Business entities include any legal entities, as well as organizations operating without forming a legal entity, and individual entrepreneurs.
The organizational and legal form is understood as a way of fixing and using property by an economic entity and its legal status and business objectives arising from this.
Based on the goals of entrepreneurial activity, business entities that are legal entities are divided into organizations that pursue profit making as the main goal of their activities (commercial organizations) or do not have profit making as such a goal and do not distribute profits among participants (non-profit organizations) .
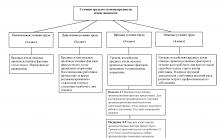
The Civil Code of the Russian Federation defines the types of organizational and legal forms of enterprises. On fig. 1.1 presents the structure of organizational and legal forms.
Rice. 1.1.
The description and definitions of organizational and legal forms will be presented in the form of table 1.1.
Table 1.1. The structure of organizational and legal forms provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
|
Name of OPF |
Short title |
Definition |
|
Commercial organizations |
Organizations whose main goal is to make a profit and distribute it among the participants |
|
|
Business partnerships |
Commercial organizations in which contributions to the share capital are divided into shares of the founders |
|
|
General partnership |
A partnership whose participants (general partners) on behalf of the partnership are engaged in entrepreneurial activities and are liable for its obligations not only with their contributions to the share capital of the PT, but also with their property |
|
|
Faith partnership |
A partnership in which, along with general partners, there is at least one participant of a different type - a contributor (limited partner), who does not participate in entrepreneurial activities and bears risk only within the limits of his contribution to the share capital of TNV |
|
|
Business companies |
Commercial organizations in which contributions to the authorized capital are divided into shares of the founders |
|
|
Limited Liability Company |
A business company, the participants of which are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk only within the limits of their contributions to the authorized capital of the LLC |
|
|
Additional Liability Company |
A business company, the participants of which jointly and severally bear subsidiary (full) liability for its obligations with their property in the same multiple for all of the value of their contributions to the authorized capital of the ALC |
|
|
public corporation |
A business company, the authorized capital of which is divided into a certain number of shares, the owners of which can alienate their part without the consent of other shareholders. Shareholders bear risk only to the extent of the value of their shares |
|
|
Closed Joint Stock Company |
A joint-stock company whose shares are distributed only among its founders or other predetermined circle of persons. Shareholders of a CJSC have a pre-emptive right to acquire shares sold by its other shareholders. Shareholders bear risk only to the extent of the value of their shares |
|
|
Subsidiary business company* (subtype of business company, not OPF) |
A business company is recognized as a subsidiary if the decisions it makes, due to one circumstance or another, are determined by another business company or partnership (predominant participation in the authorized capital, according to an agreement or otherwise) |
|
|
Dependent economic company (a subtype of a business company, not an OPF) |
A business company is recognized as dependent if another company has more than 20% of the voting shares of a joint-stock company or more than 20% of the authorized capital of a limited liability company (LLC) |
|
|
Production cooperatives |
Voluntary association of citizens on the basis of membership for joint production or other economic activities based on personal labor participation and association by its members of property share contributions (to the cooperative's share fund) |
|
|
Agricultural artel (collective farm) |
A cooperative created for the production of agricultural products. It provides for 2 types of membership: a member of a cooperative (works in a cooperative and has the right to vote); associate member (has the right to vote only in certain cases provided for by law) |
|
|
Fishing artel (collective farm) |
A cooperative established for the production of fish products. It provides for 2 types of membership: a member of a cooperative (works in a cooperative and has the right to vote); associate member (the right to vote is vested only in certain cases provided for by law) |
|
|
Cooperative farm (koopkhoz) |
A cooperative created by the heads of peasant farms and (or) citizens leading personal subsidiary plots for joint activities in the production of agricultural products based on personal labor participation and the combination of their property shares (land plots of peasant farms and private household plots remain in their ownership) |
|
|
Unitary enterprises |
A unitary enterprise is recognized as an enterprise that is not endowed with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it by the owner. Only state and municipal enterprises can be unitary |
|
|
State (state) enterprise |
A unitary enterprise based on the right of operational management and created on the basis of property that is in federal (state) ownership. A state-owned enterprise is created by decision of the Government of the Russian Federation |
|
|
municipal enterprise |
A unitary enterprise based on the right of economic management and created on the basis of state or municipal property. It is created by decision of the authorized state body or local self-government body |
|
|
Peasant (farm) economy* |
The legal form of the organization of agricultural production, the head of which, from the moment of its state registration, is recognized as an individual entrepreneur, is vested with the right to make all decisions on its management, and bears full responsibility for its obligations. Within the framework of the KFH, its members unite their property, take part in its activities by personal labor. For the obligations of the KFH, its members are liable within the limits of their contributions |
|
|
Non-Profit Organizations |
Organizations that do not pursue the goal of making a profit and do not distribute the profits received among the participants |
|
|
consumer cooperative |
Voluntary association of citizens and legal entities on the basis of membership in order to meet the material and other needs of the participants, carried out by pooling property shares by its members. Provides 2 types of membership: member of the cooperative (with the right to vote); associate member (has the right to vote only in certain cases provided for by law) |
|
|
Public and religious organizations |
Voluntary association of citizens on the basis of common interests to meet spiritual or other non-material needs. The right to carry out entrepreneurial activities only to achieve the goals of the organization. Participants do not retain ownership of the property transferred to the organization |
|
|
An organization that does not have membership, established by citizens and (or) legal entities on the basis of voluntary property contributions, pursuing social, charitable, cultural, educational or other socially useful goals. The right to engage in entrepreneurial activities to achieve their goals (including through the creation of business companies and participation in them) |
||
|
Institutions |
An organization created by the owner to carry out managerial, socio-cultural or other functions of a non-commercial nature and financed by him in whole or in part |
|
|
Associations of legal entities |
Associations (unions) created by legal entities in order to coordinate business activities and protect their property interests. Members of the association retain their independence and the rights of a legal entity |
Next, we will consider information characterizing the main provisions of organizational and legal forms: types of membership, existing restrictions, constituent and other documents required for registration, bodies and basic principles of management, the degree of responsibility of participants for the obligations of the enterprise, the nature of the distribution of profits based on the results of economic activity, the procedure for exit participant and settlements with them, positive and negative aspects (table 1.2).
