1 of 15
Presentation - Teaching Methods
Text of this presentation
Teaching methods

Plan Analysis of approaches to defining the concept of “teaching methods”. The relationship between teaching and teaching methods Approaches to the classification of teaching methods Traditional teaching methods Innovative teaching methods

There are several approaches to defining the concept of “teaching method.” A teaching method is... is a way of pedagogically expedient organization of educational and cognitive activities of students. (V.A. Slastenin, I.F. Isaev) - the way the teacher and students work, with the help of which the latter achieves the acquisition of knowledge, skills and abilities. (M. A. Danilov, B. P. Esipov). - this is a way of interrelated activities of teachers and students to implement the tasks of education, upbringing and development (Yu. K. Babansky). - these are the methods of the teacher’s teaching work and the organization of educational and cognitive activities of students (I. F. Kharlamov). - this is a way of joint activities of the teacher and students aimed at achieving their educational goals. (L.P. Krivshenko)

Methods in the learning process perform the following functions: Educational 2. Developmental 3. Educational 4. Motivational (act as a means of inducing learning) 5. Control and correction (diagnosis and management of the learning process of students)

The relationship between admission and teaching method
- A teaching method is an integral part or a separate side of a teaching method, i.e. a particular concept in relation to the general concept of “method”. - Individual techniques can be part of different methods - The same method in one case acts as an independent method, in another - as a teaching method Technique and method can change places The method includes a number of techniques, but it itself is not a simple sum of them .

There are different approaches to classifying teaching methods.
The perceptual approach (N.M. Verzilin, E.I. Petrovsky) takes as its basis the source of information transmission and the nature of its perception. Teaching methods
Verbal methods
Visual methods
Practical methods
(the source of information is the spoken or printed word)
story explanation - conversation discussion, lecture work with a book
(the source of information is observed objects, phenomena, visual aids)
demonstration method illustration method
(designed to develop practical skills)
practical exercises and laboratory work

Management approach (M.A. Danilov, B.P. Esipov). is based on didactic goals that are solved at one or another stage of training. Teaching methods: - acquiring new knowledge - developing skills and abilities - applying knowledge - consolidating and testing knowledge, skills and abilities

Gnostic approach (I.Ya. Lerner, M.N. Skatkin) is based on the nature of students’ cognitive activity
Teaching methods
Information-receptive (explanatory-illustrative)
(the teacher communicates ready-made information using various means, and students perceive it, understand it and record it in memory)
Reproductive method
(the teacher communicates and explains knowledge in a ready-made form, and students assimilate it and can reproduce and repeat the method of activity according to his instructions)
Method of problem presentation
(the teacher poses a problem and solves it himself, thereby showing the train of thought in the process of cognition)
Partial search (heuristic) method
(students independently solve a complex educational problem not from beginning to end, but only element by element)
Research method
(the teacher formulates the problem together with the students, and they solve it independently)

The subject-object approach (E.Ya. Golant) is based on the level of activity of students in the learning process
Teaching methods
Passive
- story - lecture, explanation excursion demonstration observation
Active
- laboratory method - practical method - working with a book

The binary approach (M.I. Makhmutov) is based on a combination of methods of activity of teachers and students
Teaching methods
Teaching methods
- informational-informative - explanatory - instructive-practical - explanatory-stimulating - stimulating
Teaching methods
- executive - reproductive - productive-practical - partially search - search

The logical approach (A.N. Aleksyuk) provides for the logic of the teacher’s presentation of the material and the logic of its perception by students. Teaching methods: - inductive (from particular cases, examples, facts - to generalizations and conclusions) - deductive (from conclusions, generalizations - to examples, particular cases, individual facts)

Methods of organizing and implementing educational and cognitive activities
- perceptual (transmission and perception of educational information through the senses); - verbal (lecture, story, conversation, etc.); - visual (demonstration, illustration); - practical (experiments, exercises, completing assignments); - logical (inductive, deductive, analogies, etc.); - Gnostic (research, problem-search, reproductive); - self-management of educational activities (independent work with a book, equipment, etc.).
Methods of stimulating and motivating learning
- methods of developing interest in learning (cognitive games, educational discussions, creating problem situations, etc.); - methods of forming duty and responsibility in teaching (encouragement, approval, censure, etc.).
Methods of control and self-control in training
- methods of oral control (individual, group questioning, oral test, exam) - methods of written control (tests, essays, written tests, etc.) - methods of laboratory and practical control (control and laboratory work); - methods of self-control
Holistic approach (Yu.K. Babansky)

Traditional teaching methods These methods were developed in centuries-old pedagogical practice and are the basis for the organization and implementation of the learning process
The following traditional teaching methods are distinguished:
- Story (story-introduction, story-narration, story-conclusion) - Explanation - Conversation (introductory, conversation-communication of new knowledge, Socratic heuristic, consolidating, control-corrective conversation) - Lecture (informational, problem, introductory, review, episodic ) - Educational discussion - Working with a textbook and book (note-taking, thesis, summarizing, drawing up a text outline, citing, etc.) - Demonstration (showing) - Illustration method - Exercise (oral, written, graphic, educational and labor exercises, introductory, basic, training, etc.) - Laboratory work - Practical work

Innovative teaching methods have the following features: - “forced activity” of students - forced activation of thinking and activity - increased emotional involvement of students - creative nature of classes - mandatory direct interaction between students and the teacher - formation of collective efforts aimed at intensifying the learning process

