Site preparation |
StroyConsulting |
|||
|
Installation of the necessary equipment to start construction |
Construction equipment and accessories. OOO "Arlit" |
|||
|
Digging a pit |
StroyConsulting |
|||
|
Transport work |
LLC "Business Auto" |
|||
|
Foundation pouring |
StroyConsulting |
|||
|
Procurement work |
StroyConsulting |
|||
|
Construction and installation works |
||||
|
Construction of vertical structures (floors) |
Construction company "Ventall" |
|||
|
Room equipment |
Construction company "Ventall" |
|||
|
Exterior finish |
Exterior and interior decoration of buildings. LLC "Business Stroy" |
|||
|
Interior decoration |
Exterior and interior decoration of buildings. LLC "Business Stroy" |
|||
|
Installation and adjustment of working equipment |
Firm "Aqwaland" |
|||
|
Special works |
Construction company "Ventall" |
|||
When carrying out general construction works, a number of subcontractors were involved in the process, with each of which a contract is concluded for the construction and operation of the necessary equipment for a period in accordance with the project documentation. List of subcontractors in table 5.
Table 5. Subcontracts.
For construction, according to contracts with subcontractors, construction machines and equipment are needed. Taking into account market prices and possible price increases within two years for the operation and maintenance of construction machinery and equipment, a preliminary list of costs is compiled.
Table 6 Construction equipment.
|
Name of equipment |
Quantity, pcs. |
Price per hour of work, thousand rubles |
Number of page hours |
Total, thousand rubles |
||
|
jib crane |
||||||
|
concrete pump |
||||||
|
Small Material Conveyor |
||||||
|
Single bucket excavator |
||||||
|
Road preparation machines |
||||||
|
Plitovoz |
||||||
|
Panelevoz |
||||||
|
Truck crane |
||||||
|
Construction cradles |
||||||
Hotel equipment and furniture will be ordered from elite Russian salons, which explains the high price level.
Table 7. Equipment for a private hotel.
|
Name of equipment |
Quantity, pcs. |
Price per piece, thousand rubles |
Total, thousand rubles |
||
|
garage building |
|||||
|
Hotel building |
|||||
|
Chevrolet Niva car |
|||||
|
Aquarium hexagonal |
|||||
|
billiard table |
|||||
|
Fan |
|||||
|
Exhibition cabinet |
|||||
|
Banknote detector |
|||||
|
Air conditioning |
|||||
|
Cash register |
|||||
|
Computer equipment |
|||||
|
washing machine |
|||||
|
Drying machine |
|||||
|
A set of furniture in the rooms |
|||||
|
Kitchen equipment |
|||||
|
Dishes in the room stock |
|||||
|
Towel |
|||||
|
Linens |
|||||
|
Robe mahr. |
|||||
|
split system |
|||||
|
Sport equipment |
|||||
|
TV set |
|||||
|
Fridge |
|||||
|
electric kettle |
|||||
Table 8 shows the cost of fixed production assets, from which depreciation costs are subsequently charged.
Table 8. The cost of fixed production assets.
|
Name of equipment |
Total, thousand rubles |
||
|
garage building |
|||
|
Hotel building |
|||
|
Chevrolet Niva car |
|||
|
Aquarium hexagonal |
|||
|
billiard table |
|||
|
Fan |
|||
|
Exhibition cabinet |
|||
|
Furniture (reception and accommodation service) |
|||
|
Banknote detector |
|||
|
Air conditioning |
|||
|
Cash register |
|||
|
Computer equipment |
|||
|
washing machine |
|||
|
Drying machine |
|||
|
A set of furniture in the rooms |
|||
|
Conference room equipment |
|||
|
Kitchen equipment |
|||
|
Dishes in the room stock |
|||
|
Towel |
|||
|
Linens |
|||
|
Robe mahr. |
|||
|
split system |
|||
|
Sport equipment |
|||
|
TV set |
|||
|
Fridge |
|||
|
electric kettle |
|||
For construction, raw materials and materials will be needed. All raw materials and materials will be purchased in Kamyshin and Volgograd.
Table 9. Raw materials and materials.
|
Name of materials |
Quantity, piece, mesh, m3 |
Price per unit, thousand rubles |
Total, thousand rubles |
||
|
concrete mix |
|||||
|
floor slabs |
|||||
|
Wall panels |
|||||
|
Coating slabs |
|||||
|
Roof insulation |
|||||
|
Synthetic materials |
|||||
|
Thermal and sound insulation materials |
|||||
|
Ruberoid |
|||||
|
Drywall |
|||||
|
Stair flights, landings |
|||||
|
Decoration Materials |
|||||
The number of production personnel is determined based on the functional feasibility and the number of employees of similar construction companies.
The wage system, in accordance with its creative nature, is based on the use of a time-bonus form. In the future, it is envisaged to switch to a point system for organizing remuneration, which takes into account the quantity and quality of labor expended more flexibly.