Table 1.2. The main characteristics of the organizational and legal forms provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation
|
LLC (limited liability company) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
|
|
Registration documents |
|
|
Control |
Governing bodies: general meeting of participants, management. The number of votes by agreement of the participants is specified in the constituent documents (recommendation: in proportion to the share in the authorized capital). |
|
Responsibility |
Participants bear the risk of losses within the value of their contributions to the authorized capital of the company. |
|
Upon withdrawal, the participant has the right: to receive a share in money, in kind, to transfer part of it or all of it to another person (participants in this have an advantage over third parties). |
|
|
ALC (additional liability company) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
Provides one type of membership -- member. It can be an individual or a legal entity (their possible number is from 1 to 50). Another company cannot be the only member if it consists of 1 person. |
|
Registration documents |
Charter, memorandum of association, minutes of the organizational meeting, application for registration |
|
Control |
Governing bodies: general meeting of participants, management. The number of votes of a participant is proportional to the share of his contribution to the authorized capital (unless otherwise provided). |
|
Responsibility |
Participants are jointly and severally liable with their property in an equal for all multiples of the value of their contributions. Responsibility for the obligations of the bankrupt participant is transferred to other participants. |
|
The profit allocated for dividends is distributed among the participants in proportion to their shares in the authorized capital. |
|
|
When leaving the ALC, the participant has the right: to receive his share in money, in kind, to transfer part of it or all of it to another participant (participants in this have a preemptive right over third parties). |
|
|
CJSC (closed joint stock company) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
One type of membership is a shareholder. It can be an individual or a legal entity (the number is not limited). Another company cannot be the sole shareholder if it consists of 1 person. Shares are distributed only among the founders or a predetermined circle of persons. |
|
Registration documents |
|
|
Control |
|
|
Responsibility |
|
|
In order to “leave” a CJSC, a shareholder sells his shares to the company or its shareholders. A shareholder leaving for the creation of a peasant farm is allocated a land plot and property in accordance with the charter. |
|
|
JSC (open joint stock company) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
One type of membership is a shareholder. It can be an individual or a legal entity (the number is not limited). Another economic company cannot be the sole shareholder if it consists of 1 person. |
|
Registration documents |
Charter, memorandum of association, application for registration |
|
Control |
Governing bodies: general meeting of shareholders, supervisory board, board (management) headed by the chairman (director). The share of preferred (non-voting) shares must not exceed 25%. |
|
Responsibility |
Shareholders are liable to the extent of the value of their shares. |
|
Dividend profit is distributed among shareholders in proportion to the number of shares they own. |
|
|
In order to "leave" the OJSC, the shareholder sells all his shares to any person. A shareholder leaving for the creation of a peasant farm is allocated a land plot and property in accordance with the charter. |
|
|
DHO (subsidiary business company) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
Participants can be individuals and legal entities (partnerships, companies). DHO does not have the right to independently determine its decisions, as it depends on another economic (main or parent) company, partnership. |
|
Registration documents |
Charter, memorandum of association, application for registration |
|
Control |
|
|
Responsibility |
The participant (main or parent company) is liable for the debts of the DHO, if they arose due to his fault. DHO is not liable for the participant's debts. |
|
The profit allocated for dividends is distributed among the participants in proportion to their shares in the authorized capital. |
|
|
ZHO (dependent business company) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
Participants can be individuals and legal entities (companies). A business company (JSC or LLC) is recognized as dependent if: more than 20% of the voting shares of the JSC or more than 20% of the charter capital of the LLC belongs to another, the so-called. dominant or participating society. The number of participants is not limited. |
|
Registration documents |
Charter, memorandum of association, application for registration. |
|
Control |
Governing bodies: meeting of participants, board, chairman. |
|
Responsibility |
The Participant is liable within the limits of the value of his shares or stake in the charter capital of the WCO. |
|
Profit allocated to dividends is distributed among the participants in proportion to the number of shares they own or shares in the authorized capital. |
|
|
In accordance with the constituent documents, depending on the type of OPF. |
|
|
TNV (faith partnership) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
There are two types of membership -- full fellow and contributor. General partners can be individual entrepreneurs (IP) and (or) commercial organizations. Contributors can be citizens and legal entities. There must be at least 1 general partner and 1 contributor in TNV. You can only be a general partner in one partnership. The number of general partners and contributors is not limited. |
|
Registration documents |
Memorandum of association, minutes of the organizational meeting, applications from general partners (they become individual entrepreneurs), application for registration of TNV |
|
Control |
Governing bodies: meeting of general partners, authorized (director) TNV. The number of votes of general partners, as agreed by the parties, is stipulated in the memorandum of association (recommendation: in proportion to shares in the share capital). |
|
Responsibility |
General partners are liable with all their property, investors - the risk of loss in the amount of the value of their contributions to the share capital. |
|
Profit allocated to dividends is distributed among general partners and investors in proportion to their shares in the share capital. First of all, dividends are paid to investors. The amount of dividend per unit of contribution for general partners cannot be higher than for investors. |
|
|
When leaving the TNV, the general partner receives a share in the share capital, and the investor receives the value of his contribution. A general partner has the right: to transfer part of the share or all of it to another participant (to a third party - with the consent of the general partners). the depositor does not need such consent. |
|
|
PT (general partnership) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
One kind of membership is a full comrade. They can be individual entrepreneurs (IP) and (or) commercial organizations. A person can only be a member of one PT. The number of participants is at least two. |
|
Registration documents |
Memorandum of association, minutes of the organizational meeting, applications for IP and registration of PT. |
|
Control |
Governing bodies: meeting of participants, authorized (if provided). Each participant has the right to represent the partnership, has 1 vote, and the decision is considered adopted if approved by all participants (unless otherwise specified in the UD) |
|
Responsibility |
Participants jointly and severally bear subsidiary liability with their property for the obligations of the PT (including those who are not the founders). |
|
The profit allocated for dividends is distributed among general partners in proportion to their shares in the share capital. |
|
|
When leaving the PT, the participant has the right: to receive the value of his share in the UK (in kind - by agreement), to transfer part or all of it to another participant (to a third party - with the consent of the other general partners). |
|
|
SPK (agricultural production cooperative) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
There are two types of membership - a member and an associate member (they can only be individuals). The minimum number of members of the SPK is 5 people. |
|
Registration documents |
|
|
Control |
