The provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulating the procedure for attracting disciplinary responsibility, have not been changed since 2006. Despite this, questions and litigation still arise regarding the application of certain legal norms on disciplinary sanctions. How long should an employee who has committed a disciplinary offense be held accountable? Is the demand for explanations from the employee mandatory for bringing to disciplinary responsibility? What are mandatory requirements imposed on the procedure for issuing an order to impose a disciplinary sanction? What decisions do judges make when considering these issues?
General rules for bringing to disciplinary responsibility
The general rules for bringing to disciplinary responsibility are defined in Art. Art. 192 and 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
So, for the commission of a disciplinary offense, that is, for non-performance or improper performance by an employee through his fault of the labor duties assigned to him, the employer has the right to apply the following disciplinary sanctions to him:
- remark;
- reprimand;
- dismissal on the appropriate grounds.
Besides, federal laws, statutes and discipline regulations for certain categories employees may be subject to other disciplinary sanctions. It is not allowed to apply disciplinary sanctions that are not established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other regulatory legal acts.
Only one disciplinary sanction may be imposed for each disciplinary offence.
When imposing a disciplinary sanction, the gravity of the misconduct committed and the circumstances under which it was committed must be taken into account.
A disciplinary sanction may be appealed by an employee to the state labor inspectorate and (or) bodies for the consideration of individual labor disputes.
Deadlines for disciplinary action
A disciplinary sanction is applied no later than one month from the date of discovery of the misconduct, not counting the time of illness of the employee, his stay on vacation, as well as the time necessary to take into account the opinion of the representative body of employees. This issue is considered in more detail below.
In accordance with the Decree of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation of March 17, 2004 N 2 "On the application by courts Russian Federation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation "the day of detection of a misconduct, from which the month period begins, is considered the day when the person to whom the employee is subordinate at work (service) became aware of the misconduct, regardless of whether it is vested with the right to impose disciplinary sanctions. VS The Russian Federation clarified that within a month for the application of a disciplinary sanction, the time of illness of an employee, his stay on vacation, as well as the time necessary to comply with the procedure for taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees (Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) are not counted. other grounds, including in connection with the use of rest days (time off), regardless of its duration (for example, when shift method organization of works), does not interrupt the course of the specified period. It was also clarified that all holidays provided by the employer in accordance with the current legislation, including annual (basic and additional) holidays, holidays in connection with studying at educational institutions, holidays without pay should be attributed to leave interrupting the course of a month. .
If an employee commits a disciplinary offense, it must be recorded in writing. As a rule, an appropriate act is drawn up, which is signed by several employees of the organization. In some cases, official or memorandums are prepared to the head about the commission of a violation by an employee. These documents are sent to the head. From the date of receipt by him of the indicated documents, a monthly period begins to be calculated for bringing the employee to disciplinary liability.
Also, violation by employees of the organization of labor duties can be detected during the audit.
Checks can be carried out on the subject entrepreneurial activity other organizations (eg. government bodies exercising control and supervisory functions). If they reveal any violations, the day of discovery of a misconduct committed by an employee of the audited organization will be the day the act is received based on the results of the audit. In this situation, as a rule, there are no difficulties with determining the start date of the monthly period.
Otherwise, the issue of the day of discovery of a misconduct revealed during an internal audit, that is, an audit conducted by a unit or authorized officials of the organization itself, is resolved.
By general rule the monthly period is calculated from the date of drawing up the act of such an inspection, which is quite logical, since the results of the inspection, including the identified violations, are documented in this way. At the same time, it does not matter when this act was received by the person exercising the powers of the employer: it is necessary that the act be received by the person to whom the employee who committed the violation is subordinate, which follows from the Decree of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of March 17, 2004 N 2. This position is confirmed by materials of judicial practice. In the Cassation Ruling of the Supreme Court of the Chuvash Republic dated January 11, 2012 in case No. 33-102-12, the monthly period for bringing to disciplinary liability based on the results of an audit of financial and economic activities was calculated by the court from the day when official, who had the right to impose disciplinary sanctions, received an act drawn up based on the results of the audit. Wherein this person was a leader in relation to the employee who committed the violation.