The remuneration of labor of managers and other categories of employees is built on the basis of official salaries and depending on the amount of time actually worked and the achievement of the final results of the enterprise.
Table 10. The number of production personnel and the wage fund for 2 years.
|
Speciality |
Wage fund for 2 years, thousand rubles |
|||||
|
Installer |
||||||
|
Supplier |
||||||
|
plumber |
||||||
|
Electrician |
||||||
|
Roofer |
||||||
|
Mason |
||||||
|
Plasterer |
||||||
|
Driver |
||||||
|
Finisher |
||||||
|
Handymen |
||||||
Table 11. Number of managers and other categories of employees and wage fund for 2 years.
|
Speciality |
Number of employed people |
Monthly salary of an employee, thousand rubles |
Monthly payroll fund, thousand rubles |
Payroll fund for 2 years, thousand rubles |
||
|
Gene. Director |
||||||
|
Ch. Accountant |
||||||
|
Ch. Engineer |
||||||
|
Process Engineer |
||||||
|
Head of Financial Department |
||||||
|
Head of production department |
||||||
|
Section chief |
||||||
|
Architect |
||||||
|
Designer |
||||||
|
Head Warehouse |
||||||
|
Cleaning woman |
||||||
Below are calculations of the economic elements of construction costs.
Water for technological purposes and wastewater intake:
Where: - water costs, thousand rubles;
N is the number of months;
Monthly consumption, cubic meters m.;
Price for 1 cu. m. of water, rub.
Z B \u003d 24 * 680 * 16.35 \u003d 266.8 thousand rubles.
Energy costs will be:
Where: - the cost of electricity consumed by the equipment for lighting, thousand rubles;
The amount of electricity consumed, kWh per month.
Tariff rate for one kWh of electricity, rub.
E sv \u003d 24 * 14000 * 3.92 \u003d 1317.1 thousand rubles.
The cost of heating the production premises will be:
Where: - the cost of heating costs, thousand rubles;
Heated period, months;
Price of 1 Gcal of thermal energy;
The amount of consumed thermal energy, Gcal.
Z from \u003d 12 * 824.43 * 140 \u003d 1385.0 thousand rubles.
The cost of gasoline for a car is:
Where: - the cost of gasoline, thousand rubles;
100 km - average daily car mileage
340 - the number of days of operation;
The consumption rate of gasoline per 1 km is 0.15 liters;
C - the price of 1 liter of gasoline is 26 rubles.
Z b \u003d 100 * 340 * 0.15 * 24 \u003d 122.4 thousand rubles.
Labor costs for the enterprise for 2 years will be, thousand rubles.
Where: F - wage fund of the enterprise for 2 years, thousand rubles;
Payroll fund for production personnel for 2 years, thousand rubles;
Payroll fund for managers and other categories of employees for 2 years, thousand rubles.
Ф = 5 592 + 3 336 = 8928 thousand rubles.
The unified social tax is charged at a rate of 26% and will be:
8928 * 26% = 2321 thousand rubles
The absolute value of depreciation charges is determined on the basis of the current depreciation rates for each element of fixed assets in the amount of 20% per year of the initial cost table 12.
Table 12. The absolute value of depreciation deductions of fixed production assets for two years.
|
Name of equipment |
Total, thousand rubles |
Depreciation rate, % |
Amortization amount, thousand rubles |
||
|
garage building |
|||||
|
Hotel building |
|||||
|
Chevrolet Niva car |
|||||
|
Aquarium hexagonal |
|||||
|
billiard table |
|||||
|
Fan |
|||||
|
Exhibition cabinet |
|||||
|
Furniture (reception and accommodation service) |
|||||
|
Banknote detector |
|||||
|
Air conditioning |
|||||
|
Cash register |
|||||
|
Computer equipment |
Similar Documents
The history of the origin and development of entrepreneurship in Russia. The activities of famous Russian entrepreneurs S.I. Mamontova, P.M. Tretyakova, A.M. Sibiryakov. The procedure for state registration of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs.
abstract, added 12/05/2010
The concept and general features of individual entrepreneurship. The procedure for state registration and licensing of individual entrepreneurs. Tax system and responsibility. Small and medium business support programs.
thesis, added 01/19/2011
Study of the concept, subjects and main activities of small business. Characteristics of the structure of small businesses in terms of the number of employees. Analysis of the legislative framework and taxation, state support for entrepreneurs.
term paper, added 01/17/2012
Essence, functions, subjects of entrepreneurship and business. The value of state support for small businesses in a market economy. Analysis of the current state, problems and prospects for the development of small businesses in the Karaganda region.
term paper, added 10/27/2010
Modern problems of small business development in Russia. Sequence of business unit registration. Business plan of the computer club "Victoria". Characteristics of a new business, competitiveness assessment, financial plan.
