Codes are a specific sequence of numbers. They encrypt the type of business practice of the organization. Knowing the basic principle of the definition, it is not difficult to independently choose a code according to OKVED 2 household goods.
Before starting business activities, any company must register. It is at this stage that codes are assigned. They contain encrypted information about what exactly the organization does. OKVED values are required in the process of preparing a number of documents.
The code specified in the application affects, for example,:
- belonging to a specific industry;
- direction of work;
- taxes that will need to be paid;
- the volume of insurance contributions to the funds;
- determining whether licensing is required.
The registered person chooses the economic activity code independently, but it is approved by the statistics body. The code is indicated in the application and consists of four, five, or six characters.
How to use the classifier
Before choosing a code, you need to understand what kind of activity the company plans to engage in: wholesale or retail sales. To register, one type is enough, but there may be several.
In retail trade, the term “specialty store” is used. It can sell any product, if not tobacco, medicinal products, food and beverages. You can apply encodings:
- 47.11 – stores where, in addition to basic food products, there is also a non-food assortment.
- 47.19.1 – non-specialized, most of which deal with industrial and household goods.
- 47.78 – specialized stores selling various equipment, souvenirs, fuel, etc., not included in other groups.
- 47.78.9 is a non-food group that is not included in other lists and is sold in specialized stores.
Selecting the appropriate OKVED 2
In order to correctly determine the code, it is necessary to carefully track all subsections in the classifier and most accurately indicate the activities that the entrepreneur conducts.
If the company, for example, is engaged in the wholesale trade of household goods, in section G we select item 46. We determine the clarifying (child) code - 4. In it, the ninth, for example, is most suitable - wholesale trade of other household items.
To the resulting value of 46.49, select one more, for example, 4 - other consumer items. If there are no specific specifics, you can take the last one - 9. These are goods not included in other groups.
No additional clarifications are provided. 46.49.49 - this will be the type of classification according to OKVED 2. Similarly, you can select other areas for the entire range of services provided or products sold.
Note! The longer the specified code, the more detailed the specifics of the enterprise are indicated, the more clearly the focus of the work is shown.
You should not indicate too much, this will complicate not only your work, but also tax specialists and statisticians.
The All-Russian Classifier of Types of Economic Activities (OKVED) is a universal reference book of basic information that can be obtained using one or another code. OKVED for household goods, like any other area of economic activity, is regulated in detail.
The use of OKVED significantly simplifies the procedure for foreign economic regulation of the market, allows you to carefully develop a taxation system and optimize the accounting process at the enterprise.
The OKVED code is assigned to the enterprise upon registration, regardless of its status. Any legal entity or individual that is a business entity receives this code, which allows you to further identify a specific enterprise and obtain the necessary information of a financial and economic nature.
The tax department determines the appropriate code when the applicant submits a package of necessary documentation, including an application for registration and related documents. If a person intends to register individual entrepreneur status, he can simultaneously submit an application to switch to a simplified taxation system.
All changes in the legal status of the taxpayer are carefully recorded and will be entered into his tax history in the future. You can obtain this information at any time by using the search system using the individual taxpayer number (TIN), which also displays OKVED, as one of the basic characteristics of the economic activity of the subject.
The OKVED code is a combination of a group of numbers, each of which is an integral indicator of a certain segment of modern commerce. Using these combinations, you can obtain detailed information about the nature of the subject’s employment, and even predict its production potential. The code in question is a kind of cipher for economic activity, which is quite easy to read if you have the necessary key.
The structure of the code under consideration can be represented as follows:
- class of economic activity;
- subclass;
- group;
- subgroup;
If the activity of the subject is somewhat innovative and does not fall under any of the existing headings, it is possible to register a new code, within the framework of logical affiliation.
In total, the classifier consists of seventeen sections, each of which corresponds to a specific area of ED.

As for the sphere of household goods, it is quite wide, and includes both primary production and supply and sales - wholesale and separately. Each of these large market segments, in turn, is subdivided into groups, subgroups and types of economic activity, according to the above structure.