Active teaching methods are teaching methods in which the student’s activity is productive, creative, and exploratory in nature. Active learning methods include - didactic games, - analysis of specific situations, - solving problematic problems, - learning using an algorithm, - brainstorming, - out-of-context operations with concepts.
Intensive training methods are used to provide training over a short period of time in long, one-time sessions (“immersion method”). These methods are used in teaching business, marketing, foreign languages, practical psychology and pedagogy.
Types of innovative teaching methods
Code for embedding a presentation video player on your website:
Slide presentation
Slide text: Any human training is nothing more than the art of promoting nature’s desire for its own development. I. Pestalozzi
Slide text: There are only as many good methods as there are good teachers. D. Polya Prepared by G.V. Bortnikova
Slide text:
Slide text:
Slide text:
Slide text:
Slide text:
Slide text:
Slide text:
Slide No. 10
Slide text: The story involves an oral narrative presentation of educational material, uninterrupted by questions to the students. An educational lecture is a systematic presentation of the material. Conversation is the presentation of information in the form of a dialogue between a teacher and a student on a set of issues on a topic. Discussion – discussion of a problem.
Slide No. 11
Slide text: Illustration - showing students various illustrative aids: posters, tables, diagrams, drawings from a textbook, sketches and notes on the board, models of geometric shapes, natural objects, etc. Demonstration of instruments, experiments, showing films, filmstrips, slides, etc.
Slide No. 12
Slide text: Exercise - repeated performance of educational actions in order to develop skills and abilities. Laboratory work - students conducting experiments, calculations, and experiments in a laboratory setting that allow them to study processes. Practical work - performing tasks on processing materials, making objects, working in school areas, in workshops, etc.
Slide No. 13
Slide text:
Slide No. 14
Slide text:
Slide No. 15
Slide text:
Slide No. 16
Slide text:
Slide No. 17
Slide text:
Slide No. 18
Slide text:
Slide No. 19
Slide text: Method of didactic games. The essence is modeling and simulation. Algorithm training.
Slide No. 20
Slide text:
Slide No. 21
Slide text: Solving a problem by coming up with ideas to solve it
Slide number 22
Slide text: Recognition of a term Definition of a concept Disclosure of the scope and content of a concept Establishing connections between a given concept and another Practical interpretation of a concept
Slide No. 23
Slide text: Positive emotions towards activities. The presence of a cognitive side to this emotion. The presence of a direct motive coming from the activity itself.
Slide No. 24
Slide text: Educational games. The method is based on the creation of game situations in the educational process. Educational discussions are a method of creating a situation of cognitive dispute. Creating a situation of success in learning by differentiating assistance to students in completing educational tasks of the same complexity
Slide No. 25
Slide text:
Slide No. 26
Slide text: Compliance of methods with teaching principles. Compliance with learning goals and objectives. Compliance with the content of this topic. Compliance with the educational capabilities of the students: age, psychological; level of preparedness. Compliance with the available conditions and allotted training time. Compliance with the capabilities of learning aids. Compliance with the capabilities of the teachers themselves
Slide No. 27
Slide text: Name of the decision Characteristics of this level of decision-making Stereotypical decisions The teacher invariably gives preference to a certain stereotype of the use of teaching methods, regardless of the specifics of the content tasks and the characteristics of the students. Trial-and-error solutions The teacher tries to change the choice of methods taking into account specific conditions, but does this through spontaneous trials, making mistakes, choosing a new option and again without scientific justification for the choice. Optimized decisions Decisions that are made by scientifically based selection of the most rational methods for given conditions in terms of some specified criteria.
Slide No. 28
Slide text: 1. By the source of knowledge Verbal Visual Practical 2. By the nature of cognitive activity Explanatory-illustrative Problem presentation Partial-search Research 3. Active and intensive methods Method of didactic games Training using an algorithm 4. Methods of science as educational methods Brainstorming Out-of-context operations with concepts
Nomination "Modern methods and techniques of teaching students and pupils."
Topic: "Teaching methods in primary school lessons."
Teaching methods in lessons in primary school.
“There are only as many good methods ashow many good teachers there are.”
D.Poya
Modern society is in a state of continuous development and change. The education system in such a society must also change and improve in order to meet the demands of society and the state. And one of these ways, the ability of the education system to meet the challenges of the time, is innovation - introduction, and qualitatively new ones, into the established education system.
The need for students to assimilate a large amount of information and develop practical skills in its application leads to teachers creating new ways of presenting information, new technologies and teaching methods, and forces them to look for creative approaches to teaching methods.
Based on the degree of activity of students in the educational process, teaching methods are conventionally divided into two classes: traditional and active. The fundamental difference between these methods is that when they are used, students are created conditions under which they cannot remain passive and have the opportunity for active exchange of knowledge and work experience.
From this we can conclude that one of the sources of innovative teaching methods is the use of active forms of work with students, who can work both in a group and individually.
The goal of using active teaching methods by a teacher is to create sustainable motivation in students to learn and understand the world as a whole. The ability not only to learn, remember and reproduce information, but also to apply it in practice allows students to significantly improve their performance in studying school subjects and develops the ability to process information (classification, generalization, similarities and differences, etc.).
A Chinese proverb says: “Tell me and I will forget, show me and I will remember, involve me and I will understand.”
The preference for using active learning methods is justified and supported by the following data obtained by teachers and psychologists as a result of experience in teaching activities and experiments, from which it follows that a person remembers:
10% of what he reads;
20% of what is heard;
30% of what he sees;
50-70% is remembered when participating in group discussions;
80% when the student independently discovers and formulates the problem;