Governing bodies: general meeting of members; supervisory board (elected if the number of members is at least 50); board (or chairman). Associate members have the right to vote only in certain cases. Each member of the cooperative has 1 vote. |
|
Responsibility |
The cooperative is liable for its obligations with all its property. Members of the cooperative bear subsidiary liability for the obligations of the cooperative in the amount provided for by the charter of the cooperative, but not less than 0.5% of the mandatory share. |
|
The profit distributed among the participants is divided into 2 parts: dividends paid in proportion to the contributions of associate members and additional shares of members; cooperative payments issued to members in proportion to labor participation. |
|
|
When withdrawing from the SEC, the participant has the right: to receive the value of his share contribution in money, in kind, to transfer part or all of it to another Participant (to a third party - with the consent of the other participants). |
|
|
OSKK (serving agricultural consumer cooperative) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
Two types of membership - a member and an associate member (they can be individuals and legal entities). The minimum number of members of the PSUC is 5 citizens or 2 legal entities. |
|
Registration documents |
Charter, minutes of the organizational meeting, application for registration. |
|
Control |
Governing bodies: general meeting of members, supervisory board, board (or chairman). Associate members have the right to vote only in certain cases. Each member of the cooperative has 1 vote. |
|
Responsibility |
The cooperative is liable for its obligations with all its property. Members of the cooperative are obliged to repay the losses by making additional contributions. |
|
The income distributed among the participants is divided into 2 parts: dividends paid in proportion to the contributions of associate members and additional shares of members; cooperative payments issued to members in proportion to their use of the main types of services of the cooperative (the charter may provide otherwise) |
|
|
When leaving the OSKK, the participant has the right: to receive the value of his share contribution in money, in kind, to transfer part or all of it to another participant (to a third party - with the consent of the other Participants). |
|
|
KFH peasant (farm) economy |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
Two types of membership - the head and a member of the KFH (maybe one - the head of the KFH). The number of members is not limited. |
|
Registration documents |
An application for registration of a peasant farm, an application for the allocation of a land plot on account of land shares, an agreement between members of a peasant farm (at their discretion) |
|
Control |
All decisions on the management of a peasant farm are made by its head (unless otherwise provided by the agreement) |
|
Responsibility |
The head of the KFH bears full responsibility for the obligations of the KFH, and the members of the KFH bear the risk within the limits of the value of their contributions. |
|
Distributed by the head of the KFH at his discretion (unless otherwise specified in the agreement between the members of the KFH) |
|
|
Those who left the peasant farm have the right to receive monetary compensation in the amount of their share in the property of the farm. Land and property upon withdrawal of a member shall not be subject to division. The sizes of shares are considered equal (unless otherwise specified in the agreement between the members of the peasant farm) |
|
|
GKP state (state) enterprise |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
The participant of the enterprise is its founder - the Government of the Russian Federation. A state-owned enterprise is based on the right to operational management of the Federal property transferred to it. |
|
Registration documents |
Charter approved by the Government of the Russian Federation |
|
Control |
|
|
Responsibility |
He is liable for his obligations with all his property. Not responsible for the obligations of the founder. The Russian Federation bears subsidiary liability for the obligations of a state-owned enterprise in case of insufficiency of its property |
|
The liquidation of the enterprise is carried out by decision of the Government of the Russian Federation |
|
|
MP (municipal enterprise) |
|
|
Membership types, restrictions |
The participant of the enterprise is its Founder - an authorized state body or local self-government body. This type of unitary enterprise is based on the right of economic management. |
|
Registration documents |
Charter approved by the authorized state body or local self-government body |
|
Control |
All decisions on the management of the enterprise are made by the head or another body appointed by the owner of its property. |
|
Responsibility |
By its obligations with all its property. Not responsible for the obligations of the founder. The owner of the property is liable for the obligations of the enterprise if its bankruptcy occurred due to the fault of the owner of the property |
|
The conditions for the use of profits are stipulated in the charter approved by the founder |
|
|
The liquidation of the enterprise is carried out by the decision of the founder - the owner of its property |
The main role in the choice of organizational and legal forms belongs to the factors that determine the effectiveness of management. These include:
features of the leader (degree of compliance with the requirements of the position, the level of confidence in him on the part of the participants);
The ratio of the level of qualification of the head and other employees of the management;
· features of participants (number, relationships, share of employees in the economy);
parameters of the enterprise (the number of employees, the area of agricultural land, the compactness of the territory and the location of objects, the state of the economy),
the level of development of the production base (production, processing, storage),
Availability of reliable and efficient distribution channels,
the degree of production risk,
the need to increase confidence on the part of creditors,
The choice of participants
· features of state policy in the field of agriculture (the presence of tax incentives currently stimulates the creation of peasant farms).
Non-Profit Organizations are created for other purposes and do not pursue profit as the main goal of their activities. Such goals, as a rule, include: social, cultural, educational, spiritual, charitable and other types of goals. Non-profit organizations have the right to engage in entrepreneurial activities only if this activity is aimed at achieving the goals of the organization.
Properties of business partnerships and companies
Business partnerships and companies are recognized as corporate commercial organizations with authorized (share) capital divided into shares (contributions) of founders (participants). The property created at the expense of the contributions of founders (participants), as well as produced and acquired by a business partnership or company in the course of its activity, belongs to the business partnership or company by the right of ownership. As a rule, the scope of rights and responsibilities of the organization's participants is determined in proportion to their shares in the authorized capital.
In addition to the general features presented above, there are fundamental differences between business partnerships and companies.
Member Responsibility . The participants in the partnership are liable for its debts with all their property, which may be levied. The participants of the company are not liable for the debts of the company and are liable for its obligations within the limits of their shares.
List of participants . Only individual entrepreneurs or commercial organizations can become members of the partnership. Members of a business partnership can be both organizations and individuals.
Change of membership . In economic societies, this is much easier. Any participant can leave the company or sell his share, while the company continues to function.
To withdraw from the partnership, it is required to declare this at least 6 months before the withdrawal. In case of withdrawal, the participant is paid the value of his share in the property of the partnership, unless otherwise provided by the constituent agreement. Upon withdrawal of any of the participants, the partnership ceases to operate, unless otherwise provided by the founding agreement or agreement of the remaining participants.
Organization of activities . The partnership is run by the members themselves. The organization of the company's activities is carried out through its management bodies. For a company, the main constituent document is the charter, for a partnership it is an agreement.
