1 slide

2 slide
Composition (structure) of the population Age composition Ethnolinguistic composition Religious composition Gender composition

3 slide
Sex composition of the world population Typically, about 5% more boys are born than girls. Boys' bodies are weaker and infant mortality is higher. Around the age of 20, the ratio of men to women levels off. This is explained by the higher mortality rate among men than among women.

4 slide
Countries Countries that are male-dominated Countries that are female-dominated Reasons why these countries are male-dominated Reasons why these countries are female-dominated Oil-producing countries have a lot of male migrants Women's life expectancy is higher than men's These countries have unequal status of women: early marriages Losses in the Second World War Countries with approximately equal numbers of men and women Give examples of countries

5 slide
Age composition of the world's population Two opposing trends are observed in the age structure of the world's population. In developed countries, the proportion of older people is increasing – the population is aging. In developing countries, with their high birth rates, there is a rejuvenation of the population. Between these two poles there is an intermediate group of countries in which the share of older people and children is in balance. Determine which of the graphs shows: Progressive type - ? Regressive type - ? Stationary type - ?

6 slide
Ethnolinguistic composition of the world's population There are about 4 thousand ethnic groups (peoples) in the world. unity of territory at the initial stages of cultural development based on their language of economic and everyday characteristics. Ethnicity is a historically established social group that has a set of characteristics: Nations Nationalities Tribes Nationalities Peoples or ethnic groups

7 slide
The classification of peoples is most often based on the linguistic principle. The total number of currently known languages is more than 5.5 thousand, and one and a half thousand of them are considered to be completely unformed or endangered. The most common peoples: Chinese - 1100 million people, Americans - 190 million people, Hindustani - 220 million people, Bengalis - 180 million people. The most common languages: Chinese - 907 million people, English - 456 million people, Hindi - 383 million people, Spanish - 320 million people.

8 slide
The national composition of the population of the countries of the world is very different. In general, three main groups of countries can be distinguished. Name the groups and give examples of countries
Slide 1
Composition (structure) of the World Population
Geography lesson in 10th grade.

Slide 2
Topic study plan
Sex composition of the population. Age composition of the population; labor resources Educational composition of the population as an indicator of its “quality”. Ethnic (national) composition of the population; the world's largest nations and language families. Single- and multinational states. Religious composition of the population; world religions and their history and geography. The main centers of ethno-religious conflicts.

Slide 3
Sex composition of the population
characterized by a predominance of men. The number of men is 20-30 million higher than the number of women. On average, 104-107 boys are born per 100 girls. However, the differences across countries around the world are quite significant.

Slide 4

Slide 5

Slide 6
Age composition of the population; labor resources
children (0-14 years); adults (15-64 years); elderly (65 years and older).
When analyzing the age composition of the population, it is customary to distinguish three main age groups:
In the structure of the world's population, the share of children is on average 34%, adults - 58%, elderly - 8%.

Slide 8
The influence of the age structure of the population on labor resources and the economically active population (EAP)
In the world, about 45% of the total population is considered economically active; in the countries of Foreign Europe, North America, and Russia this figure is 48-50%, in the countries of Asia, Africa, and Latin America - 35-40%. This is due to the level of women’s employment in social production and the share of children in the age structure of the population. The ratio between the working population and the non-working (children and elderly) is called the demographic burden. The demographic burden in the world averages 70% (that is, 70 unemployed per 100 able-bodied), in developed countries - 45-50%, in developing countries - up to 100%.

Slide 9
Age and sex pyramids
For graphical analysis of the age and sex structure of the population, sex and age pyramids are used, which look like a bar chart

Slide 11

Slide 12

Slide 13

Slide 14
Ethnic (national) composition of the population
Humanity is usually divided into three main races: Caucasoid (countries of Europe, America, South-West Asia, North Africa); Mongoloid (countries of Central and East Asia, America); Negroid (most African countries).