90% when the student directly participates in real activities, in independently posing problems, in developing and making decisions, formulating conclusions and forecasts.
These data confirm the statements of many teachers and psychologists about the need to use active learning methods to achieve student performance and motivation, as N. A. Umov said:
“All knowledge remains dead if initiative and initiative do not develop in students: students must be taught not only to think, but also to want.”
Thus, we see that active teaching methods expand the creative component of the lesson, contribute to the active work of each student in the lesson,
fully involving him in the process of learning new material, allow the student
form your own point of view and gain real experience in applying the acquired knowledge.
An essential component of pedagogical technologies are teaching methods. Teaching methods are ways of interrelated activities of teachers and students to implement the tasks of education, upbringing and development. (Yu. K. Babansky). Teaching methods are ways of a teacher’s teaching work and organizing students’ educational and cognitive activities to solve various didactic tasks aimed at mastering the material being studied. (I.F. Kharlamov).
“The methods used in educational activities should arouse the child’s interest in understanding the world around him, and the educational institution should become a school of joy. The joys of knowledge, creativity, communication." V.A. Sukhomlinsky.
Requirements for teaching methods:
scientific methods
accessibility of the method, its compliance with the psychological and pedagogical development capabilities of schoolchildren
the effectiveness of the teaching method, its focus on solid mastery of educational material, on fulfilling the tasks of educating schoolchildren
the need to systematically study and use innovative methods in one’s work.
The choice of teaching methods depends on:
From general and specific learning goals; content of the material of a particular lesson.
From the time allocated for studying this or that material.
Depending on the age characteristics of the students and the level of their cognitive abilities.
Depending on the level of preparedness of students.
From the material equipment of the educational institution, the availability of equipment, visual aids, and technical means.
From the capabilities and characteristics of the teacher, the level of theoretical and practical preparedness, methodological skills, and his personal qualities.
The modern lesson is a free lesson, a lesson freed from fear: no one scares anyone and no one is afraid of anyone. A friendly atmosphere is created. A high level of motivation is formed. Great importance is attached to methods of educational work. Special attention is paid to the development of students' skills in independent cognitive activity and a creative attitude to the educational process.
Everyone works in class and everyone works. Everyone's opinion is interesting and everyone's successes are pleasing. Everyone is grateful to everyone for their participation, and everyone is grateful to everyone for their progress towards knowledge. Trust in the teacher as the leader of group work, but everyone has the right to an initiative proposal. Anyone and everyone has the right to express an opinion regarding the lesson.
A student is an active subject of the educational process, showing independence in developing and making decisions, ready to take responsibility for his actions, self-confident, purposeful.
A teacher is a consultant, mentor, partner.
The teacher’s task is to determine the direction of work, create conditions for student initiative; competently organize students' activities.
Features of modern teaching methods:
A method is not the activity itself, but the way it is carried out.
The method must necessarily correspond to the purpose of the lesson.
The method does not have to be wrong, only its application can be wrong. Each method has its own subject content.
The method always belongs to the actor. There is no activity without an object, and there is no method without an activity.
The learning process should evoke in the child an intense and internal urge for knowledge and intense mental work. The success of the entire educational process largely depends on the choice of methods used.
Based on modern achievements of pedagogy, psychology and methodology, I proceed from the following provisions:
The need for knowledge is one of the most important human needs.
Interest in knowledge as a deep orientation of the individual and a stable motive for learning awakens creative thinking and creates favorable conditions for the manifestation of creative individuality.
The leading principles that make it possible to implement the assigned tasks are: the principle of developing and educating education; the principle of developing students' creative abilities; the principle of creating a positive emotional background of educational activities; the principle of humanization of primary education.
My activities are aimed at providing conditions for personal development, making the process streamlined and manageable, and forming thinking subjects. I try to combine scientific teaching with accessibility, vivid clarity with play, and ensure that all students work with enthusiasm. This is facilitated by the set of teaching skills that I possess.
Skills: I demonstrate to children my complete trust in them; I organize the presentation of new material in the form of an exciting dialogue; I do not violate the unity of the logical structure of the lesson; I assume that students have internal motivation to learn; I try to involve students in activities that awaken the joy of learning and arouse persistent curiosity.
An individual approach to students helps create an atmosphere of success in educational activities.
To ensure cognitive activity and cognitive interest of students at various stages of the lesson, I use active forms and methods of work. I consider the most productive:
Game forms;
Organization of group, pair and individual work;
Organization of independent activities of students;
Creation of specific situations, their analysis;
Posing questions that activate dialogue.
Problem-based learning.
I believe that in my work I need to use a variety of methods and find new ones. The school should be a pedagogical laboratory, the teacher should show independent creativity in his teaching and educational work.
A game
S. Frenet said: “The child does not get tired of work that meets his functional life needs.”
Didactic games - arouse keen interest in the process of cognition, intensify the activity of students, and help to more easily assimilate educational material.
Role-playing games are a small scene played out by students, helping to visualize, see, and revive circumstances or events familiar to students. In mathematics lessons, to develop activity and attention, I conduct mental calculations with game elements.
Couples and groups
This method gives students more opportunities to participate and interact. Working in pairs and groups develops in children the ability to accept a common goal, share responsibilities, agree on ways to achieve the proposed goal, correlate their actions with the actions of their partners, and take part in comparing goals and work.