Types of business partnerships
The types of business partnerships include: general partnership and limited partnership.
General partnership- a partnership, the participants of which (general partners), in accordance with the agreement concluded between them, on behalf of the partnership, are engaged in entrepreneurial activities and are liable for the obligations of the organization with their property.
Please note that a participant in a general partnership that is not its founder is liable on an equal basis with other participants for obligations that arose before he joined the partnership. A participant who has left the partnership shall be liable for the obligations of the partnership that arose before the moment of his withdrawal, on an equal basis with the remaining participants within two years from the date of approval of the report on the activities of the partnership for the year in which he left the partnership.
A general partnership requires a minimum of two members, each of whom can only be a member of one partnership. Profit allocated to dividends is distributed among general partners in proportion to their shares in the share capital.
We can safely say that participation in a general partnership implies too high a responsibility for its participants. Any wrong decision threatens with serious consequences, even if you have already left the composition of its participants.
Faith partnership(limited partnership) - a partnership in which, along with participants engaged in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership and liable for the obligations of the partnership with their property (general partners), there are one or more participants - investors (limited partners) who bear the risk of losses associated with the activity partnerships, within the limits of the amounts of contributions made by them and do not take part in the implementation of entrepreneurial activities by the partnership.
As we noted earlier, only individual entrepreneurs or commercial organizations can be full partners. While both legal entities and citizens can act as contributors. A limited partnership requires at least one general partner and one contributor, with no maximum limit.
Profit allocated to dividends is distributed among general partners and investors in proportion to their shares in the share capital. First of all, dividends are paid to depositors, however, the amount of dividend per unit of contribution for general partners cannot be higher than for depositors.
Thus, business partnerships can attract a significant amount of capital, since the composition of its participants is unlimited. The joint and several subsidiary liability of its participants is an advantage for creditors, but creates high risks of doing business. The management of a general or limited partnership requires a high level of trust and agreement on fundamental issues, otherwise the management of the organization will be difficult.
Currently, business partnerships are used extremely rarely. The principles of creation and management of business partnerships are described in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Articles 66-86.
Types of business companies
Economic companies are one of the main forms of business organization in Russia. These include: a limited liability company, an additional liability company and a joint stock company.
Limited Liability Company(LLC) - a legal entity established by one or more persons, the authorized capital of which is divided into certain shares (the amount of which is established by the constituent documents). Members of an LLC bear the risk of loss only to the extent of the value of their contributions.
In practice, LLC is the most popular form of business organization in Russia, largely because it avoids the main disadvantages of partnerships. First, the liability for the obligations of the organization is limited by the size of its authorized capital. Secondly, the process of leaving society is easier. At the same time, the former participant may not only sell his share, but also demand payment of the value of a part of the property corresponding to his share in the authorized capital, if this is provided for by the charter. Accordingly, if the value of the property of the LLC has increased, then the participant leaving it will receive not only his initial contribution, but also an increased share in the property.
In addition, an LLC is characterized by the fact that operational management in a company (unlike partnerships) is transferred to an executive body, which is appointed by the founders either from their own number or from among other persons. The members of the company retain the rights to strategic management of the company. These measures reduce differences of opinion in the management of the organization.
Limited Liability Companies Federal Law No. 14 and Articles 87-94 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are regulated. In one of the previous articles, we examined one of the forms of business management without forming a legal entity. In our opinion, an individual entrepreneur, along with an LLC, is one of the best forms for starting a business.
Additional Liability Company(ODO) - a company whose authorized capital is divided into shares determined by the constituent documents. ALC participants bear subsidiary (full) liability for its obligations with their property in the same multiple for all to the value of their contributions to the authorized capital. For example, the authorized capital of an ALC is 50 thousand rubles. The charter determines that the company bears an additional five-fold liability. This means that if the property of the company is insufficient, creditors can receive up to 250 thousand rubles from participants.
In practice, an additional liability company was rarely met, therefore, in 2014 they were abolished. Previously created ALCs are subject to the provisions of the Civil Code governing the activities of LLCs, with the exception of liability for obligations.
Joint-Stock Company(JSC) is a company whose authorized capital is divided into a certain number of shares; participants of a joint-stock company (shareholders) are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company within the limits of the value of their shares.
It should be noted that previously joint-stock companies were usually divided into open and closed. However, since 2014, new designations have been introduced: public joint stock company(PJSC) and non-public joint-stock company(AO).
A public joint-stock company is a joint-stock company whose shares can be freely traded on the market. A non-public JSC is a joint-stock company whose shares are distributed only among the founders or a predetermined circle of persons. In addition to the above, there are several other differences between PAO and JSC.
- Authorized capital . The minimum authorized capital for a PJSC is higher than for a JSC and amounts to 100 thousand rubles. For a non-public company, its size is 10 thousand rubles.
- Acquisition of shares by shareholders . Shareholders of a joint-stock company are provided with the right of pre-emption to buy shares of the company from other shareholders. PJSC shareholders acquire new shares on a general basis.
- Publication of statements . A public joint stock company is obliged to publish annual reports on the official resources of the company. The correctness of the reporting is checked by audit companies. This requirement is necessary for investors to understand the financial condition of the business. A non-public joint-stock company, as a rule, may not disclose its own financial statements.
The activity of joint-stock companies is one of the most strictly regulated by law. Among the main laws, articles 96-104 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as well as Federal Law No. 208 "On Joint Stock Companies" can be distinguished. In one of the following articles, we will compare joint-stock companies and limited liability companies in more detail.
So, we see that business companies provide entrepreneurs with a wider range of opportunities not only in raising funds, but also in managing the company. Joint-stock companies and limited liability companies allow founders and investors to limit their losses in case of problems with the company, while still providing ample opportunities to generate income.
Production cooperatives and unitary enterprises
Production cooperative(artel) - a voluntary association of citizens on the basis of membership for joint production or other economic activities based on personal labor participation and the association of property shares by its members. The charter of a production cooperative may also provide for the participation of legal entities in its activities. The minimum number of members to form a cooperative is five.
Members of a production cooperative bear subsidiary responsibility and are divided into those who take and those who do not take personal labor participation in the activities of the PC. The profit of the cooperative is distributed among its members in accordance with their labor participation and contributions to the share fund of the cooperative. The property remaining after the liquidation of the cooperative and the satisfaction of the claims of its creditors are distributed in the same manner.