If in the course of the audit any detected violations are recorded by separate documents (for example, acts, certificates of individual actions), the date of discovery of the misconduct should be considered the day when such documents were received by the immediate supervisor of the offending employee, regardless of the date of receipt of the relevant documents. This position is confirmed in the materials of judicial practice, in particular in the Appellate ruling of the Court of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District dated October 21, 2013 in case No. 33-2307 / 2013. The court found that improper performance official duties on the part of an employee who was brought to disciplinary responsibility (the head of the motor transport section), resulted in a violation of the technology for accounting for operating time Vehicle and registration of waybills, approved by a local legal act. The head of the motor transport section is directly subordinate to the head of the ground support service, which follows from job description the last one. The fact of violations when filling out waybills became known to the employer's officials on 04/04/2013, since the inventory of fuels and lubricants (POL) was carried out, including according to the data contained in the waybills. This circumstance follows from the act of removing the remnants of fuel and lubricants dated 04/05/2013, signed by the head of the ground support service as the chairman of the commission. Accordingly, the period for bringing to disciplinary liability must be calculated from the specified date. However, the order to impose a disciplinary sanction was issued only on May 17, 2013, that is, outside the monthly period established by the legislator. The arguments of the appeal that the inventory was completed only on 04/17/2013 and the period for bringing to disciplinary responsibility should be calculated from that date were not taken into account by the court.
Similarly, the date of discovery of the misdemeanor is set in the Cassation ruling of the Oryol Regional Court dated 01/11/2012 in case No. 33-17. An internal audit was appointed in the JSC on the facts of violation of credit activities by one of the branches, as a result of which the fact of illegal use of the premises rented by the branch was revealed. According to the conclusion internal check dated 09/08/2011 within six months starting from 02/10/2011 on the territory of the additional office on the oral order of an employee of the branch, subsequently brought to disciplinary responsibility, without registration contractual relations located outside commercial organization. By order dated 05.10.2011, the specified employee was brought to disciplinary liability for failure to perform labor duties, expressed in violation of the decision-making procedure for real estate management, provided for by local regulatory legal act.
The court established that on May 6, 2011, the manager of the additional office informed the director of the branch about this violation in a memo. Under these circumstances, since the director of the branch, empowered to bring employees to disciplinary liability, became aware of the commission of a disciplinary offense on 05/06/2011, and the order to bring the employee to disciplinary liability was issued only on 05/10/2011, the court concluded that the contested disciplinary the penalty was applied in violation of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for a month. In addition, the court noted that the disciplinary offense was committed by the employee in February 2011, therefore, based on the provisions of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a disciplinary sanction could be applied no later than September 2011.
Demanding explanations from the employee
Before applying a disciplinary sanction, the employer must request a written explanation from the employee. The employee's failure to provide an explanation is not an obstacle to the application of a disciplinary sanction to him. If, after two working days, the specified explanation is not provided by the employee, an appropriate act is drawn up.
Note! If the employee does not give an explanation, two working days must pass from the date of the misconduct. This requirement is mandatory. Failure to comply with it entails the recognition of illegal application of a disciplinary sanction.
As the court pointed out in the Appellate ruling of the Astrakhan Regional Court of October 23, 2013 in case N 33-3162/2013, from the analysis of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation directly follows that the legislator granted the employee the right, within two working days from the date of requesting an explanation from him on the fact that he committed a disciplinary offense, to submit a written explanation or refuse to submit it. Therefore, a disciplinary sanction, including in the form of dismissal, can be applied to the employee only after receiving an explanation from him in writing or after the employee fails to provide such an explanation (refusal to provide it) after two working days from the date of requesting an explanation.