Problematic methods.
Not from knowledge to problem, but from problem to knowledge.
Problem-based methods contribute to the development of intellectual, subject-related and practical motivational spheres of the individual.
A problematic question is a question that requires intellectual effort, analysis of connections with previously studied material, an attempt to compare, and highlight the most important provisions.
A problematic situation is a comparison of two or more mutually exclusive points of view.
Problem-based assignments are assignments that pose problems for students and direct them to independently search for solutions.
Project method
A method based on children's needs and interests, stimulating children's initiative; with its help, the principle of cooperation between a child and an adult is realized, allowing one to combine the collective and the individual in the educational process. Focused on the development of research and creative activity of students, on the formation of universal educational activities. I use it mainly in lessons about the surrounding world and literary reading. For example, “Visiting winter”, “My pets”, “The secret of my last name”.
Discussion method
Where a person is a creator, there he is a subject. The need for communication is the first manifestation of the subject’s activity.
The ability to communicate with each other and conduct a discussion allows each child to develop the ability to listen, speak in turns, express their opinions, and experience a sense of belonging in a joint collective search for truth. Students must know the rules of discussion. The teaching comes from the students, and I direct the collective search, pick up the right thought and bring them to conclusions. Students are not afraid to make a mistake in their answer, knowing that their classmates will always come to their aid, and together they will make the right decision.
The use of information technology in lessons in primary school is one of the most modern means of developing the personality of a junior
schoolchildren, the formation of his information culture in accordance with the needs of modern society. The use of information and computer technologies by teachers allows primary schoolchildren to develop the ability to work with information, develop students’ research skills and communicative competence, and also more actively involve students in
educational process. The use of ICT makes the lesson spectacular and visual; working with a computer arouses increased interest in children and increases motivation to learn.
The use of ICT by primary school teachers in the educational process allows:
develop students' research skills and creative abilities;
strengthen learning motivation;
to form in schoolchildren the ability to work with information, to develop communicative competence; actively involve students in the learning process; create favorable conditions for better mutual understanding between teachers and students and their cooperation in the educational process.
Summarizing methods
This method allows you to effectively, competently and interestingly summarize the lesson and complete the work in the form of a game. For me, this stage is very important, because it allows me to find out what the children have learned well and what they need to pay attention to in the next lesson. For example, “Chamomile”... Children tear off chamomile petals, pass colorful sheets around in a circle and answer the main questions related to the topic of the lesson written on the back.
Relaxation methods
If you feel that your students are tired, take a break and remember the restorative power of relaxation! Method "Earth, air, fire and water". Students, at the teacher’s command, depict one of the states - air, earth, fire and water. I myself take part in this, helping insecure and shy students to participate more actively in the exercise. In my work I use “Physical exercises for the eyes”.
“Many subjects at school are so serious that it is good to take every opportunity to make them a little fun.”
Lessons using active learning methods are interesting not only for students, but also for teachers. But their unsystematic, ill-considered use does not give good results. Therefore, it is very important to actively develop and implement your own gaming methods into the lesson in accordance with the individual characteristics of your class.
Literature:
Yagodko L.I. Using problem-based learning technology in elementary school / L.I. Yagodko // Elementary school plus before and after. - 2010.
School teaching methods
Slides: 15 Words: 1111 Sounds: 0 Effects: 5Content. Definition of the concept of “teaching method”. Various approaches to the classification of teaching methods in modern didactics. Classification of teaching methods in higher education. Means of education. Teaching methods. The term "method" comes from the Greek. "Methods" is the path to the truth. Classification of educational institutions according to the source of knowledge (verbal, visual, practical). Modern classification of educational institutions in higher education. There are 2 groups of methods: Methods of the first group are divided into 2 subgroups: Information and development Problem-search. Reproductive methods: Retelling educational material. Perform the exercise according to the sample Laboratory work according to the instructions. - Teaching methods at school.ppt
Forms and methods of teaching
Slides: 18 Words: 1588 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0The concept of teaching methods and techniques. Active learning methods. The problem of choosing teaching methods. The concept of teaching methods. The implementation of the educational, educational and developmental functions of training depends on the choice of method. The concept of teaching techniques. Verbal methods (methods of presentation). The presentation of educational material can be in the form of an explanation or description. Explanation is a form of mastering theoretical educational material. The duration of the story is no more than 10-15 minutes. in elementary grades, 30-40 minutes for seniors. Conversation is a question-and-answer form of mastering educational material. - Forms and methods of teaching.ppt
Technologies and teaching methods
Slides: 61 Words: 3577 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0INNOVATIVE EDUCATIONAL METHODS AND TECHNOLOGIES Head of the Department of Development and Quality of Education Ph.D. Taranukha S.N. Necessity of use: Criterion of the state accreditation indicator “Methodological work” “Use of innovative methods in the educational process.” The Federal State Educational Standard for Higher Professional Education, which established a competency-based approach, established the requirement for the use of interactive methods in the educational process. Innovative methods can be implemented in both traditional and distance learning technologies. Thus, the dependence of educational technologies on the goals of education. - Technologies and teaching methods.ppt
Teaching methods