The minimum size of the share fund of a production cooperative is not established by law. However, at least 10% of their share contributions, members of the cooperative are required to pay before the state registration of the cooperative, and the rest - within one year from the date of registration. Contributions to a mutual fund may be made in cash, securities, other property, intangible assets.
One of the main advantages of production cooperatives is tax optimization: you can switch from a general to a simplified taxation system with any number of PC members, as well as reduce the amount of insurance premiums paid and increase salaries for employees. Other advantages are: an unlimited number of members, equal rights in management, etc.
But there are also disadvantages, among them: the subsidiary liability of PC members, the pooling of labor contributions, not capital, which can create problems in determining the real contribution of each participant, especially for a complex commercial structure.
Issues of the legal status and features of the PC are regulated by Article 106 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as well as federal law No. 41-FZ “On production cooperatives”.
unitary enterprise- a commercial organization that is not endowed with the right of ownership of the property assigned to the owner. The property of a unitary enterprise is indivisible and cannot be distributed by contribution (shares, shares), including among the employees of the enterprise. In the form of unitary enterprises, only state and municipal enterprises can be created that are liable for their obligations with all their property, but are not liable for the obligations of the owner of his property.
State (state) enterprise - a unitary enterprise based on the right of operational management and created on the basis of property that is in federal (state) ownership. A state-owned enterprise is created by decision of the Government of the Russian Federation.
municipal enterprise - a unitary enterprise based on the right of economic management and created on the basis of state or municipal property. It is created by the decision of the authorized state body or local self-government body.
The right of economic management is the right of an enterprise to own, use and dispose of the property of the owner within the limits established by law or other legal acts. The right of operational management is the right of an enterprise to own, use and dispose of the property of the owner assigned to it within the limits established by law, in accordance with the goals of its activities, the tasks of the owner and the purpose of the property.
The right of economic management is wider than the right of operational management, i.e. an enterprise operating on the basis of the right of economic management has greater independence in management. The legal status of unitary enterprises is determined by Articles 113-114 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and Federal Law No. 161-FZ “On State and Municipal Unitary Enterprises”.
This concludes our consideration of the forms of commercial organizations in Russia. Next, let's talk about non-profit organizations and doing business without forming a legal entity.
Non-Profit Organizations
As mentioned earlier, non-profit organizations, firstly, do not pursue profit as the main goal of their activities. And, secondly, they do not distribute the profit (if it was nevertheless received) between the participants. In Russia, there are quite a few different forms of NGOs, let's consider the main ones.
consumer cooperative- a voluntary association of citizens and legal entities on the basis of membership in order to meet the material and other needs of the participants, carried out by combining its members with property shares. Provides two types of membership: member of the cooperative (with the right to vote); associate member (has the right to vote only in certain cases provided for by law).
Fund- an organization that does not have membership, established by citizens and (or) legal entities on the basis of voluntary property contributions, pursuing social, charitable, cultural, educational or other socially useful goals. The right to engage in entrepreneurial activities to achieve their goals (including through the creation of economic companies and participation in them).
institution- an organization created by the owner to carry out managerial, socio-cultural or other functions of a non-commercial nature and financed by him in whole or in part. This is the only type of non-profit organizations that have property on the basis of the right of operational management.
Association (union)- a voluntary association of legal entities established in order to coordinate business activities and protect their property interests. Association members retain their independence and have the right to join other associations.
There are other types of public organizations: public and charitable organizations, non-profit partnerships, religious organizations, etc. All these organizations are created either to achieve “lofty” goals, or to protect and coordinate the activities of citizens and organizations.
A complete list of non-profit organizations is presented in Art. 123 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Business without formation of a legal entity
There are two types of entrepreneurial activity without forming a legal entity: individual entrepreneurs and simple partnerships.
Individual entrepreneur(IP) - an individual registered in the manner prescribed by law and carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity, while having many of the rights of legal entities. Sole proprietorship has a lot of advantages, especially for start-up entrepreneurs: the sole proprietorship registration procedure is faster and easier, simplified reporting is possible, liability and fines are much lower, and much more. We discussed the pros and cons of IP in more detail in previous articles.
simple partnership is a form of activity carried out by persons who undertake to act jointly without creating a legal entity in order to achieve a specific goal that does not contradict the law. Only commercial companies and individual entrepreneurs can be parties to a partnership.
In order to carry out joint activities, partners make contributions in the form of: property, property rights, cash, securities; skills, knowledge, business connections, business reputation, etc. The amount and type of contribution made by each partner is determined by the specific goals of joint activities, the capabilities of each of the partners and their agreements among themselves.
A simple partnership, for all the complexity of its application, is a unique tool that allows not only to combine several companies with the goal of achieving a joint result, but also to be flexible enough to regulate the tax consequences of the activities of each of the partners. This type of organizational and legal form is regulated by Chapter 55 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Thus, we have considered all organizational and legal forms of enterprises in Russia. They differ in the goals of creation, responsibility for obligations, opportunities for attracting investments, etc. Below is a summary table for all types of organizations in Russia. And in one of the following articles we will talk about foreign forms of doing business.
Table of organizational and legal forms of enterprises

Useful resources:
3.3. Organizational and legal forms of enterprises in the Russian Federation
Organizational and legal form is a form of business organization, fixed in a legal way. It defines responsibility for obligations, the right to deal on behalf of the enterprise, the management structure and other features of the economic activity of enterprises. The system of organizational and legal forms used in Russia is reflected in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, as well as in the regulations arising from it. It includes two forms of unincorporated entrepreneurship, seven types of commercial organizations and seven types of non-profit organizations.
Let us consider in more detail the organizational and legal forms of legal entities that are commercial organizations. Entity- an organization that has separate property in ownership, economic management and operational management, is liable for its obligations with this property and can acquire and exercise property rights and incur obligations on its own behalf.
Commercial called organizations that pursue profit as the main goal of their activities.
Economic partnership is an association of persons directly involved in the activities of the partnership, with the share capital divided into shares of the founders. The founders of a partnership may be members of only one partnership.
Complete a partnership is recognized, the participants of which (general partners) are engaged in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership. If the property of the partnership is insufficient to pay off its debts, creditors have the right to demand satisfaction of claims from the personal property of any of its participants. Therefore, the activity of the partnership is based on the personal and trusting relationships of all participants, the loss of which entails the termination of the partnership. The profits and losses of the partnership are distributed among its participants in proportion to their shares in the share capital.