If the issue of imposing a disciplinary sanction is resolved before the expiration of two working days after requesting a written explanation from the employee, the procedure for applying a disciplinary sanction in the form of dismissal is considered violated, and dismissal by virtue of Art. 394 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation - illegal.
A different interpretation of these norms would mean that the employer does not have to comply with the deadline for the employee to submit an explanation and the employer can ignore the requirements of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Consequently, this would entail the loss of the meaning of these norms and a significant violation of the employee's right to submit an explanation within the period established by law.
Also, the obligation to demand explanations when applying disciplinary sanctions is indicated in the Appeal ruling of the Kemerovo Regional Court dated May 28, 2013 in case No. 33-4822. Thus, the court of appeal found that the claims for contesting disciplinary sanctions were rightfully satisfied, since when bringing the plaintiff to disciplinary liability, the employer violated the procedure for applying a disciplinary sanction, in particular, did not demand a written explanation from him, in connection with which the order was declared illegal and subject to cancellation.
Issuing a disciplinary order
After requesting explanations from the employee, an order (instruction) is prepared, signed by the person exercising the powers of the employer, on the application of a disciplinary sanction with the obligatory indication of the grounds for bringing to disciplinary responsibility. The Labor Code does not contain a direct indication that this basis should be reflected in the order. However, from the definition of the concept of "disciplinary offense", given in Art. 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it follows: there must be a failure to perform or improper performance of official duties, which, if necessary, the employer should be able to confirm. As a basis, the order may also refer to a document in which the violations committed by the employee are recorded.
Thus, in the Appellate Ruling of the Arkhangelsk Regional Court dated July 22, 2013 in case N 33-4289 / 2013, it was noted that the court of first instance reasonably proceeded from the fact that when applying a disciplinary sanction to the plaintiff for violating the deadlines for submitting executive documents to the bailiff service, the employer did not submit evidence of both the plaintiff's violation of the provisions of the employment contract and job description, and the commission of the indicated misconduct by the plaintiff. Moreover, the court directly indicated that the appealed order for disciplinary action does not contain any indication of legal norms or clauses of local acts, which, in the opinion of the defendant, were violated by the plaintiff.
The order (instruction) of the employer to impose a disciplinary sanction is announced to the employee against receipt within three working days from the date of its issuance, not counting the time the employee is absent from work. If the employee refuses to familiarize himself with the specified order (instruction) against receipt, an appropriate act is drawn up.
Interesting is the Determination of the Kemerovo Regional Court dated February 29, 2012 in case N 33-1984. Thus, the court found that the plaintiff (employee) was not familiarized with the order to impose a disciplinary sanction in a timely manner. Having satisfied the plaintiff's claims and recognizing the dismissal order as illegal, the court indicated that the defendant violated the procedure for imposing a disciplinary sanction (this was reflected in the fact that the plaintiff was not familiarized with the order against receipt within the period established by Article 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Meanwhile, the Judicial Collegium of the Kemerovo Regional Court recognized the indicated conclusions of the court of first instance as unfounded and illegal on the following grounds.
Familiarization of the plaintiff with the contested order to impose a disciplinary sanction after the expiration of the period established by Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the current labor legislation is not prohibited. The employer is imperatively obliged to familiarize the employee with the order to apply a disciplinary sanction, and therefore, in order to obtain the employee's signature on familiarization with such an order, the employer has the right to perform this action without any restrictions. Provided for Part 6 of Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the period during which the employee must be familiarized with the order to apply a disciplinary sanction is not restrictive, its violation does not entail the recognition of the imposed disciplinary sanction as illegal.
The plaintiff had the right to challenge the order to apply a disciplinary sanction on the day when he learned about its publication.
According to Part 1 of Art. 14 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the period with which the Labor Code of the Russian Federation connects the emergence of labor rights and obligations begins from the calendar date on which the beginning of the emergence of these rights and obligations is determined. Consequently, it is from the date of familiarization with the appealed order that the period established by Art. 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for the employee to go to court.