Slide 15
The ethnic composition of the population is the result of a long historical process of mixing and relocation of representatives of different races and ethnic groups. Ethnicity (people) is an established stable group of people, characterized by a common language, territory, peculiarities of life, culture and ethnic identity. In total there are 3-4 thousand ethnic groups in the world. Some of them have turned into nations, others are nationalities and tribes.

Slide 16
Classification of ethnic groups
The peoples of the world vary in size. The vast majority of peoples are small in number. Only 310 nations have a population of more than 1 million people, but they account for about 96% of the Earth's population.

Slide 17
The largest nations in the world by population include:
Chinese (1,120 million people); Hindustani (219 million people); US Americans (187 million people); Bengalis (176 million people); Russians (146 million people); Brazilians (137 million people); Japanese (123 million people).

Slide 18
Classification by language:
By language, peoples are united into language families, which, in turn, are divided into language groups. There are 20 language families in the world

Slide 19

Slide 20
Single- and multinational states.
with a sharp predominance of one nation in the presence of more or less significant national minorities (Great Britain, France, Spain, China, Mongolia, Turkey, Algeria, Morocco, USA, Commonwealth of Australia); binational (Canada, Belgium); with a complex but ethnically homogeneous national composition (Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Laos); with a complex and ethnically diverse national composition (Russia, India, Switzerland, Indonesia).
Single-national
Many national
The main nationality makes up 90% of the total population.
Denmark, Sweden, Germany, Poland, Italy, Japan, Saudi Arabia, Egypt, most Latin American countries.
These are countries within whose state borders several ethnic groups live.

Slide 21
The main centers of ethno-religious conflicts
with the actual economic and social inequality of peoples in some developed countries, the infringement of the cultural identity of national minorities (Basques in Spain, Corsicans in France, Scots in Great Britain, French-Canadians in Canada); with the process of uniting related tribes into nationalities, and nationalities into nations in many developing countries (India, Indonesia, Nigeria, Zaire, Sudan); with the consequences of European colonization, which continues to oppress the indigenous population (Indians, Eskimos, Australian aborigines); with racial discrimination (South Africa, USA); with the formation of new states in the territories of the former USSR and the socialist countries of Eastern Europe.
The problem of interethnic relations is currently quite acute. It's connected:

Slide 22

Slide 23

Slide 24
Religions and social life
Most religions of the world attach special importance to continuity, traditions, and adherence to certain norms of behavior. From this point of view, religions definitely play a conservative role in society. Religions are often an obstacle to demographic policy. Religions have an indirect influence on agricultural development by limiting the consumption of certain foods (at certain times of the year) and by attaching symbolic significance to domestic animals. More than 260 million Buddhists are vegetarians, Hindus do not eat beef, and Muslims do not eat pork.

Slide 25

Slide 26
A religion based on the teachings of Jesus Christ.
Christianity
Number of adherents of Christianity by country in percentage.

Slide 27
appeared at the beginning of the first millennium AD in the east of the Roman Empire, on the territory of modern Israel, as a protest against Judaic exclusivity. It quickly spread among slaves and the poor. Having proclaimed the equality of all people, Christianity rejected the existing slave-owning social order, giving the desperate hope of gaining freedom through the knowledge of the divine truth that Christ brought to earth. According to Christianity, God exists in three persons - the Father, the Son and the Holy Spirit. God the Son accepted martyrdom to atone for the sins of people and come to Earth a second time to establish the kingdom of heaven. The holy book of Christians is the Bible, consisting of the Old Testament and the New Testament. The main ethical standards are patience and forgiveness. In 1054 there was a complete break between the Roman (western) and Constantinople (eastern) branches of Christianity, it was divided into Catholicism and Orthodoxy. The main differences between them are the question of the origin of the Holy Spirit: Catholics believe that it came from God the Father and God the Son, Orthodox believe that it came from God