business plan, added on 12/15/2010
The essence of small business, the stages of its formation in Russia. Startup Support Program - grants to start your own business. Program to promote the support of entrepreneurs by the municipality of non-urban territories.
term paper, added 12/22/2011
The concept of small business, a brief economic description of small business. Features and place of small business in the economy. Evolution and classification of problems, possible solutions. Prospects for the development of small business in Russia.
term paper, added 05/06/2010
The procedure for state registration, re-registration and termination of activities. Peculiarities of regulatory and legal regulation of the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation. Comparative analysis of traditional entrepreneurship and network business.
term paper, added 04/09/2009
The essence and characteristics of a small business, its place in the economy of developed countries. The history of the formation of small business in the Russian Federation, an assessment of its current state. The system of state support and regulation of small business.
term paper, added 06/26/2014
Social and economic essence of small business. Prerequisites for the formation of innovative foundations for small business. Analysis of the current state and development trends of small business in Russia and the Republic of Tatarstan.
To create a business, you need to decide on the ultimate goal. About 70% of all new business projects do not overcome the 3-year milestone and are closed. Over the next three years, approximately 2/3 of the remaining number of projects is eliminated. Thus, only 10% of all companies survive in today's market.
Basic goals:
- To work for yourself. Such a goal is doomed to failure from the outset. In order for a business to develop, you need to be well versed in the chosen niche and love your job.
- Financial independence. Another bad goal setting. Business is not created initially for money. Finance is a natural extension of running a successful business, not the original goal.
- Creation of a quality product/service. Such a goal may well be realized. Focusing on quality is always the key to the success of any business.
There are also intermediate subgoals, which include market, innovation, economic, social and other goals.
Basics
To successfully open a business, it is necessary to take into account the competition in the existing market. Even if the goods or services provided are of high quality, they may not be in demand due to competition. A low level of knowledge in the chosen niche is the most common reason for closing a business. It is necessary to understand not only the product or service itself, but also be able to competently provide them to the consumer.
To achieve success in business, it is necessary to adhere to generally recognized fundamentals:
- Theoretical and psychological preparation. You need to understand that starting a business is not a matter of a few days or even months. A successful business can begin to generate a stable income only after a few years. Pay special attention to financial management. For example, predetermine the taxation system.
- Business idea. A good business idea is half the battle. A high-quality idea is characterized by the following features: high profitability, useful properties of the product/service, need for the provided product, high quality. Once identified with an idea, it is recommended to create a marketing plan.
- Selling mechanism. Due to the competent drawing up of a mechanism for the sale of a product or service, it is possible to achieve a reduction in cost, and hence an increase in competitiveness.
- Finance appraisal. It is necessary to provide not only the costs of starting a business, but also possible financial injections to support it even in the worst case scenario. You should also calculate the payback period of the business, and when it will begin to make a profit.
- Choice of organizational-legal form. Sole proprietorship, LLC, joint-stock company or other form of company - this choice should be made in advance. To do this, you need to know how many employees will be in the company, what rights each of the co-founders has, whether financial injections from outside are needed, and what form of taxation is preferable.
- Room, equipment. For any type of business, you will definitely need at least a room. At the same time, it is important to choose the material base in accordance with the estimated capacities so that there are no unnecessary overpayments. You also need to decide whether to rent a room or buy a property.
Creating your own business in Russia is carried out in accordance with the current civil legislation, federal laws on individual organizational and legal forms of participants in entrepreneurial activity and regulations that regulate the entire process of creating and functioning of entrepreneurial organizations. Creating your own business in one or another organizational and legal form involves the following prerequisites
- availability of property for the formation of initial capital;
- the availability of a certain amount of financial resources necessary to form the minimum amount of the authorized (share) capital;
- the availability of non-residential premises necessary to accommodate the office of the future organization and the implementation of the intended activities, or the availability of opportunities for renting non-residential premises;
- preliminary study of the intended market, in which the entrepreneur will offer the result of entrepreneurial activity for implementation;
- formation of a team of qualified founders (partners) of their own business, who are well aware of the technology for carrying out certain types of activities, accounting and tax accounting, etc.
It is important for the entrepreneur himself to objectively answer the following question: do I have everything necessary to run my own business? Since the entrepreneur will be the most important worker in his company, he needs to give an objective assessment of his positive and negative features. Here are a few questions he should ask himself: Can I start my own business? How can I get along with people? How firm am I in making decisions? Do I have enough physical strength and emotional potential to successfully conduct business? How well do I plan and organize my affairs?
You also need to answer the question: what type of business should you choose? Usually the best type of business is the one in which the future entrepreneur is most interested, as well as the one for which there are already certain skills. You can consult with business support services about the potential of various types of businesses in your area. Matching his qualifications to local market opportunities will increase the chances of success.