Faith partnership(limited partnership) - a kind of general partnership, an intermediate form between a general partnership and a limited liability company. It consists of two categories of participants:
General partners carry out entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership and are fully and jointly and severally liable for obligations with all their property;
Investors make contributions to the property of the partnership and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the partnership within the limits of the amounts of contributions to the property.
Economical society Unlike a partnership, it is an association of capital. The founders are not required to directly participate in the affairs of the company, members of the company can simultaneously participate in property contributions in several companies.
Limited Liability Company (LLC) – an organization created by agreement between legal entities and citizens by combining their contributions for the purpose of carrying out economic activities. Mandatory personal participation of members in the affairs of the LLC is not required. Members of an LLC are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the LLC to the extent of the value of their contributions. The number of participants in an LLC should not be ^1 be more than 50.
Additional Liability Company (ALC) – a type of LLC, so all the general rules of an LLC apply to it. The peculiarity of the ALC is that if the property of this company is insufficient to satisfy the claims of its creditors, the participants in the company can be held liable, and jointly and severally with each other.
Joint Stock Company (JSC)- a commercial organization, the authorized capital of which is divided into a certain number of shares; JSC participants are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company, within the value of their shares. Open Joint Stock Company (JSC)- a company whose members can alienate their shares without the consent of other members of the company. Such a company has the right to conduct an open subscription for shares issued by it in cases established by the Charter. Closed Joint Stock Company (CJSC)- a company whose shares are distributed only among its founders or other specific circle of persons. CJSC is not entitled to conduct an open subscription for its shares or otherwise offer them to an unlimited number of persons.
Production cooperative (artel) (PC)- a voluntary association of citizens for joint activities, based on their personal labor or other participation and the association of property shares by its members. The profit of the cooperative is distributed among its members in accordance with their labor participation, unless otherwise provided by the charter of the PC.
unitary enterprise- a commercial organization that is not endowed with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it. The property is indivisible and cannot be distributed among contributions (shares, shares), including between employees of the enterprise. It is respectively in state or municipal ownership and is assigned to a unitary enterprise only on a limited property right (economic management or operational management).
unitary enterprise on the right of economic management- an enterprise that is created by decision of a state body or local government. The property transferred to the unitary enterprise is credited to its balance sheet, and the owner does not have the rights of possession and use in relation to this property.
unitary enterprise on the right of operational management- This is a federal state-owned enterprise, which is created by decision of the Government of the Russian Federation on the basis of property that is in federal ownership. State-owned enterprises are not entitled to dispose of movable and immovable property without special permission from the owner. The Russian Federation is liable for the obligations of a state-owned enterprise.
| |
An independent business entity operating in a market economy is an enterprise. An enterprise is created to produce products, perform work and provide services in order to meet consumer demand and make a profit. It independently carries out its activities, sells its products, uses the profit remaining at its disposal after paying taxes and other obligatory payments.
Enterprises that are federal property, state property of the republics within the Russian Federation, territories, regions, autonomous regions, autonomous districts, municipal and private property may be created and operate in the Russian Federation. The relations of the enterprise with other enterprises, organizations, institutions, bodies of state and municipal administration and citizens are regulated by law.
The constituent documents of the enterprise are its charter, as well as the decision on its creation and the agreement of the founders. The charter defines the organizational and legal form of the enterprise, management and control bodies, the procedure for distributing profits and forming funds. Termination of the activity of the enterprise can be carried out in the form of liquidation or reorganization. The forms of reorganization of an enterprise are merger, accession, division, separation from the previous structure or transformation into another organizational and legal form.
The scale and nature of the organizational problems facing the manager vary depending on the size of the enterprise. For example, the organizational problems of small businesses focus on the division of work, the establishment of responsibility, and the determination of the scope of control. Medium-sized enterprises are more concerned with the use of functional organization, staff rationalization and coordination. Large organizations have problems with decentralization, balancing the efforts of various departments as enterprises grow.
The degree of involvement of enterprises in market forms of management largely depends on its focus on consumer needs and the production of competitive products. Well organized businesses are more efficient. If an enterprise is created and operates on the basis of modern principles, then the satisfaction of its employees with the results of labor is higher. An irrational organization requires much more time to solve problems, many of which are generated by the organization itself.
The activity of the enterprise is cyclical. Failures and disturbances in this activity are symptoms of the emergence of problems in the organization itself. It is important to study these symptoms, to carry out changes and organizational adjustments, to control how problems are solved. From these positions, the organizational structure of the enterprise should be based on such principles as the ability to respond flexibly to changing market needs, ensuring the optimal level of decentralization of management decisions, personalized responsibility for organizing and performing the functions of the enterprise. These principles should be reflected in the approved regulation on the organizational structure of the enterprise. The main range of issues regulated by this provision can be reduced to the following:
the main activities of the enterprise;
basic functions of enterprise management (marketing, organization of production, finance, economics, accounting, personnel, information service);
the composition of the service functions of the enterprise;
determination of the type of structure (linear, linear-functional, divisional, matrix, combined);
the composition of the organizational units of the enterprise, the functions assigned to them and the determination of the procedure for their implementation (rights, obligations, terms, incentives and punishments);
the allocation of independent units (auxiliary, servicing), the formation of profit centers;
determination of the procedure for monitoring the compliance of the organizational structure with the areas of activity of the enterprise and the personification of responsibility for the implementation of the specified control function.
Types of organization of business entities
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in force since the beginning of 1995, legal entities that are commercial organizations can be created in various forms (Fig. 3.3).
Rice. 1.3
Business partnerships and companies are commercial organizations with joint (share) capital, divided into shares (contributions) of its participants. Business partnerships can be created in the form of a general partnership and a limited partnership (limited partnership). Business companies may be created in the form of a joint-stock company, a limited liability company or an additional liability company. Participants in general partnerships and general partners in limited partnerships may be individual entrepreneurs and (or) commercial organizations. Citizens and legal entities may be participants in economic companies and contributors in limited partnerships. State bodies and bodies of local self-government are not entitled to act as participants in economic companies and investors in limited partnerships, unless otherwise provided by law.