Slides: 18 Words: 1171 Sounds: 0 Effects: 94Teaching methods. Ways of joint activity between teacher and students. Classification of teaching methods. Classification of methods by “source of knowledge”. Classification according to increasing degree of independence of students. Three main groups of methods. Organizational methods. Requirements for the effectiveness of methods. Verbal methods. Demonstration. Exercises. Independent work. Control methods. Practical methods. Didactic workshop. Basis for classification of teaching methods. - Teaching methods.ppt
Ways of learning
Slides: 46 Words: 2155 Sounds: 0 Effects: 52Active forms of work with teachers. Great blessing. Developing empathy for teachers. Advantages and disadvantages. Introduction by the training director. Category of participants. Glossary. Teaching methods. Active and interactive teaching methods. Forms of interactive learning. Binary lesson. Choosing a method and form of training. What distinguishes a modern lesson from a traditional one? Means of education. Learning process. Learning outcomes. A fireplace filled to the brim with wood. Food for thought. Mechanisms for organizing the educational process. Explanatory way of teaching. Stages of a creative lesson. Problem-based learning. - Ways of learning.ppt
Approaches in education
Slides: 59 Words: 2442 Sounds: 0 Effects: 18Educational and methodological support for the introduction of Federal State Educational Standards LLC. Competency-based approach in education. The essence of the competency-based approach. Assimilation of the amount of information. Competence-based approach. Knowledge. Level of education. Competence and competency. Competence. Individual psychological feature. Competence. Educational competence. Educational competencies. System-activity approach in education. Conceptual provisions. Parameters of personal development. Social and professional personality characteristics. Collaboration between teachers and students. Development occurs in activity. - Approaches in education.ppt
Differentiation and individualization of learning
Slides: 12 Words: 1123 Sounds: 0 Effects: 164DIFFERENTIATION and INDIVIDUALIZATION OF TRAINING IN A MODERN UNIVERSITY: problems of methodology and technology. Differentiation and Individualization of Learning Process in Modern High School. New meanings of differentiation and individualization New Philosophy of Differentiation and Individualization. Differentiation of Learning – Part of the Educational Management. Differentiation as part of educational management. Differentiation as a principle of ordering a set Differentiation as a Principle. According to the level of current development (IQ, special abilities). According to learning objectives (according to the final tasks that will be solved). - Differentiation and individualization of learning.ppt
Teaching Strategies
Slides: 46 Words: 1666 Sounds: 0 Effects: 84Strategies for teaching in new conditions. Lecture. Conceptual apparatus. Basic concepts. Passive strategies. Methods of communication. Forms of embodiment. Selection conditions. Save time. Active strategies. Joint discussion. Individual questions and comments. Increased public interest. Ability to prevent topic drift. Interactive strategies. Organizer. Group work. Prepare for the topic being discussed. Expansion of the resource base. Strategies for working with information. Systematic approaches. Creative approaches. Subordination. Strategy comparison positions. Factors for choosing a strategy. - Teaching Strategies.ppt
Active learning
Slides: 15 Words: 410 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Active learning technology. History of origin. Dewey, K.D. Ushinsky and others. Views from proponents of student activism. Socrates (399 BC) saw the surest way to manifest human abilities in self-knowledge. He insisted that education should teach one to think. V. A. Sukhomlinsky (1918-1970) called for special measures and techniques to support students’ desire to be pioneers. Didactic prerequisites. Active learning technology includes: It embodies the following principles: personal activity; problematic; unity of training and education. Game learning has proven the high effectiveness of using game, competitive, and team teaching methods. - Active learning.ppt
Methods of training and education
Slides: 33 Words: 721 Sounds: 0 Effects: 2Teaching methods Educational methods Research methods. Six figures of thinking. The goal is a triangle figure. Accuracy - circle figure. The point of view is a square figure. Interest – heart figure. Value - diamond figure. The result is a rectangle shape. Teaching methods. Method (from the Greek method - a way, a path to something) is a way of implementing an activity as a system. A teaching technique (teaching technique) is a short-term interaction between a teacher and students aimed at transferring and assimilating specific knowledge, skills, abilities. Classification of teaching methods according to Babansky. - Methods of training and education.pptx
Individual educational route
Slides: 16 Words: 568 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Individual educational route. Regulatory and legal basis for organizing IOM. Organizational and pedagogical document. Humanitarian and system-activity approaches. Individual educational trajectory. Differentiated educational program. Educational program. IOM design principles. Tutor support. Stages of IOM implementation technology. Organizational and pedagogical conditions. Content basis of IOM. Temporary structure of the IOM. Forms of implementation. Controlling structure. Possible risks and preventive measures. - Individual educational route.ppt
Forms of study at the university
Slides: 46 Words: 879 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Forms of organization of training at a university. Lecture. The main form of organization of training at a university. Requirements for the lecture. Analysis of different points of view. Types of lectures. Introductory lecture. Lecture-information. Review lecture. Problem lecture. Lecture-visualization. Binary lecture. Lecture with pre-planned errors. Lecture-conference. Lecture-consultation. The variety of species speaks of the creativity and skill of the teachers. Functions of lectures. The lecture informs the student about the achievements of science. The lecturer explains and explains the essence of the theory. The lecture is carried out through the evidence of the lecturer’s statements. - Forms of study at the university.ppt
Research Seminar
Slides: 14 Words: 947 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Research seminar. The history of Russian everyday life. Mastering primary skills. Familiarity with accepted practices in the academic community. Mastering the primary skills of academic work. Learner competencies. Genres of historical writing. History of everyday life. Searches for information resources. Bibliographic search. Informational resources. Research project. Compiling a bibliography. - Research Seminar.ppt
Systems approach