The future entrepreneur must be competent in the field in which he intends to create his own business.
An entrepreneur must be able to calculate the expected consequences of risk, keep business secrets, have all the information about the activities of his own
Creating your own business in the Russian Federation
Creation own business in Russia is carried out in accordance with the current civil legislation, federal laws on certain organizational -legal forms companies and various regulations governing the entire process education and functioning private firms.
For entrepreneur The most important types of legislation are:
- civil legislation regulating relations between individuals and legal entities;
- tax legislation that establishes the obligations of persons for deductions to the budget;
- a code of administrative offenses that regulates relations between individuals and the state, but does not require litigation;
- labor legislation governing relations between an employee and an employer;
- consumer protection legislation;
- criminal law governing relations between the state and individuals.
Most people think about opening own case in one area or another.
The following advantages and disadvantages of creating own affairs(Table 1):
Table 1
Advantages and disadvantages of starting your own business
To create your own business, you must go through a series of mandatory steps, which are presented in Fig. one.
Rice. one. Stages of creating your own business
Let's consider each stage in detail.
Self-esteem. When deciding to create their own business, an entrepreneur must objectively assess their abilities and capabilities, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of independent entrepreneurial activity.
When choosing a career in business, you must also conduct a clear analysis of all your qualities. The characteristic features of entrepreneurs include the following:
- competence in the field of activity in which he intends to create his own business;
- knowledge of market rules and laws;
- ability and ability to take risks;
- leadership and communication;
- initiative;
- innovation;
- good business reputation;
- emotional stability;
- confidence in yourself and in the success of your business;
- flexibility and ability to adapt to changes in the market;
- education and knowledge;
- the desire to change and expand your business;
- energy and perseverance;
- good health.
Of course, it is impossible to possess all these qualities at once, but one must strive to develop them. The entrepreneur must decide for himself how much he has them in order to run his own business.
Entrepreneurial idea. Entrepreneurial activity begins with an idea, which is further implemented into a specific entrepreneurial project. An entrepreneur must be sure that his project will be commercially viable, that there will be a sufficiently large number of people willing to pay for the goods or services produced by his company. A critical element of success is the belief that the entrepreneur will produce the right quality product that the consumer wants at the price they are willing to pay, and that this will bring in enough profit to grow and improve the business.
Any idea is realized with a goal. It is impossible to engage in entrepreneurship without formulating a realistically achievable goal. Goals should be commensurate with business opportunities, quantitatively and qualitatively defined, have clear time frames. The more precisely the goal is defined, the more likely it is to be achieved.
The art of goal setting is first and foremost the art of managing your own business. The goal makes it possible to control the progress and results of work, the possibility of proper motivation of employees. Therefore, when starting your own business, you should first decide and agree on goals and objectives. After that, you need to move on to drawing up a business plan.
Market assessment. Before making a final decision to start a business, you should once again analyze the situation in the area in which the entrepreneur will work and choose an economic and market niche. It is necessary to clearly define the type of activity, the location of the company and the geographical boundaries of the business. An entrepreneur must study the market of potential customers and competitors in order to determine their strengths and weaknesses. This study may be included in the business plan as a separate section.
Attracting the necessary resources. An important step in creating your own business is solving questions about the financial capabilities of the entrepreneur, deciding where to get the money to start a business, that is, to purchase raw materials, equipment, and hire labor resources. Sources of funds can be the savings of the entrepreneur, loans received from banks, funds from the sale of securities, as well as subsidies from government agencies.
At this stage, it is necessary to consider the possibility of acquiring an already operating enterprise. Buying an existing business has its advantages. The entrepreneur actually acquires the necessary resources (premises, equipment, vehicles, etc.), as well as what in the business world is called "the reputation of the company." Usually, a novice entrepreneur has to achieve the appropriate reputation of his company himself, which requires a fairly large amount of time. If he buys an operating enterprise, then this saves him a lot of problems.
When making a decision to buy a business, you need to make sure that the chosen business is really suitable. It is necessary to pay attention to the location of the enterprise, the availability of the necessary equipment, the condition of the premises, vehicles, as well as financial stability. The entrepreneur must also be sure that he is buying an operating business at a reasonable price.
If the financial possibilities of the entrepreneur are limited, then it is necessary to consider the option of renting real estate and purchasing the appropriate equipment. It is also necessary to analyze the labor market in order to subsequently recruit workers with the required qualifications.
An entrepreneur at this stage may also consider organizing a business in the form of franchising, using a trademark, technology, standards, advertising, and often management methods that are developed and applied by another, usually a large firm. Such a system has received the greatest distribution in the hotel business, in car rental and car maintenance, as well as restaurant services. Franchising has certain advantages for the entrepreneur:
- the opportunity to become an independent entrepreneur;
- the right to conduct your business under a recognized trademark;
- use of already proven forms of entrepreneurship.