Thus, familiarizing the plaintiff with the contested order beyond the time limits provided for by Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is not a violation of the procedure for bringing the plaintiff to disciplinary responsibility, but affects the timing of the employee's application to the court for the protection of his rights.
Based on the foregoing, we come to the following conclusions.
Before applying a disciplinary sanction, the employer must require the employee to provide a written explanation of the reasons for the misconduct. If, after two working days, the specified explanation is not provided by the employee, an appropriate act is drawn up. The employee's failure to provide an explanation is not an obstacle to the application of a disciplinary sanction to him.
A disciplinary sanction is applied no later than one month from the date of discovery of the misconduct, not counting the time of illness of the employee, his stay on vacation, as well as the time necessary to take into account the opinion of the representative body of employees.
A disciplinary sanction may not be applied later than six months from the day the misconduct was committed, and based on the results of an audit, audit of financial and economic activities or an audit, later than two years from the day it was committed. The above time limits do not include the time of criminal proceedings.
For each disciplinary offense, only one disciplinary sanction may be applied.
The order (instruction) of the employer on the application of a disciplinary sanction is announced to the employee against receipt within three working days from the date of its issuance, not counting the time the employee is absent from work. If the employee refuses to familiarize himself with the specified order (instruction) against receipt, an appropriate act is drawn up.
It secures for the employer, that is, the manager, the right to bring the employee to disciplinary responsibility if the latter allowed the improper performance of his official duties or did not perform them at all without a good reason and through his own fault. Such disregard for labor discipline in labor law falls under the concept of "disciplinary offence".
Depending on the severity of the misconduct, as well as on their number, a remark, reprimand may be applied to the offending employee, or the employee may be dismissed on negative grounds.
In order to insure yourself against unreasonable disciplinary liability, you must carefully read your own job description, which lists all job responsibilities. In addition, Article 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides general rules labor discipline which are the same for all categories of workers. First of all, this is the need to comply with internal regulations, labor protection and safety requirements, as well as the implementation of the standards provided for a specific position.
Most often, the reasons for imposing a disciplinary sanction are absenteeism, appearing at the workplace in a state of intoxication, or refusing to comply with the order of the head, if any. employment contract.
Often, employers use this provision of the law as leverage to put pressure on their employees who decide to go on strike and not come to work in connection with this. Of course, absence from the workplace without presenting a supporting document will be regarded as absenteeism. However, participation in a strike, according to Art. 414 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is not a violation of labor discipline. Therefore, it cannot serve as a basis for prosecution. There is only one exception to this rule - the recognition of a strike as illegal in judicial order.
The procedure for bringing to disciplinary responsibility
The first thing a manager must do when identifying a disciplinary violation is to request a written explanation from the alleged perpetrator. This obligation is enshrined in Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and there are no exceptions to it.
Wanting to avoid responsibility, the employee often refuses to provide an explanation. This is a rash decision, because, firstly, such a refusal in no way prevents the imposition of a disciplinary sanction, and secondly, an explanation is a great opportunity to state your own vision of the situation. Sometimes the reasons given are so weighty that the employer may abandon the intention to punish the employee.
Disciplinary liability, like any other, has a statute of limitations set out in the same Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, the punishment can be applied no later than a month from the moment the misconduct was discovered and no later than 6 months from the moment it was committed. The favorite tricks of the guilty in the form of emergency sick leave in this case will not help - the time of illness, as well as being on vacation, are not included in the statute of limitations.
The punishment must be properly executed, that is, an appropriate order is issued about its imposition, which the guilty person gets acquainted with by signature within three days from the date of publication. The time of absence from work during this period is also not taken into account.