In some cases, it is also possible to have subtypes, as the smallest category of entrepreneurship, covering a narrow range of specialized activities.
Therefore, the codification of this industry is quite voluminous and includes a huge number of combinations and digital combinations. We will not analyze each of them in detail; we will limit ourselves to pointing out some of them as the most clear example of the diversity of codification to which household goods are subject.
For example, the main codes for trade in household goods are classes 51 (wholesale trade) and 52 (retail). Further headings require detailed detailing for each category of goods separately.
Supply of household products falls into class 17.
There are also groups of codes of mixed origin, including products from different industries and for different purposes.
You should choose the code very carefully, based on the basic characteristics.
It is important to note that choosing the correct code when registering a business is of paramount importance. If you made a mistake with the required codification, or indicated it inaccurately, the tax authority will not be able to correct your error, and it will become the reason for refusal of registration. And this, in turn, will entail additional hassle, material waste and wasted time.

Codification of economic activity: prospects for expansion
The OKVED system has been introduced into the Russian economy for quite a long time and has proven its effectiveness. For 2019, it is planned to make some changes to the existing codification system, but it will not be reversed.
Based on OKVED, data on a specific subject is entered into the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Individuals, depending on the status of the subject.
It is worth noting that when registering an individual entrepreneur, it is enough to only indicate a certain code in the application, while when establishing an LLC or other form of legal entity, the OKVED code should be indicated in the statutory documents, in accordance with the current tax legislation.
In addition, information about the scope of activity of the subject is received from the tax authority also to the Social Insurance Fund, where it is entered into local registers.
If, during the development process, a company or enterprises begin to engage in related activities not specified in the original code, this situation should be documented, preferably, the code should be expanded. Such activities are not directly prohibited by law, but clear legal regulation will help avoid various unpleasant conflicts.
Related posts:
No similar entries found.
- resale (sale without conversion) of new and used goods for personal or household use, or use by shops, department stores, tents, postal trade enterprises, persons delivering goods on a door-to-door basis, traders, consumer cooperatives, etc. d. Retail trade is classified primarily by type of trading enterprise (retail trade in general assortment stores - groupings from 47.1 to 47.7, retail trade outside stores - groupings from 47.8 to 47.9). Retail trade in general merchandise stores includes: retail sales of used goods (group 47.79). For retail sales in department stores, a further distinction is made between retail sales in specialized stores (groups 47.2 to 47.7) and retail sales in non-specialized stores (group 47.1). The above-mentioned groups are further subdivided according to the range of products sold. Sales of goods not through general stores are classified according to forms of trade, such as retail sales in stalls and markets (group 47.8) and other retail sales not through general stores, such as mail order, door-to-door, vending machines, etc. d. (grouping 47.9). The range of goods in this group is limited to goods usually referred to as consumer goods or retail goods. Therefore, goods that are not usually sold in retail trade, such as cereal grains, ores, industrial equipment, etc. are not included in this group
- retail sale of goods such as personal computers, stationery, paints or wood, although these products may not be suitable for personal or household purposes. Processing of goods traditionally used in trade does not affect the basic characteristics of goods and may include, for example, only their sorting, separating, mixing and packaging
Checks can serve as protection for both the client and the seller. In the event of conflict situations (discovered shortage, discrepancy between the price in the check and the stated price), each party keeps evidence of correctness. And in court cases that arise at the initiative of customers, a check is the only opportunity for a store to prove its case and preserve its image.