A small business with the help of franchising can quickly open a business, and the constant support from the franchisor allows you to quickly overcome the problems that arise at the initial stage of creating an enterprise.
So, at this stage, specific goals and objectives are determined to create all the necessary conditions for the functioning of the company. This information is also included in a separate section of the business plan.
Choice of organizational-legal form. The choice of the legal form in which the business will be carried out is one of the most difficult and important decisions that an entrepreneur must make when organizing a new business. It is necessary to make a decision on the choice of one or another organizational and legal form when creating a company in each specific case, depending on the type of activity, goals and strategic plans of the company, the nature of the relationship between its founders.
In accordance with the civil legislation of the Russian Federation, any citizen can carry out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity, registering as an individual entrepreneur, or create their own business in a certain organizational and legal form.
The issue of legal form should be carefully considered by the entrepreneur, and he should do this by working closely with a lawyer and a tax audit specialist.
When choosing a legal form of business, an entrepreneur needs to carefully analyze three main aspects: responsibility, control, taxes.
Currently in Russia there are various organizational and legal forms of entrepreneurial activity.
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (CC RF), legal entities that are commercial organizations are classified as follows:
- self employed;
- production cooperatives;
- unitary enterprise;
- business partnerships - full partnerships and limited partnerships;
- economic companies - a joint-stock company, a company with limited and additional liability.
Self employed- a natural person who is independently engaged in economic activity. The following advantages and disadvantages of private entrepreneurship (individual labor activity - ITD) can be distinguished (Table 2):
table 2
Advantages and disadvantages of private enterprise
production cooperative(artel) is a voluntary association of citizens for joint production or other economic activities (production, processing, marketing of industrial, agricultural and other products, performance of work, trade, consumer services, provision of other services).
- The charter is the founding document.
- The number of members of the cooperative should not be less than five people.
- The property owned by the cooperative is divided into shares in accordance with the charter.
- The profit of the cooperative is distributed among its members in accordance with their labor participation, unless otherwise provided by the charter of the cooperative.
- The supreme governing body of a cooperative is the general meeting of its members.
- A cooperative with more than 50 members may have a supervisory board.
- The executive bodies of the cooperative are the board and/or the chairman.
unitary enterprise a commercial organization is recognized that is not endowed with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner. The property of a unitary enterprise is indivisible and cannot be distributed among deposits (shares). Only state and municipal enterprises can be created in the form of unitary enterprises.
- The property of a state or municipal unitary enterprise is, respectively, in state or municipal ownership.
- A unitary enterprise is managed by a manager who is appointed by the owner or a body authorized by the owner and is accountable to him.
- A unitary enterprise is liable for its obligations with all its property.
- A unitary enterprise based on the right of economic management is created by decision of an authorized state body or local self-government body.
- A unitary enterprise based on the right of operational management, a state-owned enterprise, is created by decision of the Government of the Russian Federation. (In case of insolvency of state-owned enterprises, the Russian Federation is liable for its obligations, i.e. such an enterprise cannot be bankrupt. It is created on the basis of a model charter.)
Business partnerships and companies are the most common form of collective entrepreneurship. According to the Civil Code, business partnerships and companies are recognized as commercial organizations with the authorized capital divided into shares (contributions) of the founders (participants). The following similarities and differences between these legal forms can be distinguished. Common features:
- are legal entities and may be members of other companies and partnerships;
- all property created at the expense of the contributions of the founders and acquired in the course of economic activity belongs to the company on the right of the owner.
Differences:
- partnerships - associations of persons, companies - associations of capital;
- societies can be created by one person, partnerships cannot.
General partnership is created and operates on the basis of the founding agreement, which must be signed by all its participants.
- Profits and losses of a full partnership are distributed among its participants in proportion to their shares in the share capital, unless otherwise provided by the founding or other agreement of the participants.
- An agreement on the elimination of any of the participants in the partnership from participation in profits or losses is not allowed.
- If the property of the partnership is insufficient to pay off its debts, creditors have the right to demand satisfaction from the personal property of any of the participants (or all together).
- A charter is not required, as any of the participants in a general partnership is engaged in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership. The only constituent document of such a commercial organization is the memorandum of association.
Faith partnership is a kind of general partnership and consists of two groups of participants - general partners and investors.
Investors have property rights:
- the right to receive a part of the partnership's profit due to their share;
- contributors retain the opportunity to freely withdraw from the partnership with the receipt of their contribution;
- the investor may transfer his share or part of it both to another investor and to a third party, while the consent of the partnership or general partners is not required;
- in case of liquidation of a limited partnership, investors have a preferential right over general partners to receive their contributions or their monetary equivalent from the property of the partnership after satisfying the claims of other creditors.