https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Preview:
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
Preview:
To use presentation previews, create a Google account and log in to it: https://accounts.google.com
Slide captions:
The world economy is the sum of the national economies of all countries of the world... united by global economic relations and Trade Tourism Scientific and technical cooperation Credit and financial relations
World globalization is the process of development of the world economy, implying:
World economic globalization Form of economic globalization No. 1 - the creation of transnational corporations In what ways can we deepen economic ties more strongly and actively?
Transnational corporations TNCs are giant financial and industrial associations, international in capital. Built on the principle of centralized planning and management. They differ from simple firms by the presence of a wide network of foreign branches and subsidiaries. There are more than 40,000 TNCs in the world.
What benefits does TNC bring to different countries? Capturing new sales markets Savings in production and sales Reducing transportation costs Savings on wages Expanding the economy beyond the country's borders Cheaper "foreign" goods Jobs Tax revenues
For many years, the list of the world's main TNCs includes: Apple Inc. Bacardi-Martini Bayer BMW Boeing Benetton Group Bosch BP Campina Coca-Cola Daimler Danone DuPont Epson Ford Gazprom General Electric General Motors Honda IKEA Intel LG Lufthansa Lukoil McDonald's Microsoft Michelin Nestlé Nike Nintendo Nissan PepsiCo Pirelli Rusal Siemens Sony Toshiba Toyota Vodafone The Walt Disney Company Yahoo ! Is there a pattern between these companies?
Major TNCs
Symbols of globalization?
World economic globalization Form of economic globalization No. 2 - international economic integration What other way can we deepen economic ties between countries? Union... of some states
INTERNATIONAL economic integration Unions.. Alliances... Associations... Industry associations Regional associations THIS IS THE PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT OF DEEP AND SUSTAINABLE RELATIONS OF SEPARATE GROUPS OF COUNTRIES, BASED ON THEIR IMPLEMENTATION OF CONSERVED INTERSTATE POLICIES
The emergence and spread of transnational corporations Forms of world economic globalization No. 1 No. 2 Development of international unions in the form of economic integration
The emergence and spread of transnational corporations Forms of world economic globalization No. 1 No. 2 Development of international unions in the form of economic integration GLOBALISM IS MORE COMPLEX THAN IT APPEARS...
Demands of anti-globalists? Write off debts from the countries of the “Third World” Limit the ecological expansion of underdeveloped countries Limit TNCs, their exploitation of the population and resources Radically change the IMF and the World Bank, which increase the debts of undeveloped countries, global poverty and inequality Limit the management of the world, the control of world organizations (UN, World Bank , IMF) of the G7 countries Non-interference by the governments of the United States and other Western countries in the affairs of other countries Open Western markets to goods from developing countries,
Making the fruits of globalization available to the maximum number of countries is one of the tasks facing the world community. Globalization: good or not so good?
Slide 1
Slide 2
 Number Over the entire history of mankind, more than 100 billion people were born on Earth. Throughout history, population growth has been slow, accelerating only in modern and especially modern times. At the beginning of our era, 230 million people lived on Earth. The population reached 1 billion in 1820. In 1927 there were 2 billion, in 1960 - 3 billion, in 1974 - 4 billion, in 1987 - 5 billion, in 1999 - 6 billion people. In 2006, the world's population was 6.5 billion people. In 2011 – 7 billion people. The five largest countries in the world by population are China, India, USA, Brazil, Indonesia. The world population forecast for 2050 is 9.2 billion people. Reproduction (natural movement) of the population is a set of processes of fertility, mortality and natural increase that ensure the continuous renewal and change of human generations.
Number Over the entire history of mankind, more than 100 billion people were born on Earth. Throughout history, population growth has been slow, accelerating only in modern and especially modern times. At the beginning of our era, 230 million people lived on Earth. The population reached 1 billion in 1820. In 1927 there were 2 billion, in 1960 - 3 billion, in 1974 - 4 billion, in 1987 - 5 billion, in 1999 - 6 billion people. In 2006, the world's population was 6.5 billion people. In 2011 – 7 billion people. The five largest countries in the world by population are China, India, USA, Brazil, Indonesia. The world population forecast for 2050 is 9.2 billion people. Reproduction (natural movement) of the population is a set of processes of fertility, mortality and natural increase that ensure the continuous renewal and change of human generations.