A general partnership is a partnership whose participants (general partners), in accordance with the agreement concluded between them, are engaged in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership and are liable for its obligations with all their property.
A limited partnership (limited partnership) is a partnership in which, along with the participants who carry out entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership and are liable for the obligations of the partnership with their property (general partners), there are one or more contributors (limited partners) who bear the risk losses associated with the activities of the partnership within the limits of the amounts of contributions made by them, and do not take part in the entrepreneurial activities of the partnership.
A limited liability company is a company established by one or more persons, the authorized capital of which, in accordance with the constituent documents, is divided into shares of a certain size; participants in a limited liability company are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company, within the value of their contributions.
An additional liability company is a company founded by one or more persons, the authorized capital of which, in accordance with the constituent documents, is divided into shares of a certain size; the participants of such a company jointly and severally bear subsidiary liability for its obligations with their property in the amount of a multiple of the value of their contributions, determined by the constituent documents of the company.
A joint-stock company is a company whose authorized capital is divided into a certain number of shares; participants of a joint-stock company (shareholders) are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company, to the extent of the value of their shares. A joint stock company whose members may alienate their shares without the consent of other shareholders is recognized as an open joint stock company. Such a joint-stock company has the right to conduct an open subscription for shares issued by it and their free sale on the terms established by law and other legal acts. A joint stock company whose shares are distributed only among its founders or other predetermined circle of persons is recognized as a closed joint stock company. Such a company is not entitled to conduct an open subscription for shares issued by it or otherwise offer them for purchase to an unlimited number of persons.
A production cooperative (artel) is a voluntary association of citizens for joint production or other economic activities (production, processing, marketing of industrial, agricultural and other products, performance of work, trade, consumer services, provision of other services), based on their personal labor and other participation and consolidation of their property share contributions.
A unitary enterprise is a commercial organization that is not endowed with the right of ownership of the property assigned to it. The property of a unitary enterprise is indivisible and cannot be distributed among contributions (shares, shares), including among employees of the enterprise. The property of a state or municipal unitary enterprise is, respectively, in state or municipal ownership and belongs to such an enterprise on the basis of economic management or operational management.
A non-profit organization is an organization whose main purpose is not to extract profit and distribute it among the participants. Non-profit organizations can be created to achieve social, charitable, cultural, educational, scientific and managerial goals, to protect the health of citizens, develop physical culture and sports, satisfy the spiritual and other interests of citizens and organizations, resolve disputes and conflicts, provide legal assistance, as well as for other purposes aimed at achieving public benefits. Non-profit organizations can be created in the form of public or religious organizations (associations), non-profit partnerships, institutions, autonomous non-profit organizations, social, charitable and other funds, associations and unions, consumer cooperatives, as well as in other forms provided for by federal laws.
The distribution of registered economic entities by form of ownership is evidenced by the following data (as of January 1, 1999): state and municipal property - 11.4%, private property - 76.1%, mixed Russian property - 5.8%. Of the privately owned organizations, 74.7% were founded by individual citizens. The share of enterprises established by citizens in trade and public catering is 90%, in industry - 82.4%, in construction - 82.5%, in real estate operations - 83.9%.
In the Russian Federation, enterprises with foreign investment can be created and operate in the form of:
enterprises with equity participation of foreign investments (joint ventures), as well as their subsidiaries and branches;
enterprises wholly owned by foreign investors (foreign enterprises), as well as their subsidiaries and branches;
branches of foreign legal entities.
There are legislative and normative orienting regulators of business relations. At the same time, the following functions are assigned to the state:
establishment of regulatory requirements for the content and quality of entrepreneurial activity and, accordingly, products, goods, services (quality standards, environmental, sanitary standards, etc.);
determination of procedures for conducting economic affairs by issuing licenses, adopting documents on the procedure for carrying out economic activities;
the introduction of prohibitions and sanctions for deviation from the norms of the law;
control and supervision over compliance with the law in business activities.
What is an OPF? Each organization has its own OPF. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws determine which OPFs can have organizations (legal entities) in the Russian Federation. Haven't guessed yet? Then we answer what it is:
OPF is defined by law and enshrined in the charter of each company or non-profit organization, its legal form. The literal decoding of the abbreviation OPF is a legal term: legal form. You can read more about what the organizational and legal form means for an organization and what types of organizational and legal forms are for commercial and non-profit organizations in Russia, you can read below, in the paragraph Types of OPF.
Meanwhile, decoding OPF may have another meaning - economic, namely: main production assets. What's happened"main production assets"? In the science "Economics of the enterprise", OPF is means of labor involved in the production process for a long time and retaining their natural form.
The main production assets of the enterprise include: buildings, structures and facilities, communication and power lines, machinery, vehicles and equipment, tools, inventory, etc. (these are the main types of OPF, as fixed production assets). Because the OPF in this context, this is an economic concept, and does not affect the main topic of our site - the state registration of non-profit organizations of various organizational and legal forms, those who are important to get more complete information on the topic of the main production assets of the enterprise, we dare to send to the information resource of economic topics. 🙂
verbatim decoding OPF contains no definition what is the legal form. Strange as it may seem, the main current Russian legislation with the Civil Code at the head does not contain it either! The only, rather vague and vague explanation of the concept of OPF is contained in the All-Russian Classifier of Legal Forms OK 028-2012. According to him, " organizational-legal form means a way of securing (forming) and using property by an organization and its legal status and business goals arising from this. "Well, now everything is clear, isn't it? 🙂
Let's try to give our own, more intelligible definition:
The organizational and legal form (OPF) is abbreviated letter abbreviation or full verbal designation of the type of organization, always located immediately before its own (individual) name, characterizing the commercial or non-commercial orientation of the organization (in some cases reflecting the main purpose of its activity), as well as characterizing the assignment of this organization to one of the regimes provided for by law fixing and use of property, activities and procedures for managing the organization.
Types of OPF
Here we will decipher the OPF of organizations in detail, while we will be guided by the same All-Russian OPF classifier.
The main types of OPF of commercial enterprises and organizations:
IP - individual entrepreneur
LLC - limited liability company
ALC - additional liability company
OJSC - open joint stock company
CJSC - closed joint stock company
PC - production cooperative
KFH - peasant (farm) economy
SUE - state unitary enterprise
The main types of OPF of non-profit organizations (OPF of NPOs):
PC - consumer cooperative
NGO - public organization
OD - social movement
ANO is an autonomous non-profit organization
SNT - horticultural non-profit partnership
DNP - dacha non-profit partnership
Homeowners association - homeowners association
Of course, the whole range of organizational and legal forms is wider.