Table 3
Advantages and disadvantages of a partnership
| Partnership Benefits |
Disadvantages of partnership |
| Ability to accumulate significant funds in a relatively short time |
There must be a trusting relationship between full partners, otherwise this organization may collapse |
| Each general partner has the right to engage in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership on an equal basis with others |
Cannot be a "one person company" |
| General partnerships are more attractive to creditors, since their members bear unlimited liability for the obligations of the partnership |
In the event of bankruptcy, each general partner is liable not only with his contribution, but also with personal property |
Entrepreneurial activity in the form of a partnership has not become widespread in Russia, since it does not establish limits on their liability for the partnership's debts.
Limited Liability Company- a company founded by one or more persons, the authorized capital of which is divided into shares of the sizes determined by the constituent documents.
- Members of a limited liability company are liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company within the value of their contributions.
- The number of members of the society should not exceed 50 people.
- The authorized capital cannot be less than 100 times the minimum wage.
- The founding documents of a limited liability company are the memorandum of association signed by its founders and the charter approved by them. If a company is founded by one person, its founding document is the charter.
- The supreme body of a limited liability company is the general meeting of its participants.
- The Company may be voluntarily liquidated or reorganized by unanimous decision of its participants.
Additional Liability Company is a type of limited liability company. It differs from an LLC in that in the event of bankruptcy, the participants in the company can be held liable in the same way for all participants in a multiple of the value of their contributions, determined by the constituent documents of the company (for example, three times). Occupies an intermediate position between societies and partnerships.
Table 4
Advantages and disadvantages of society
A joint-stock company is a company whose authorized capital is divided into a certain number of shares. Joint-stock companies can be open and closed.
Table 5 summarizes the similarities and differences between a limited liability company and a closed joint stock company. CJSC and LLC, despite their similarities, differ in many ways. Thus, an LLC has a simpler management structure and decision-making procedure. The LLC does not issue shares, so there is no need to register share issues with the Securities Market Commission.
Table 5
Similarities and Differences of a Limited Liability Company (LLC)
and a closed joint stock company (CJSC)
| Organizational and legal form |
Differences |
Similarities |
|
|
|
|
- A joint stock company whose members may alienate their shares without the consent of other shareholders is recognized as an open joint stock company. Such a joint-stock company has the right to conduct an open subscription for issued shares and their free sale on the conditions established by law.
- The minimum authorized capital of an open JSC is 1,000 times the minimum wage.
- An open company is obliged to annually publish for general information the annual report, balance sheet, profit and loss statement.
- A joint stock company whose shares are distributed only among its founders or other predetermined circle of persons is recognized as a closed joint stock company. It is not entitled to conduct an open subscription for shares issued by it or otherwise offer them for purchase to an unlimited number of persons.
- The number of founders of a CJSC should not exceed 50 people (otherwise it is subject to transformation into a JSC or liquidation).
- The minimum authorized capital of a CJSC is equal to 100 times the minimum wage.
- The founding document of a joint-stock company is the charter approved by the founders.
- The existence of a “company of one person” is allowed.
- The supreme governing body of a joint-stock company is the meeting of shareholders.
- In a company with more than 50 shareholders, a Board of Directors (Supervisory Board) is created.
- The executive body of the company may be collegiate (Board) or sole (director, general director).
- The share of preferred shares in the total volume of the authorized capital of a joint-stock company must not exceed 25%.
- A joint-stock company has the right to issue bonds for an amount not exceeding the amount of the authorized capital or the amount of security provided to the company for this purpose by third parties.
An open joint stock company is the most promising form of large business. It gives its participants the opportunity to freely dispose of their shares, combines the interests of owners and makes it easy to raise additional capital by issuing shares, provides its participants with the opportunity to dispose of their shares, combining the interests of owners of large blocks of shares and small shareholders.
Limited liability companies and production cooperatives can be successfully used in the field of small and medium-sized businesses.
Determination of the composition of the founders. When selecting founders, one should take into account: solvency, business qualities, decency, complete mutual trust. Practice shows that often the founders, having barely started their business, disperse. Therefore, founders should be selected very carefully.
The founders bear property and criminal liability for the proper conduct of the establishment process, the development and submission of constituent documents, the formation of capital, the organization, registration of a company of management bodies.
It is necessary to distinguish between the founders of the company and shareholders. Legal entities and individuals can act as founders. Founders are responsible for conducting due process of establishment. The founder may be required to subscribe to a certain number of shares in the company. Shareholders are all legal entities and individuals who own shares of the company.
Company registration. The legislation of the Russian Federation on state registration consists of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the Federal Law "On State Registration of Legal Entities" and regulatory legal acts issued in accordance with them. Currently, most entrepreneurs use the services of specialized companies involved in the registration of companies. However, the entrepreneur must clearly understand the registration procedure, which is presented in Fig. 2.