Slide 3
 Population reproduction Reproduction (natural movement) of the population is a set of processes of fertility, mortality and natural increase that ensure the continuous renewal and change of human generations. We can talk about two types of population reproduction.
Population reproduction Reproduction (natural movement) of the population is a set of processes of fertility, mortality and natural increase that ensure the continuous renewal and change of human generations. We can talk about two types of population reproduction.
Slide 4
 First type The first type of population reproduction is a demographic crisis. Low rates of birth rate, death rate and, accordingly, natural increase. The birth rate is 11, the death rate is 10 people per 1000 population. The natural increase in countries of this type is on average 1 person per 1000 population. There are countries with an average annual natural population growth of 5 people per 1000 inhabitants (USA, Canada, Australia), countries with zero or close to natural growth (Belgium, Denmark, Portugal, Poland, Sweden) and countries with negative natural growth (Ukraine, Russia , Bulgaria, Latvia, Belarus, Hungary, Estonia, Lithuania, Germany, Austria, Romania, Slovenia, Czech Republic).
First type The first type of population reproduction is a demographic crisis. Low rates of birth rate, death rate and, accordingly, natural increase. The birth rate is 11, the death rate is 10 people per 1000 population. The natural increase in countries of this type is on average 1 person per 1000 population. There are countries with an average annual natural population growth of 5 people per 1000 inhabitants (USA, Canada, Australia), countries with zero or close to natural growth (Belgium, Denmark, Portugal, Poland, Sweden) and countries with negative natural growth (Ukraine, Russia , Bulgaria, Latvia, Belarus, Hungary, Estonia, Lithuania, Germany, Austria, Romania, Slovenia, Czech Republic).
Slide 5
 Second type The second type of population reproduction is a demographic explosion. High and very high fertility and natural increase rates and relatively low mortality rates. The birth rate is 24, the death rate is 8 people per 1000 inhabitants. Natural increase is 16 people per 1000 population. This type of reproduction is typical primarily for developing countries. Countries with the highest natural increase are Yemen, Uganda (35), Oman (33), Madagascar, DR Congo, Chad (30), Mauritania, Somalia, Guatemala (29).
Second type The second type of population reproduction is a demographic explosion. High and very high fertility and natural increase rates and relatively low mortality rates. The birth rate is 24, the death rate is 8 people per 1000 inhabitants. Natural increase is 16 people per 1000 population. This type of reproduction is typical primarily for developing countries. Countries with the highest natural increase are Yemen, Uganda (35), Oman (33), Madagascar, DR Congo, Chad (30), Mauritania, Somalia, Guatemala (29).
Slide 6
 Average life expectancy Average life expectancy is the expected life expectancy of the population, which is determined using calculations based on probability theory. Depends both on biological and hereditary characteristics, as well as on nutrition, work, and living conditions. Measured in number of years. At the beginning of the 21st century, this figure is on average 66 years for the whole world (64 years for men and 68 years for women). The corresponding indicators for economically developed countries are 72 and 80, for developing countries – 62 and 66, including for the least developed countries – 51 and 53 years. The average life expectancy in Russia is 65.3 years (59 years for men and 27 years for women). No other country in the world has such a huge gap between the rates of both sexes.
Average life expectancy Average life expectancy is the expected life expectancy of the population, which is determined using calculations based on probability theory. Depends both on biological and hereditary characteristics, as well as on nutrition, work, and living conditions. Measured in number of years. At the beginning of the 21st century, this figure is on average 66 years for the whole world (64 years for men and 68 years for women). The corresponding indicators for economically developed countries are 72 and 80, for developing countries – 62 and 66, including for the least developed countries – 51 and 53 years. The average life expectancy in Russia is 65.3 years (59 years for men and 27 years for women). No other country in the world has such a huge gap between the rates of both sexes.
Slide 7