Retail trade OKVED
Retail sale of goods such as personal computers, office supplies, paint or wood, although these products may not be suitable for personal or household use. Processing of goods traditionally used in trade does not affect the basic characteristics of goods and may include, for example, only their sorting, separating, mixing and packaging
Resale (sale without conversion) of new and used goods for personal or household use, or use by shops, department stores, tents, postal service enterprises, persons delivering goods on a door-to-door basis, traders, consumer cooperatives, etc. . Retail trade is classified primarily by type of trading enterprise (retail trade in general assortment stores - groupings from 47.1 to 47.7, retail trade outside stores - groupings from 47.8 to 47.9). Retail trade in general merchandise stores includes: retail sales of used goods (group 47.79). For retail sales in department stores, a further distinction is made between retail sales in specialized stores (groups 47.2 to 47.7) and retail sales in non-specialized stores (group 47.1). The above-mentioned groups are further subdivided according to the range of products sold. Sales of goods not through general stores are classified according to forms of trade, such as retail sales in stalls and markets (group 47.8) and other retail sales not through general stores, such as mail order, door-to-door, vending machines, etc. d. (grouping 47.9). The range of goods in this group is limited to goods usually referred to as consumer goods or retail goods. Therefore, goods that are not usually sold in retail trade, such as cereal grains, ores, industrial equipment, etc. are not included in this group
OKVED: retail trade of non-food products
- photographic, optical or measuring instruments;
- services of specialists in optics;
- souvenirs, handicrafts, religious items;
- services for commercial galleries;
- liquid boiler fuel, bottled gas, coal, wood fuel;
- weapons and ammunition;
- numismatic and philatelic goods;
- non-food products that are not included in other groups;
- in commercial galleries.
45 group includes actions that are related to the sale and repair of cars or motorcycles. 46 and 47 include all activities that are related to sales. The main difference between 46 and 47 (wholesale and retail) is based on the predominance of a particular type of buyer in each group.
OKVED table for retail trade in 2019
- Classification of organizations, private and individual enterprises and firms of any organizational and legal form according to the type of their activity.
- Assigning a separate code to each type of activity.
- Regulation of this activity.
- Monitoring companies.
- Going international.
- Informing higher authorities.
OKVED in this industry makes it possible to regulate the activities of official organizations of various sizes: specialized and non-specialized stores, kiosks, stalls, tents, as well as sales at home, handing over goods in person, courier delivery, delivery by mail, etc.
Retail trade, except trade in motor vehicles and motorcycles
The website of the Consensus Consulting Company presents new OKVED codes that will help you when registering LLCs and individual entrepreneurs. To do this, just select what your company will do, for example, “production of tobacco products” - and write down the code of this type of economic activity in the application for registration.
- resale (sale without conversion) of new and used goods for personal or household use, or use by shops, department stores, tents, postal trade enterprises, persons delivering goods on a door-to-door basis, traders, consumer cooperatives, etc. d. Retail trade is classified primarily by type of trading enterprise (retail trade in general assortment stores - groups from 47.1 to 47.7, retail trade outside stores - groups from 47.8 to 47.9). Retail trade in general merchandise stores includes: retail sales of used goods (group 47.79). For retail sales in department stores, a further distinction is made between retail sales in specialized stores (groups 47.2 to 47.7) and retail sales in non-specialized stores (group 47.1). The above-mentioned groups are further subdivided according to the range of products sold. Sales of goods not through general stores are classified according to forms of trade, such as retail sales in stalls and markets (group 47.8) and other retail sales not through general stores, such as mail order, door-to-door, vending machines, etc. d. (grouping 47.9). The range of goods in this group is limited to goods usually referred to as consumer goods or retail goods. Therefore, goods that are not usually sold in retail trade, such as cereal grains, ores, industrial equipment, etc. are not included in this group
52 Retail trade, except trade in motor vehicles and motorcycles; repair of household products and personal items old 47 Retail trade, except trade in motor vehicles and motorcycles new
[Old OKVED] 52.11 Retail trade in non-specialized stores primarily of food products, including drinks, and tobacco products
[New OKVED] 47.11 Retail trade primarily in food products, including drinks, and tobacco products in non-specialized stores
[Old OKVED] 52.11.2 Retail trade in non-specialized stores of non-frozen products, including drinks, and tobacco products
[New OKVED] 47.11.2 Retail trade of non-frozen products, including drinks and tobacco products, in non-specialized stores
OKVED codes for retail trade in 2019
Why does a company, in fact, need an OKVED code? Firstly, it is necessary from the point of view of collecting statistical data – This makes it easier for Rosstat to know how many organizations in the country are involved in a particular business activity. Secondly, OKVED is necessary for the correct taxation of certain organizations: depending on the type of economic activity, companies use certain taxation systems. That is, a notary office cannot be subject to a single tax on imputed income, and gold mining – be on the simplified tax system.