Here we have deciphered the OPF of the most common types. We hope that you liked this article and that you have learned all the information on the topic " decoding OPF". If you want to clarify how the abbreviation of organizational and legal forms that are not present in the above list is deciphered, or you need to find out the OPF code for OKOPF of your organization, please look in the OPF classifier located at the following link:
All-Russian classifier of organizational and legal forms (OK 028-2012)
With regard to the process of state registration of an NPO or a commercial organization, the correct and accurate indication of the full and abbreviated name of the legal form (OPF) when preparing documents is a necessary condition for its successful completion.
Sincerely,
staff of the Center for Registration of Non-Commercial Organizations of St. Petersburg and Leningrad Region
Classification of organizational and legal forms
Types of organizational and legal forms of organizations are a classification of business entities in modern conditions.
The main feature of this classification is the division of economic entities in accordance with the organizational and legal form of companies.
The types of organizational and legal forms of organizations are regulated by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (CC RF), which introduced the concepts of "commercial organization" and "non-profit organization".
Types of organizational and legal forms of organizations
In accordance with the nature of the activities of enterprises, the types of organizational and legal forms of organizations include:
- commercial enterprises,
- Non-commercial enterprises,
- Organizations without forming a legal entity;
- state (municipal) organization;
- state (unitary) enterprise.
Currently, there are the following types of organizational and legal forms of organizations that carry out commercial activities: a company, a partnership, a joint-stock company, unitary enterprises.
In the field of non-profit organizations, one can single out a consumer cooperative, public organizations (movements, associations), a foundation (non-profit partnership), partnerships (gardening, summer cottage, homeowners), an association (union), autonomous non-profit companies.
For enterprises that do not form a legal entity, the following types of organizational and legal forms of organizations may be provided: mutual investment funds, simple partnership, branch (representative office), individual entrepreneur, farm (peasant) economy.
Shape selection
The types of organizational and legal forms of organizations, in addition to the nature of the main activity, are also influenced by some other factors, among which may be organizational, technical, economic and social.
In accordance with organizational and technical factors, the types of organizational and legal forms of organizations are determined based on the number of founders, their characteristics, the area of commercial activity, the nature and novelty of the products produced. When taking into account the social and economic factors, the amount of start-up capital and the personal characteristics of the entrepreneur and his team are taken into account.
Also, the types of organizational and legal forms of organizations may be limited by the current legislation. For example, commercial organizations with the status of a legal entity can only be created in the form of a partnership of any type, a company (open or closed, with limited liability).
Types of organizational and legal forms of commercial organizations
Types of organizational and legal forms of organizations of a commercial nature can also be classified into several types:
- A business partnership, divided into full and based on faith, the difference between which lies in the degree of responsibility of the participants (partners).
In a full society, partners in obligations are liable with all their property, but in a society based on faith, they are liable in accordance with the amount of their contributions.
- Economic company (LLC), joint-stock company (JSC). The capital of an LLC includes the contributions of the participants and is divided into shares; in a JSC, the capital is divided into the corresponding number of shares.
- A production cooperative is a voluntary association of members (citizens), it is based on membership and share contributions, as well as on the personal labor of the participants.
- Economic partnerships are very rare, almost never mentioned in the Civil Code. Such enterprises are regulated by a separate law.
- Peasant farms are an association for the purpose of conducting agriculture, based on the personal participation of citizens in business and their property contributions.
Examples of problem solving

Organizational and legal forms of enterprises
The organizational and legal form of the enterprise fixes the property and the nature of its use, from which the legal status of the organization subsequently follows.
Thus, the organizational and legal forms of enterprises determine the legal status and nature of entrepreneurial activity.
In our country, there is a classifier of organizational and legal forms (OKOPF), according to which each form is assigned a digital code.
Classification and types of organizational and legal forms
Depending on the nature of the enterprise, OPF can be divided into:
- commercial organizations (enterprises);
- non-profit organizations;
- organizations without forming a legal entity;
- state and municipal organizations;
- state and unitary enterprises.
At present, there are four types of organizational and legal forms for enterprises conducting commercial activities:
- partnerships;
- society;
- joint-stock companies;
- unitary enterprises.

For non-profit organizations:
- consumer cooperatives;
- public associations, movements and organizations;
- foundations and non-profit partnerships;
- partnerships (gardening, country, homeowners);
- associations and unions;
- non-profit autonomous organizations.
For enterprises that do not form a legal entity, the following types of OPF are provided:
- Mutual investment funds - mutual investment funds;
- simple partnerships;
- branches, representative offices;
- individual entrepreneurship;
- farming (peasant) farms.

Criteria for choosing an organizational and legal form
In addition to the nature of the main activity of the enterprise, a number of other factors also influence the choice of organizational and legal form. Among the most significant are:
- organizational and technical;
- social and economic.
In the first case, the choice of form is based on the number of founders and their characteristics, the scope of commercial activity, the nature and novelty of the product being produced, in the second case, the amount of start-up capital and personal characteristics of both the entrepreneur and his team.
In addition, the choice of the form of the enterprise is limited by the current legislation. So, for example, commercial organizations that have the status of a legal entity have the opportunity to be created only in the form of a partnership of any type, a company (limited liability, open, closed type).

The scale of the enterprise is also important. So, for small enterprises of small, medium-sized businesses, it is optimal to make a choice in favor of a closed joint-stock company. In this case, the sale of shares is carried out only within a narrow circle of people, as a rule, the founders of the company. An open type of company implies the possibility of selling shares to a wide range of people. This type of legal form is beneficial for a large-scale enterprise with a wide branch network, for example, large banks in the country.
Also, when choosing a form of enterprise, the size of the authorized capital is also important. So for CJSC it is 100 units of the minimum wage, for OJSC - 1000 units of the minimum wage.










Name lists of persons subject to medical examinations
What does the correct protocol for testing knowledge of labor protection requirements look like?
TB 3 drawings. Legendary planes
"Kukuruznik" - the legend of Soviet aviation Kukuruznik an 2 material from which it is made
How to make a camera out of cardboard in a few hours?