Removal of a disciplinary sanction and the possibility of its appeal
The decision of the commission can be appealed only in court within 10 days from the date of its receipt in writing. It is also advisable to apply for judicial protection in the event that the commission refuses to consider the dispute, as well as when all methods of pre-trial settlement of the dispute have been exhausted.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation is not a violation of labor discipline. Therefore, it cannot serve as a basis for prosecution. There is only one exception to this rule - the recognition of the strike as illegal in court. The procedure for bringing to disciplinary responsibility The first thing the manager must do, having identified a disciplinary violation, is to request a written explanation from the alleged culprit. This obligation is enshrined in Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and there are no exceptions to it. Wanting to avoid responsibility, the employee often refuses to provide an explanation. This is a rash decision, because, firstly, such a refusal in no way prevents the imposition of a disciplinary sanction, and secondly, an explanation is a great opportunity to state your own vision of the situation.
Forbidden
Is it possible to bring an employee to a disciplinary sanction if more than 6 months have passed since the misconduct was committed, but the misconduct itself was discovered less than a month ago? Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion: The procedure for applying disciplinary sanctions is not violated only if both deadlines are met: both the deadline from the day of discovery and the deadline from the day the misconduct was committed. financial and economic activities or an audit) exceeded six months, a disciplinary sanction cannot be applied to the employee. Justification of the conclusion: In accordance with the third part of Art.
Bringing to disciplinary responsibility
You can finish earlier Before the expiration of a year from the moment of imposing liability, the employer has the right to remove it from the employee of the company. This can happen at the initiative of the management team, as part of the satisfaction of an employee's request, or on the recommendation of other employees of the company. The head of the stumbled person can write a petition to CEO, head of the company.
Also, this can be done by a representative body formed from the staff of the organization. In any of the options, the abolition of disciplinary liability is carried out by issuing an internal order for the enterprise. When and how we apply In order to be able to issue an order, it is necessary to discover the grounds for disciplinary liability of employees.
This happens if some employee has violated the existing order, and signs of a disciplinary offense can be seen in the violation.
Disciplinary responsibility of employees
Terms and Conditions Is it possible to bring an employee to disciplinary responsibility if he is not at fault? No, because the presence of guilt is a prerequisite for recovery. If an employee refuses to do what he is supposed to do, because the performance of work poses a threat to health and life, he is not to blame for the violation of duties. You can also refuse to perform tasks that are contrary to labor protection standards.
Attention
No one should be engaged in heavy work, work in conditions of harmful, dangerous factors, unless otherwise specified in the employment contract. Finally, if the employer demanded that the employee leave the vacation ahead of schedule, he has the right to refuse. According to the Labor Code, the disciplinary responsibility of employees in this case is not applicable, since there is no fault.
Disciplinary responsibility of an employee
The above time limits do not include the time of criminal proceedings. For each disciplinary offense, only one disciplinary sanction may be applied. The order (instruction) of the employer on the application of a disciplinary sanction is announced to the employee against signature within three working days from the date of its issuance, not counting the time the employee is absent from work.
If the employee refuses to familiarize himself with the specified order (instruction) against signature, then an appropriate act is drawn up. A disciplinary sanction may be appealed by an employee to the state labor inspectorate and (or) bodies for the consideration of individual labor disputes.
Bringing to disciplinary responsibility from "a" to "z"
Coming to work, the employee receives a job description. He must clearly follow all the points indicated in it. Otherwise, you can put yourself in an awkward, conflict situation or get reprimanded.
Info
An employer can issue an order on disciplinary liability of an employee if a person does not do what he is supposed to do according to his job description. Important point! You can not take and just anyone to hold accountable. Of course have different types disciplinary responsibility of employees, but criticism of the actions of an employee is fair only in conditions where the employer first created the correct working conditions.
If there are none yet, no one has the right to require personnel to comply with instructions and laws. If at first a disciplinary violation was committed, and after that normal working conditions were created, it is also impossible to hold the employee accountable.
The procedure and term for bringing an employee to disciplinary responsibility
Protection and justice In order for the employer not to be tempted to unfairly discipline an employee, the legislation of our country contains a number of regulations governing this issue. So, employees can be held accountable only by a strictly defined procedure. All possible penalties are listed in the laws of the state.