Each OKVED code consists of several digital characters, their number varies from two to six. The All-Russian Classifier of Economic Activities uses a hierarchical classification method – that is, from the total – to the quotient and sequential coding method.
OKVED: codification of the sphere of household goods
It is important to note that choosing the correct code when registering a business is of paramount importance. If you made a mistake with the required codification, or indicated it inaccurately, the tax authority will not be able to correct your error, and it will become the reason for refusal of registration. And this, in turn, will entail additional hassle, material waste and wasted time.
The All-Russian Classifier of Types of Economic Activities (OKVED) is a universal reference book of basic information that can be obtained using one or another code. OKVED for household goods, like any other area of economic activity, is regulated in detail.
OKVED code 52: Retail trade, excluding trade in motor vehicles and motorcycles; repair of household products and personal items
- activities of stores selling a universal range of goods, including clothing, furniture, household electrical goods, hardware, cosmetics, jewelry, toys, sporting goods, books, newspapers, magazines, etc.
- retail trade of a universal assortment of goods in stores that, along with the main sale (more than 50% of turnover) of food products, including drinks, and tobacco products, also sell other goods (clothing, furniture, household electrical goods, hardware, cosmetic products, etc.) P.)
05 Aug 2018 783This section includes:
The physical and/or chemical processing of materials, substances or components with the aim of converting them into new products, although this cannot be used as a single universal criterion for defining production (see "waste recycling" below)
Materials, substances or transformed components are raw materials, i.e. products from agriculture, forestry, fisheries, rocks and minerals and other manufactured products. Significant periodic changes, updates or conversions of products are considered to be related to production.
The products produced may be ready for consumption or may be a semi-finished product for further processing. For example, the product of aluminum purification is used as a raw material for the primary production of aluminum products, such as aluminum wire, which in turn will be used in the necessary structures; production of machinery and equipment for which these spare parts and accessories are intended. The production of non-specialized components and parts of machinery and equipment, such as engines, pistons, electric motors, valves, gears, bearings, is classified in the appropriate grouping of Section C, Manufacturing, regardless of which machinery and equipment these items may include. However, the production of specialized components and accessories by casting/molding or stamping of plastic materials is included in Class 22.2. The assembly of components and parts is also classified as production. This section includes the assembly of complete structures from constituent components, produced independently or purchased. Waste recycling, i.e. processing of waste for the production of secondary raw materials is included in group 38.3 (activities for processing secondary raw materials). Although physical and chemical processing may occur, this is not considered part of manufacturing. The primary purpose of these activities is basic waste treatment or treatment, which is classified in section E (water supply; sewerage, waste management, pollution control activities). However, the production of new finished products (as opposed to products made from recycled materials) applies to all production as a whole, even if waste is used in these processes. For example, producing silver from film waste is considered a manufacturing process. Special maintenance and repair of industrial, commercial and similar machinery and equipment are generally included in group 33 (repair and installation of machinery and equipment). However, repair of computers and household devices is listed in group 95 (repair of computers, personal items and household items), while at the same time, automobile repair is described in group 45 (wholesale and retail trade and repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles). Installation of machinery and equipment as a highly specialized activity is classified in group 33. 20
Note - The boundaries of manufacturing with other sections of this classifier may not have a clear, unambiguous specification. Typically, manufacturing involves the processing of materials to produce new products. Usually these are completely new products. However, determining what constitutes a new product can be somewhat subjective
Processing implies the following types of activities involved in production and defined in this classifier:
Processing of fresh fish (removing oysters from shells, filleting fish) not carried out on board a fishing vessel, see 10.20;
Pasteurization of milk and bottling, see 10.51;
Leather dressing, see 15.11;
Sawing and planing of wood; impregnation of wood, see 16.10;
Printing and related activities, see 18.1;
Tire retreading, see 22.11;
Production of ready-to-use concrete mixtures, see 23.63;
Electroplating, metallization and heat treatment of metal, see 25.61;
Mechanical equipment for repair or overhaul (e.g. automobile engines), see 29.10
There are also types of activities included in the processing process, which are reflected in other sections of the classifier, i.e. they are not classified as manufacturing industries.