Slides: 29 Words: 2208 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Systems approach. The main mission of education. Achievements of Education for All. Access to preschool education. Achieving the goal of education. Problems of quality of education. Indicators. International monitoring. Some schoolchildren. The quality of education. Text. Second grade level text. The impact of poor quality education on development. Lack of resources. Continuous reproduction of global inequality. Basic starting points. Inadequate technical tools. Full analysis. Low ‘absolute’ specified criterion. UNESCO's response. Initial conditions for KDKOO. High-quality educational system. - Systematic approach.ppt
Active learning methods in primary school
Slides: 12 Words: 456 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Using active learning methods in primary school lessons. Paper properties. Method. Working on riddles. Problematic situation. Introduction to the properties of paper. Interactive technology. Active method. The participant's attitude towards his own action. Peculiarities. A way out of the current problematic situation. - Active teaching methods in primary school.ppt
Active forms of learning
Slides: 13 Words: 405 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Active forms of teaching the basics of life safety in elementary school. Goals: Ensuring a healthy lifestyle, maintaining health. Ensuring the personal safety of younger schoolchildren. Objectives: - mastering knowledge about a healthy lifestyle; - possible causes of dangerous situations of various types; safety measures and rules; rules of behavior in a dangerous situation; use of rescue equipment. Forms of work that increase the level of learning activity. Non-traditional forms of conducting lessons (business game, competition, seminar, excursion, integrated lesson); Non-traditional forms of training (integrated, united by a single theme, problem; combined, project, creative workshops, etc.); Game forms; Dialogical interaction; Problem-task approach (problematic questions, problematic situations, etc.). - Active forms of learning.ppsx
Interactive training
Slides: 31 Words: 1293 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Innovative technologies in vocational education. Classification of innovative teaching technologies. Psychology-based training. Interactive method. Passive learning method. Active learning method. Interactive teaching method. Interactive learning technologies. The role of the teacher in the implementation of the interactive method. Classification of interactive technologies. Non-imitation technologies. Imitation technologies. Forms of interactive learning. Problem lecture. Seminar - debate. Educational discussion. Brainstorm. Didactic game. Forms of work. Internship. Project-based learning technologies. - Interactive training.ppt
Active learning methods
Slides: 14 Words: 1374 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Active learning methods. Signs of active learning methods. Signs of active learning methods Problematicism. Peer education. Personalization. Research into the problems and phenomena being studied. Spontaneity and independence of students’ interaction with educational information. Motivation. The creative nature of educational and cognitive activity. Competitiveness, playful nature of classes. Emotional impact. Classification of active learning methods at universities (A.M. Smolkin). Non-imitation. Imitation. Gaming. Non-game. Active learning methods: lectures and reports. - Active learning methods.ppt
Interactive forms of training
Slides: 17 Words: 680 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Methods of using interactive forms in organizing educational activities of students when studying the ORKSE course. Interactive learning is, first of all, dialogue learning. Basic principles of interactive strategy. Types of interactive teaching methods. Positive and negative aspects of the interactive strategy. What associations does the word “Game” evoke for you? Game (in education). Own definition of the concept “Game”. The potential of game approaches in teaching. Tasks of educational games. Dangers and difficulties. Elements and characteristics of the game. Classification of games. - Interactive learning forms.ppt
Personally-oriented learning technologies
Slides: 29 Words: 3219 Sounds: 0 Effects: 101Seminar. Acquaintance with the essence of personality-oriented technology. Association method. The role of psychological and pedagogical diagnostics. Development of a knowledge system. Personality-oriented technologies. LORO technology. Technology of complete assimilation of knowledge. Technology of multi-level training. Technology of collective mutual learning. Benefits of CSR. Modular learning technology. Training module. Principles of the educational process. Results of psychological and pedagogical examination. Planning and technology. Scheme of a comprehensive lesson analysis. Generalized mechanism of learning technology. - Personally-oriented learning technologies.ppt
Traditional and learner-centered learning
Slides: 64 Words: 1564 Sounds: 0 Effects: 53Organization of the educational process. Plan for holding a teachers' meeting. Factors determining the UVP system. Pedagogical concepts. Traits of a modern mass person. Formation of the image of a person. Trends in modern society. Education. The Becoming of Man. Trends in the development of modern theoretical foundations of pedagogy. Attitude towards the student. Results of research into psychological mechanisms of personality development. Positive aspects of traditional teaching. Basic educational processes of traditional teaching. Basic educational processes of LOO learning. - Traditional and student-centered learning.ppt
Modular training system
Slides: 14 Words: 411 Sounds: 0 Effects: 82Terrible danger. The concept of "module". Module composition. Differences between modular training. The purpose of modular training. Initial scientific ideas. Sequence of teacher actions. Routing. Creating a modular program. Private didactic goals. The sequence of actions of the teacher when compiling a module. Form of educational element. - Modular training system.ppt
Modular learning at school
Slides: 17 Words: 644 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Modular learning in primary school. Research and discovery of the method. Development of the educational process. Module. MO is an independent didactic system. Basic principles of modular technology P.Ya. Jucevicien. Traditional education system. The difference between the modular system T.I. Shamova. Algorithm for compiling a module. Advantages of MO. Goals and objectives of the group. Work plan. Forms and methods of work. - Modular learning at school.ppt
Multi-level training
Slides: 33 Words: 2958 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Technology of multi-level training. Multi-level training. Activity. Appropriate level. Psychological and pedagogical diagnostics. Scientific ideas. Test results. The individuality of each student. Dividing students. The need to design goals. Principles of technology. Creation of pedagogical conditions. Working with students. Actions of the teacher and students. Preparation of educational material. Methodology of leveled training. Students. Fact. Volume of material. Level of mandatory training. Success in learning. Multi-level approach. Lessons on consolidation and generalization. Forms of work. - Multi-level training.pptx