Important
No derogations, "inventions" are allowed. The procedure for bringing an employee to disciplinary responsibility is as follows: first you need to get an explanation from the employee for what reason the misconduct was committed. Written explanation. An employee may refuse to write an explanatory note, then the personnel department draws up an act about this. The document is written in any form. It is allowed to bring an employee to disciplinary responsibility both in the case of an explanatory note and in its absence.
The procedure for applying disciplinary sanctions Before applying a disciplinary sanction, the employer must request a written explanation from the employee. If, after two working days, the specified explanation is not provided by the employee, then an appropriate act is drawn up. The employee's failure to provide an explanation is not an obstacle to the application of a disciplinary sanction.
A disciplinary sanction is applied no later than one month from the date of discovery of the misconduct, not counting the time of illness of the employee, his stay on vacation, as well as the time required to take into account the opinion of the representative body of employees. Disciplinary liability may be established and applied no later than six months from the date of commission of the misconduct, and based on the results of an audit, audit of financial and economic activities or an audit - later than two years from the date of its commission.
- why the employee does not want to sign, how he explains;
- order number;
- signatures.
This usually happens when an employee leaves or is demoted. The Notice of Request for Explanations contains:
- the essence of the violation;
- a suggestion for an explanation;
- employer data;
- registration number;
- information about the employee (including position);
- date, signature.
An internal audit report is usually approved by the company's management and includes:
- full name of the organization;
- on what basis the procedure was carried out;
- who was on the committee;
- what happened and who is to blame;
- proposed penalties;
- date, signature.
As far as encouragement or punishment is concerned (and in general in the personnel system), there are no trifles.
Can you be disciplined if you have been working for less than a year?
Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a disciplinary sanction is automatically removed one year from the date of its imposition, provided that there is no new sanction. However, the employer can do this earlier at the request of the employee himself or at the request of his immediate supervisor. As well as the imposition, the removal of the penalty is carried out by issuing an appropriate order. Disciplinary action is not always justified. Those who believe that they have been wrongfully punished have a direct road to the state labor inspectorate, which has a branch in every region. The right to appeal against the penalty is enshrined in Art. 193 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The complaint can be drawn up in any form, however, it should consistently state all the circumstances of the imposition of a penalty and indicate the reasons for the illegality of the punishment.
Disciplinary responsibility is a special type of legal liability, its application is always associated with the performance of labor or official duties. A feature of disciplinary responsibility is the application of penalties that make up its content, as a rule, by the subject of labor relations, namely the employer. In this connection, disciplinary liability is one of the manifestations of the power of the employer in relation to the employee who has concluded an employment contract with him.
Disciplinary liability consists in the application by the authorized representative of the employer to the employee who has committed a disciplinary offense of disciplinary sanctions established by law. Bringing an employee who has committed a disciplinary offense to disciplinary liability is the right of the authorized representative of the employer. Whereas an employee who has committed a disciplinary offense is obliged to endure the adverse consequences established in the legislation. Consequently, the authorized representative of the employer has the right to release the employee from the obligation to suffer adverse consequences in connection with the disciplinary offense committed by him. In this case, the position of the employee in comparison with the law is improving. Therefore, such an exemption should be recognized as complying with the requirements of labor legislation.
Thus, disciplinary liability can be defined as one of the types of legal liability, which consists in the right of the authorized representative of the employer to apply to the employee who has committed a disciplinary offense the measures of disciplinary action provided for by law and in the duty of the employee who has committed the disciplinary offense, corresponding to this right, to undergo legislation adverse effects.
There are two types of disciplinary liability of employees. First, the general disciplinary responsibility of employees. General disciplinary responsibility applies to all employees without exception. General disciplinary responsibility comes according to the rules established in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The application of general disciplinary responsibility does not require proof of additional or special legally significant circumstances. In this connection, it is recognized as a general disciplinary responsibility.