These include:
Logging classified under Section A (AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY, HUNTING, FISHING AND FISH CULTURE);
Modification of agricultural products classified in section A;
Preparation of food products for immediate consumption on premises, classified in group 56 (activities of catering establishments and bars);
Processing of ores and other minerals, classified in section B (MINERAL MINING);
Construction and assembly work carried out on construction sites, classified in section F (CONSTRUCTION);
Activities of breaking down large quantities of goods into smaller units and secondary marketing of smaller quantities, including packaging, repackaging or bottling products such as alcoholic beverages or chemicals;
Sorting of solid waste;
Mixing paints according to customer's order;
Metal cutting according to customer's order;
Explanations for various goods classified under section G (WHOLESALE AND RETAIL TRADE; REPAIR OF MOTOR VEHICLES AND MOTORCYCLES)
Despite the advent of the Internet, plastic dishes and inflatable furniture elements, well-known and familiar newspapers, books, metal household utensils and, of course, wooden furniture continue to be in demand as before. That is why many businessmen are in no hurry to change the type of activity they started many years ago. And now they continue to display it in tax documents with code .49 OKVED; its decoding is exactly what applies to all known household products and furniture elements.
To say that wholesale sales is one of the easiest steps to developing and increasing the profitability of a business will not actually work. Yes, many businessmen do not strive to conduct retail trade, preferring only wholesale sales. But everywhere there are pitfalls. And in this case, they relate to finding a potential client. Yes, now there are many manufacturers producing unusual, high-quality and even universal furniture elements and household appliances.
The same can be said about printed materials and stationery. Of course, on the one hand, having the opportunity to choose is good, but on the other hand, running a business related to wholesale sales is quite a complex undertaking with a lot of risks. Although, if we take into account that goods belonging to the OKVED code .49 have a long shelf life, then the magnitude of these risks is not so great. Ultimately, each product has its own buyer, the main thing is to find him in time.
What products are displayed with OKVED code 46.49
First of all, it is used by companies involved in the sale of wooden objects. But in addition to the wholesale sale of familiar furniture elements, OKVED .49 is also used by companies where one of the activities is the sale of wicker and cork products. This code is also displayed in documents by companies whose activities are related to printed products and office supplies. This applies not only to books, but also to magazines.
It is also often used by companies that decide to engage in the wholesale sale of leather goods and travel equipment. This code is also used in activities such as the sale of bicycles. Refers to OKVED code .49 and sales of accessories for this type of transport. Household metal utensils and cutlery sold in bulk also belong to code .49.
In the case of running a business related to the wholesale sale of toys, games and even musical instruments, this type of activity should also be displayed with code .49. It is also indicated in tax documents by companies closely involved in the wholesale trade of sporting goods. It is worth noting that this code is also suitable for reflecting sales of special sports shoes, in the form of skates or skis.



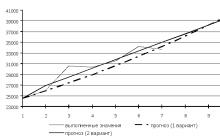






Types and methods of planning
Personal income tax - how not to frame the recipient of assistance
Requirements for hotel staff
Quotes about reading and books Quotes from writers about how to read
Head of the transport service of the enterprise