Slide 8
 Sex composition On average, for every 100 girls, 104-107 boys are born; by the age of 18-20, the ratio of both sexes levels out. But in subsequent age groups, the formation of the sex composition of the population in different countries occurs differently. In approximately 2/3 of the world's countries, women predominate numerically (CIS countries, Foreign Europe, North America). In Africa, Latin America, Australia and Oceania, the number of men and women is approximately equal. In foreign Asia, men predominate (Sri Lanka, Pakistan, India, China).
Sex composition On average, for every 100 girls, 104-107 boys are born; by the age of 18-20, the ratio of both sexes levels out. But in subsequent age groups, the formation of the sex composition of the population in different countries occurs differently. In approximately 2/3 of the world's countries, women predominate numerically (CIS countries, Foreign Europe, North America). In Africa, Latin America, Australia and Oceania, the number of men and women is approximately equal. In foreign Asia, men predominate (Sri Lanka, Pakistan, India, China).
Slide 9
 Ethnic composition In total, there are 4-5 thousand peoples, or ethnic groups, in the world, some of which have formed into nations, while others are nationalities and tribes. The classification of peoples by numbers indicates, first of all, the extremely large differences between them. The bulk of the population consists of large and especially the largest nations, for example, the Chinese. Many hundreds of small nations account for only a few percent of the world's population. For example, the number of the Botocuda tribe in Brazil is less than 1 thousand people.
Ethnic composition In total, there are 4-5 thousand peoples, or ethnic groups, in the world, some of which have formed into nations, while others are nationalities and tribes. The classification of peoples by numbers indicates, first of all, the extremely large differences between them. The bulk of the population consists of large and especially the largest nations, for example, the Chinese. Many hundreds of small nations account for only a few percent of the world's population. For example, the number of the Botocuda tribe in Brazil is less than 1 thousand people.
Slide 10
 Linguistic composition The classification of peoples by language is based on the principle of their kinship. The most widespread language family is Indo-European. The languages of this family are spoken by 150 peoples with a total population of more than 2.7 billion people. Approximately 1.4 billion people speak languages of the Sino-Tibetan family, mainly Chinese, more than 370 million speak languages of the Afroasiatic family, mainly Arabic. The number of most other families is much smaller.
Linguistic composition The classification of peoples by language is based on the principle of their kinship. The most widespread language family is Indo-European. The languages of this family are spoken by 150 peoples with a total population of more than 2.7 billion people. Approximately 1.4 billion people speak languages of the Sino-Tibetan family, mainly Chinese, more than 370 million speak languages of the Afroasiatic family, mainly Arabic. The number of most other families is much smaller.
Slide 11
 Religious composition The most widespread of the world's religions is Christianity, which is practiced by approximately 2.4 billion people, mainly in Europe, America and Australia. Islam ranks second in the number of believers - more than 1.5 billion people. Islam has been declared the state religion in many countries, located mainly in Asia and Africa. The third place among world religions in terms of the number of adherents belongs to Buddhism - 370 million people. Buddhism is widespread in Central, Southeast and East Asia. National religions include Hinduism in India, Confucianism in China, and Shintoism in Japan. Judaism also became widespread.
Religious composition The most widespread of the world's religions is Christianity, which is practiced by approximately 2.4 billion people, mainly in Europe, America and Australia. Islam ranks second in the number of believers - more than 1.5 billion people. Islam has been declared the state religion in many countries, located mainly in Asia and Africa. The third place among world religions in terms of the number of adherents belongs to Buddhism - 370 million people. Buddhism is widespread in Central, Southeast and East Asia. National religions include Hinduism in India, Confucianism in China, and Shintoism in Japan. Judaism also became widespread.
Slide 12