Rice. 2. Main stages of company registration
After determining the composition of the founders, constituent documents are developed: the charter of the company, which defines the principles of activity and the internal organization of the company, an agreement on the creation and operation of the company (agreement), which reflects issues related to the activities of the founders in the process of creating and functioning of the company. Along with this, protocol No. 1 of the meeting of the company's participants is drawn up on the appointment of a director, chairman of the audit commission.
After that, a temporary bank account is opened, where at least 50% of the authorized capital must be received within 30 days after the registration of the company.
Then the company is registered at the place of its establishment in the local authority. For example, in Moscow, registration of entrepreneurs is carried out by the Moscow
by the Moscow Registration Chamber and its branches, in the Moscow Region - by the Moscow Regional Registration Chamber and its territorial agencies.
According to Article 34 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Enterprises and Entrepreneurial Activities", entrepreneurship without registration is prohibited, and the income received from it in a judicial proceeding at the suit of the tax inspectorate is collected to the budget.
The following documents are submitted for state registration: an application of the founders for registration, a decision to establish a legal entity in the form of a protocol, agreement or other document in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, constituent documents of a legal entity (originals or notarized copies), a certificate of payment of state duty.
After receiving a certificate of registration, all information about the new company is transferred to the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation for inclusion in the trade register of enterprises.
The Russian Federation maintains a state register containing information on the creation, reorganization and liquidation of legal entities and relevant documents. The state register contains the following information and documents about a legal entity:
- full and abbreviated company name;
- organizational and legal form;
- legal entity address;
- method of formation of a legal entity (creation or reorganization);
- information about the founders of the legal entity;
- copies of constituent documents;
- date of registration of changes made to the constituent documents of the legal entity;
- method of terminating the activities of a legal entity;
- the amount of the authorized capital indicated in the constituent documents of the commercial organization;
- surname, name, patronymic and position of a person entitled to act on behalf of a legal entity without a power of attorney;
- information about licenses obtained by a legal entity.
At the final stage of the creation of a new company, the participants make their full contributions (not later than one year after registration), open a permanent bank account and the company is registered with the regional tax office. Then a round seal and a corner stamp are ordered, and the company begins to function as an independent legal entity.
In the event that a company is established as a joint-stock company, the founders must subscribe for shares. With an open subscription, a notice of the upcoming subscription is published, which indicates:
- the subject and goals of the activities of the future joint-stock company;
- the composition of the founders;
- the date of the founding conference;
- the size of the authorized fund;
- the number and types of shares, their nominal value;
- the start and end date of subscription for shares.
Share subscribers must contribute at least 30% of the nominal value of the shares before the convening of the founding conference. In the case of a closed subscription, the fee is 50%. The shareholder must fully pay the cost of the shares no later than one year after the registration of the joint-stock company.
After the completion of the subscription for shares, a founding conference is held, at which the following issues are resolved:
- creation of a joint-stock company;
- approval of the charter;
- determination of the statutory fund (after completion of the subscription for shares);
- elections of the governing bodies of the society.
Only after this is the registration of a new joint-stock company.
Having determined the optimal organizational and legal form of the company, it is necessary to choose a company name. You can use your own name or the names of business partners. It is important that the name of the company does not repeat the names of already existing companies.
It must be remembered that there are some names that cannot be used without special permission. For example: “Bank, Russian, Moscow”, etc. For the use of the names “Russia”, “Russian Federation” for commercial purposes, you must pay a fee to the tax office. For organizations engaged in entrepreneurial activities (banks, exchanges, insurance, construction companies), this will amount to 0.5% of the value of products sold. Procurement, supply and marketing and trade organizations pay 0.05% of the turnover. For other organizations, including non-profit ones, a tariff of 100 minimum wages is set.
The company name must be used in official correspondence, invoices, checks, etc., as well as used to advertise the company.
Most people think about starting their own business in an area in which they have some experience. Sometimes entrepreneurs create an entirely new product or service. But in whatever area a new firm is created, the most important thing is to be sure that it is commercially viable, that there are enough people willing to pay a set price for the goods or services produced.
Own business is the organization of one's own business by creating and operating a commercial organization in a certain organizational and legal form in accordance with civil law. Own business can be carried out by a capable individual without forming a legal entity. The organization of one's own business is a form of expression of economic freedom and motivation of capable citizens.
The motives for organizing your own business are to seek, using the accumulated professional experience, knowledge, own funds, to open your own business in order to become economically independent, to provide the necessary conditions for family members through the production of goods (work and services) for consumers and profit. An important motive is the self-realization by the individual of his abilities and knowledge.
The prerequisites for organizing your own business are a set of conditions and opportunities to independently carry out entrepreneurial activities:
1) availability of funds for the formation of initial capital, authorized (share) capital;
2) availability of non-residential premises, equipment necessary for doing business; preliminary market research;
3) availability of qualified partners;
4) knowledge of civil law governing the process of creating your own business.