Programmed learning
Slides: 27 Words: 795 Sounds: 0 Effects: 2Programmed learning. Training is considered poorly managed. Average overall pace of learning the material. The teacher’s ignorance of the progress of students’ assimilation of the communicated knowledge. Difficulty for students to work independently. The emergence of programmed learning. Optimization of building and managing the educational process. Create an optimal environment for learning mathematics. Basic forms of training programming. Linear program. Characteristics of a linear program. Questions or gaps. Program framework. Branched program. Answer. Understanding the reason. The purpose of the branched algorithm. - Programmed learning.ppt
Differentiated learning
Slides: 21 Words: 893 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Chinese parable. Technology of differentiated learning. Structure of pedagogical technology. Manufacturability criteria. History of the issue. Goals of differentiated instruction. The concept of differentiation. Differentiated learning. Types of intraclass differentiation. System of joint activity between teacher and student. Stages of organizing differentiated training. Criteria. Features of groups. Students with learning disabilities. Directions for differentiation of training. Differentiation of educational tasks. Technology system. Unjustified and inappropriate equalization of children is excluded. - Differentiated learning.ppt
Technology of pedagogical workshops
Slides: 14 Words: 395 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Technology of pedagogical workshops. The essence of technology. Principles of workshop construction. Workshop stages. Induction. Self-construction. Socioconstruction. Socialization. Break. Success analysis. Expensive technology. Restrictions on the use of technology. Lack of readiness. The restrictions are not insurmountable. - Technology of pedagogical workshops.ppt
Interactive teaching methods
Slides: 12 Words: 355 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Interactive teaching methods. Activity method. The word "interactive" (English). Interactive learning – learning through experience. Participants’ experiences of a specific experience (game, exercise, situation) Understanding of the experience gained Generalization Application in practice. Solves three main tasks: Educational and cognitive task (eg: find out, determine...) Communicative and developmental (eg: development of educational skills) Socially oriented. Main features of the interactive: Special techniques for interaction have been developed (for working in pairs, groups, collectively): Brainstorming Two, four - together Mosaic Microphone Aquarium Live line Big circle Who is bigger? - Interactive teaching methods.ppt
Student-centered learning
Slides: 16 Words: 583 Sounds: 0 Effects: 7Student-centered learning. The goal of Russian education at present. The task of the school. Personally centered education. Personality-oriented education includes the following approaches: Multi-level Differentiated Individual Subjective-personal. Features of the person-centered approach. The educational process should be aimed at... Assimilation of knowledge. Development of cognitive powers. Methods of assimilation and processes of thinking. Development of creative abilities. Pedagogical technologies based on a student-oriented approach. Technology of individual learning Collective way of learning. - Personally centered learning.ppt
Personality-oriented technologies
Slides: 19 Words: 432 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Basic conceptual ideas of technology of personality-oriented education. Trends in the development of modern foundations of pedagogy: The system of “teacher-child” relations. Conceptual provisions. 1. The center of the concept is Man. 2. Transition to the sphere of subject-subject relations. 3.Creating conditions for revealing personal potential. 4. Self-education. Values of person-centered education. Human. Culture. Creation. Model of personality-centered education. Personal development. Taking into account features. Selection of groups. Homogeneous groups. A child is a unique individual. - Personally-oriented technologies.ppt
Modular training
Slides: 33 Words: 1337 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Organization of modular training. Project program. Tasks: Program. Composition of the group. Features of modular training (ML). Distinctive features of MO. The content of the training is presented in complete independent complexes. The forms of communication between teachers and students are changing. Relations become more equal. Tasks of the Ministry of Defense. Development of intelligence, memory and speech of students. Formation of communication skills. Formation of self-knowledge skills based on reflection. Theoretical foundations of MO. Activity-based approach to learning (research by A.N. Leontiev). Theory of developmental learning (L.S. Vygotsky). - Modular training.ppt
Modular training technology
Slides: 17 Words: 1032 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Modular learning technology. The concept of pedagogical technology. The importance of modular training. Modular training. The essence of modular training. Directions for implementing modular training. Level-by-level differentiation of training. Taking into account the individual pace of learning material. Individualization through the organization of assistance and mutual assistance. Organization of individual control. Students work at their own pace. A variety of educational elements offered to the student in each module lesson. Requirement for modular training. Fundamentals of modular learning technology. - Modular learning technology.ppt
Pedagogical workshop
Slides: 14 Words: 921 Sounds: 0 Effects: 0Pedagogical workshop as a creative method of implementing the philosophy of education. What is a pedagogical workshop? Problem field of the pedagogical workshop. Pedagogical workshop as a creative process. As a result, during the process of intuitive search, something new appears in the minds of the participants. At the next stage, an understanding of the laws of the creative process occurs (reflection). The pedagogical workshop is a form of self-awareness (reflection). Reflection. In the pedagogical workshop, both types of reflection are constantly at work. Pedagogical workshop as an epiphany. The ascent is planned in advance by the workshop leader. - Pedagogical workshop.ppt
Independent work in class
Slides: 68 Words: 1952 Sounds: 0 Effects: 41Requirements for independent work. Having a specific goal. Availability of a specific task. A clear form of expressing the result cf. Determination of the form of verification cf. It is obligatory for each student who receives the task to complete the task. The content of the assignments must correspond to the specific TDC. Individualize tasks to ensure successful completion cf. Five groups. Questionnaire for students. Our teachers apply management principles when teaching. Table for collecting data characterizing the organization of independent work in the lesson. Was there independent work during the lesson? -