 Distribution of the population The world's population is distributed extremely unevenly: about 2/3 of all people live on 8% of the earth's land area. Of every 100 inhabitants of the Earth, 80 live in lowlands and plains located at an altitude of up to 500 m above sea level, which occupy only 28% of the Earth's land. Mountainous areas are less populated, although there are exceptions to this rule: in Bolivia, Peru and China (Tibet), the border of human habitation exceeds 5000 m above sea level. More than half of humanity is concentrated in a 200-kilometer strip along the coasts of seas and oceans, and almost 30% in a 50-kilometer strip, which occupies only 12% of the land. In some, mainly island and peninsular, states, this figure is even higher. In Japan, 9/10 of the population lives no further than 50 km from the sea, in Great Britain - 3/4. In Norway, Denmark, Ireland, Portugal, Chile, New Zealand, Cuba and the Philippines, the entire population lives no further than 200 km from the sea.
Distribution of the population The world's population is distributed extremely unevenly: about 2/3 of all people live on 8% of the earth's land area. Of every 100 inhabitants of the Earth, 80 live in lowlands and plains located at an altitude of up to 500 m above sea level, which occupy only 28% of the Earth's land. Mountainous areas are less populated, although there are exceptions to this rule: in Bolivia, Peru and China (Tibet), the border of human habitation exceeds 5000 m above sea level. More than half of humanity is concentrated in a 200-kilometer strip along the coasts of seas and oceans, and almost 30% in a 50-kilometer strip, which occupies only 12% of the land. In some, mainly island and peninsular, states, this figure is even higher. In Japan, 9/10 of the population lives no further than 50 km from the sea, in Great Britain - 3/4. In Norway, Denmark, Ireland, Portugal, Chile, New Zealand, Cuba and the Philippines, the entire population lives no further than 200 km from the sea.
Slide 13
 Population density The average population density of the Earth is 48 people per 1 sq. km. But the differences between countries are very large. Most often, Bangladesh is called the most densely populated country in the world, where the population density has already exceeded 1000 people per 1 sq. km. But in small, predominantly island states it is even higher: in Singapore - more than 6500, in the Maldives - 1100, in Malta 1200 people per 1 sq. km. In Monaco – 16,400 people per 1 sq. km. Along with this, about half of the inhabited landmass has an average population density of less than 5 people per 1 square kilometer. km. Areas completely undeveloped by people occupy 15% of the land area.
Population density The average population density of the Earth is 48 people per 1 sq. km. But the differences between countries are very large. Most often, Bangladesh is called the most densely populated country in the world, where the population density has already exceeded 1000 people per 1 sq. km. But in small, predominantly island states it is even higher: in Singapore - more than 6500, in the Maldives - 1100, in Malta 1200 people per 1 sq. km. In Monaco – 16,400 people per 1 sq. km. Along with this, about half of the inhabited landmass has an average population density of less than 5 people per 1 square kilometer. km. Areas completely undeveloped by people occupy 15% of the land area.
Slide 14
 Types of international migration Irrevocable (permanent) Temporary-permanent Seasonal Pendulum (border) Illegal (underground) Forced Episodic
Types of international migration Irrevocable (permanent) Temporary-permanent Seasonal Pendulum (border) Illegal (underground) Forced Episodic
Slide 15
 Migration patterns All countries are involved in the migration process Feminization of migration flows Qualitative changes (“brain drain”) Changes in the directions of migration flows Formation of migration networks Discussion of migration problems in the context of human rights
Migration patterns All countries are involved in the migration process Feminization of migration flows Qualitative changes (“brain drain”) Changes in the directions of migration flows Formation of migration networks Discussion of migration problems in the context of human rights
Population size and reproduction Demography is the science of the patterns of population reproduction, studying its size, natural growth, age and sex composition of the population. Population reproduction is a set of processes of fertility, mortality and natural increase that ensure the continuous renewal and change of human generations. In the most simplified, generalized form, we can talk about two types of population reproduction...