Each entrepreneur, starting his activity, must clearly understand the need for the future in financial, material, labor and intellectual resources, the sources of their receipt, and also be able to clearly calculate the efficiency of the use of resources in the process of organizing and developing their own business. This is explained by the fact that in the modern economy, it is enterprises that produce the bulk of goods and services that satisfy human needs. It is relying on these facts that we can talk about the relevance of the topic of the course work, especially in a market economy.
Creating your own business in Russia is carried out in accordance with the current civil legislation, federal laws on individual organizational and legal forms of participants in entrepreneurial activity and regulations governing the entire process of creating and functioning of entrepreneurial organizations. Creating your own business in one or another organizational and legal form suggests the presence of the following prerequisites:
availability of property for the formation of initial capital;
availability of a certain amount of financial resources necessary for the formation of the minimum size of the authorized (share) capital;
availability of non-residential premises necessary to accommodate the office of the future organization and the implementation of the intended activities, or the availability of opportunities to conclude a lease agreement for non-residential premises;
a preliminary study of the intended market, to which the entrepreneur will offer the results of entrepreneurial activity for implementation;
Formation of a team of qualified founders (partners) of their own business, who are well aware of the technology for the implementation of certain types of activities, accounting and financial accounting, etc.
The future entrepreneur must be competent in the field in which he intends to create his own business. According to American statistics, about 90% of new enterprises are opened by people in the field of activity in which they already have experience, or have received special training and internships, or have managed to attract highly qualified specialists to create their own business, to whom they trust their fate.
To choose a career in business, you need to conduct a clear analysis of your qualities, abilities and capabilities so that, without giving up the dream of creating your own business, clarify your weaknesses (especially in the field of people management) and constantly learn the art of being the owner of the business, being able to reasonably take risks, foresee failures and try to avoid them. Therefore, an entrepreneur must be able to calculate well the expected consequences of the risk, keep business secrets, own all the information about the activities of his own enterprise, consumers of products, customers, suppliers, competitors in particular. Considering that the business environment has not yet been formed in Russia, a huge bureaucratic layer of officials is functioning, and an aggressive external environment is operating. The future entrepreneur needs to be able to anticipate the decisions of federal and local authorities, which often infringe on the rights of entrepreneurs, learn how to protect not only their property and all assets from the encroachments of aggressive forces, but also their lives.
The future Russian entrepreneur must certainly remember the most important rule: in organizing his business (business), he must rely on his own strength, because only small business enjoys some support from the authorities.
Having decided to create their own business, the future entrepreneur must answer a number of leading questions:
· for whom his company will work, who are his future consumers (buyers), is there a place for him under the “sun of the market“. Therefore, the process of an entrepreneurial decision should begin with the formulation of an idea - for whom to produce products, goods, perform work, to whom to provide services (depending on the type and type of market);
What to produce, what specific goods, what specific services to perform, and then determine whether it has all the conditions and factors for its activities. At the same time, it should be remembered that entrepreneurs have the right to engage only in legal and (or) licensed activities;
How to produce products (goods), perform work, provide services, on what technical and technological basis, with what quality characteristics, at what costs, with what level of competitiveness. Therefore, it is very important to know what is the relationship in the market between the demand and supply of the goods that the entrepreneur is going to offer (in any field of activity - production, trade - intermediary, financial - credit) in the market, and not in the market in general, but in a certain territorial market . If the demand is large and stable, then it makes sense to create your own business and produce these goods.
A future entrepreneur, when planning to create his own business, should be guided by the most important market principles, among which are the following.
First, you need to find a need and satisfy it, since entrepreneurial activity is aimed at satisfying the needs of others. The entrepreneur does not work for himself, but to meet specific needs, and he accordingly receives profit (income).
Secondly, goods should be produced at lower costs (cost), otherwise the market may not recognize these goods, and the entrepreneur will not be able to sell (sell) them and receive the planned profit.
Thirdly, when setting the price for manufactured goods, an entrepreneur must take into account the behavior of competitors, consumer demand, and the level of market saturation. An overpriced wholesale (retail) price will not allow you to sell goods in a timely manner, and an underestimated one will not allow you to get the necessary amount of profit. The problem of pricing plays a significant role in the mechanism of creating and functioning of one's own business, the general algorithm of which can be expressed in the following brief scheme: an entrepreneurial idea - the goals of an entrepreneur - the development of an entrepreneurial project - its implementation in the form of creating one's own business - the functioning of the organization.





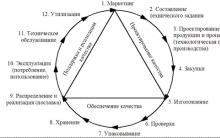



Layout of the house, plans of houses and cottages
Small Business - Home Production Ideas
History of JANOME. Sewing machines. Janome, Veritas, Pfaff Sewing machine janome manufacturer country
Working with the tattis system
Properties of copper and its application