Ulyanovsk 2012 METHODS OF TEACHING is a system of sequential interconnected actions of the teacher and students, ensuring the assimilation of the content of education, the development of mental strength and abilities of students, their mastery of the means of self-education and self-study, a method of orderly interrelated activities of the teacher and students, aimed at solving the problems of education. (Yu.K. Babansky). a system of purposeful actions of a teacher that organizes students’ learning activities, leading, in turn, to achieving learning goals. (I.Ya. Lerner). a system of regulatory principles and rules for the purposeful activity of a teacher and a group of students, implemented through a combination of methodological techniques for solving a certain range of didactic tasks (M.I. Makhmutov) METHODS OF ORGANIZATION AND IMPLEMENTATION OF LEARNING AND COGNITIVE ACTIVITIES According to the source of transmission and perception of educational information Verbal Story Lecture Conversation Dispute Conference Explanation Discussion Visual Observation Demonstration Practical Experiments Exercises Performing work tasks According to the logic of transmission and perception of educational information deductive inductive From general to specific From particular to general ACCORDING TO THE DEGREE OF INDEPENDENT THINKING OF STUDENTS reproductive Explanatory illustrative Conversation Working with a book Oral presentation Observation productive Problem presentation The problem is solved by the teacher Problem my situation Problem task Partially search reproductive Conversation Dispute (the conclusion is made jointly) Programmed training research Experimental work Creative work EXPLANATORY - ILLUSTRATIVE METHOD If a student knows from the teacher what knowledge should be based on, what intermediate tasks must be passed through, how to solve them, then his functions are reduced to memorization and reproduction. This method corresponds to the traditional view of education as the transfer of knowledge and experience of the older generation to the younger generation and remains the most common Initial conditions, planned results Methods for solving intermediate problems Intermediate tasks PROGRAMMED TRAINING METHOD If the student does not know the intermediate tasks, but everything else is open. The student knows where to start and what to do. The main concept - a training program - is a set of material and instructions for working with it. The process is completely deterministic. Means of implementation: printed manual, computer, person Heuristic method of teaching In the case when intermediate problems are open, but the method for solving them is not reported, the student has to try different paths, using many heuristics PROBLEM-BASED TRAINING METHOD You can hide both intermediate problems and their solutions, then a problem arises the contradiction between knowledge and the necessary, i.e. The student finds himself in a problematic situation. RESEARCH (MODEL) METHOD OF TRAINING Initial conditions are not identified by the teacher, but are chosen by the student depending on his understanding of the task. From these conditions, he obtains results, compares them with the planned ones, if necessary returns to the beginning, makes changes to the initial conditions and again goes the whole way. And until the student either achieves the planned results or proves that this is impossible. By hiding different elements of the scheme from the student along with the initial conditions, we will obtain varieties of the model method, for example, model-heuristic TABLE OF CLASSIFICATION OF TEACHING METHODS (according to V.V. Guzeev) Method scheme Name of the method Explanatory and illustrative Programmed Heuristic Problem-based Model CLASSIFICATION OF TEACHING METHODS (PO Guzeev V.V.) The position of the teacher is changing: from a translator of learning content, he turns into a manager, organizer of communications and an expert. His functions consist of competently setting tasks, organizing the process of solving them and examining the solutions obtained by students for compliance with the planned results. The effectiveness of training also increases sharply. Scheme of the method Name of the method Explanatory and illustrative Programmed Heuristic Problem-based Model TABLE OF CLASSIFICATION OF TEACHING METHODS (according to V.V. Guzeev) You have to pay for high efficiency. First of all, you need to change yourself. The transition from traditional “sage on the scaffold” training models to student-centered strategies and “advisor at hand” activities requires a lengthy process of professional development—one that is well beyond the resources and expertise of most educational institutions. It is necessary to create role models through which experience can be passed on to other schools. Scheme of the method Name of the method Explanatory and illustrative Programmed Heuristic Problematic Model CLASSIFICATION OF TEACHING METHODS (According to V.V. Guzeev) Position of the student: object of learning, recipient of ready-made information; active subject of learning, independently obtaining information; active subject of learning, constructing the necessary methods of action. Method scheme Name of the method Explanatory and illustrative Programmed Heuristic Problem-based Model CLASSIFICATION OF TEACHING METHODS (according to V.V. Guzeev) Position of the teacher: translator of learning content, manager, organizer of expert communications Method scheme Functions of an expert teacher: competent formulation of tasks, organization of the process of solving them, examination decisions to ensure compliance with planned results. Name of the method Explanatory and illustrative Programmed Heuristic Problem-based Model WAYS OF DETERMINING METHODS OF TEACHER WORK IN THE LESSON. Three questions are asked Initial conditions updated by the teacher no model yes Their solution was given by the teacher Intermediate tasks formulated by the teacher no yes Their solution was given by the teacher no yes Explanatory illustrative heuristic no yes Programmed problematic NATURE OF MANAGEMENT OF LEARNING WORK Under the guidance of the teacher Independent work Working with a book Completing a written assignment Laboratory work METHODS STIMULATION AND MOTIVATION OF LEARNING AND COGNITIVE ACTIVITY Methods of stimulating interest in learning Educational games Educational discussions Creating an entertaining situation Creating a situation of success Implementation of a situation of failure By the nature of the management of educational work Forming a belief in the social and personal significance of learning Presentation of requirements Exercises in fulfilling requirements Competitiveness, rewards, punishments Methods oral control and self-control in training Oral examinations Individual survey Programmed survey Frontal survey Oral self-control Oral tests





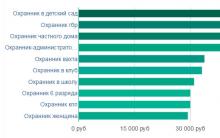




Such work" Sergey Demyanov
Unsweetened life Can a diabetic work as a security guard?
How long does it take for a parcel from China to Russia from Aliexpress?
How to find a good job - a detailed guide for those who want to get their dream job!
Presentation on the topic “Acmeism