Types of reproduction The first type is a demographic crisis. The first type of reproduction is characterized by low rates of mortality, birth rate and natural increase. It has become widespread in economically developed countries. The second type is the “demographic explosion.” The second type of reproduction is characterized by high birth rates and natural increase and relatively low mortality rates. It is typical for developing countries.

Demographic policy Demographic policy is a system of administrative, economic, and propaganda measures with the help of which the state influences the natural movement of the population (primarily the birth rate) in the direction it desires. The direction of demographic policy depends on the demographic situation in a particular country. demographic situation Average life expectancy is the expected life expectancy of the population, which is determined using calculations based on probability theory. Depends both on biological and hereditary characteristics, as well as on nutrition, work, and living conditions. Measured in number of years.

Sex and age composition of the population For graphical analysis of the age and sex composition of the population, the age and sex pyramid is widely used. The scale below is age, on the left - as a percentage of the entire population. Women numerically predominate in a number of CIS countries, in foreign Europe, and in North America. In Africa, Latin America, Australia and Oceania, the number of men and women is approximately equal. But in foreign Asia, men noticeably predominate. And yet the overall global figure is particularly affected by the predominance of men in the two most populous countries - China and India. That is why in the world as a whole there are 101 men for every 100 women.

Ethnolinguistic composition In total, there are 3-4 thousand ethnic groups in the world, some of which have formed into nations, while others are nationalities and tribes. In cases where national boundaries coincide with political ones, single-national states are formed; most of them are in Europe, the Middle East, Latin America, etc. Along with these, there are many countries that are multinational states; Some of them are home to dozens and even hundreds of peoples.

Religious composition of the population Depending on their distribution and role, all religions are divided into world and national. The most widespread of the world's religions are Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism. National religions include Hinduism in India, Confucianism in China, and Shintoism in Japan.

Distribution and population density Distribution and population density The population is distributed extremely unevenly: about 70% of all people live on 7% of the earth's land area. Along with this, about half of the inhabited land has an average population density of less than 5 people per 1 km 2. Areas completely undeveloped by people occupy 15% of the land area. Naturally, people settled and developed first of all the territories that were most favorable for life and rich in various resources. Since ancient times, the settlement of people has been greatly influenced by their employment in agriculture. With the beginning of industrial development, large population clusters formed in Europe and the USA. Finally, throughout the history of human civilization, human settlement has been strongly affected by the attraction to transport and trade routes. The average population density of the Earth is 45 people per km 2. A certain number and density of population are necessary prerequisites for the development of each country.

Population migration A large impact on the size, composition and distribution of the population in individual countries and throughout the world is exerted by its movements, called population migrations. The main reason for migration is economic, but they are also caused by political, national, religious, environmental and other reasons. International (external) migrations are migrations from one country to another. Labor migration is the relocation of people to work in another country. The main flow of labor emigrants is sent from developing countries to economically developed countries. Internal (intrastate) migrations are of several types, moving from rural areas to cities, from city to city, from city to rural areas, etc.

The concept of urbanization Urbanization is the growth of cities, an increase in the share of the urban population in a country, region, world, the emergence and development of increasingly complex networks and systems of cities. Urbanization is one of the most important components of socio-economic development. Modern urbanization as a worldwide process has three common features that are characteristic of most countries. The first feature is the rapid growth of urban populations, especially in less developed countries. The second feature is the concentration of the population mainly in large cities. The third feature is the “sprawling” of cities, the expansion of their territory.

Levels and rates of urbanization Based on the level of urbanization, all countries can be divided into 3 large groups. But the main divide still occurs between more and less developed countries. The pace of urbanization largely depends on its level. In economically developed countries that have reached a high level of urbanization, the share of the urban population has recently been growing relatively slowly. In developing countries, where the level of urbanization is lower, the urban population is increasing rapidly. However, urban population growth is much faster than their actual development. Modern processes of growth, composition and distribution of population raise many complex problems, some of them are worldwide and some are specific to different types of countries. The most important are the continued rapid growth of the world population, interethnic relations, and urbanization.




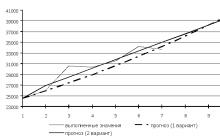






Personal income tax - how not to frame the recipient of assistance
Requirements for hotel staff
Quotes about reading and books Quotes from writers about how to read
Head of the transport service of the enterprise
What is stock clothing