Secondly, we can highlight the special disciplinary responsibility of employees, which exists along with the general disciplinary responsibility. At the same time, special disciplinary liability is applied only in cases where general disciplinary liability cannot be applied. Disciplinary responsibility is introduced by special legislation, in particular, charters and regulations on the discipline of employees. The application of disciplinary liability is always associated with proving additional, that is, special, legally significant circumstances. There are several types of legally significant circumstances that are subject to proof in the application of special disciplinary liability.
The first type of special legally significant circumstances to be proved when applying special disciplinary liability is the assignment of an employee to special subjects that are subject to disciplinary liability according to special rules. For example, prosecutors and judges are subject to disciplinary liability according to special rules. At the same time, the general rules on disciplinary liability are applicable to them insofar as they do not contradict the special legislation on bringing this type of liability to justice.
Secondly, as a type of special legally significant circumstances to be proved when applying special disciplinary responsibility, one can single out the performance by an employee of special labor duties directly related to the life and health of people. These duties include the performance of work directly related to the movement of railway transport.
Thirdly, the circumstance, the proof of which allows us to conclude on the application of special disciplinary responsibility, is the presence of a special circle of persons or bodies with the right to bring to disciplinary responsibility. For example, bringing judges to disciplinary responsibility is carried out by qualification collegiums on the recommendation of the chairman of the corresponding court. The President of the Russian Federation may bring to disciplinary responsibility the heads of federal executive bodies.
Fourth, a special type of circumstances, the proof of which allows us to conclude that special disciplinary liability is applied, is the presence of additional, that is, special, disciplinary sanctions applied to employees. For example, a special disciplinary sanction is the deprivation of the driver of the right to drive a locomotive for a period of three months to one year with the transfer with his consent to another job, dismissal from his position related to the operational work of railways, with the provision, with the consent of the employee, by way of transfer of another work.
Fifth, the circumstances, the proof of which allows us to conclude that special disciplinary liability is applied, we should recognize the existence of additional opportunities for appealing disciplinary sanctions. In particular, in addition to the judicial procedure, there may be an out-of-court procedure for appealing disciplinary sanctions, for example, to a higher authority or a higher official. For example, the decision of the regional qualification board of judges on the application of special disciplinary liability can be appealed to the High Qualification Board of Judges of the Russian Federation, and then in court. Employees of state organizations may appeal a disciplinary sanction to a higher official.
The proof of each type of the considered circumstances allows us to conclude that special disciplinary liability is applied to the employee. At the same time, when applying special disciplinary liability, circumstances that fall into various types can be proved. For example, judges belong to special subjects of disciplinary liability and appeal against special disciplinary liability in a special manner. Although the proof of a circumstance of one type allows us to conclude that special disciplinary liability is applied.
Thus, the general disciplinary responsibility differs from the special one by the proof of one or more types of circumstances considered. The proof of each of them can become the basis for recognizing special disciplinary responsibility. However, as a general rule, general disciplinary responsibility is applied along with special. In this connection, special disciplinary liability is applied only in cases where there are no grounds for applying general disciplinary liability.
procedure for disciplinary action
The main duties of an employee are to comply with the rules of conduct enshrined in the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other laws, collective agreements, an employment contract, internal labor regulations, other local acts and conscientious performance of functional duties in accordance with the job description. Accordingly, failure to perform or improper performance of these duties is the basis for bringing the employee to disciplinary liability.
An employer can bring an employee to disciplinary liability only if he has created the appropriate conditions for the employee to observe labor discipline.
Thus, a prerequisite for disciplinary liability is the presence of the employee's fault. Therefore, it is impossible to raise the issue of bringing to disciplinary responsibility an employee who refused to perform work in the event of a danger to his life and health due to violation of labor protection requirements; or from performing heavy work and work with harmful and dangerous working conditions not provided for by the employment contract; or refused to prematurely interrupt his vacation at the request of the employer.
To protect the employee, the law established a clear procedure for bringing to disciplinary responsibility and a closed list of types of disciplinary sanctions.
Before applying a disciplinary sanction, the employer must obtain a written explanation from the employee. If the employee refuses to write, an act is drawn up in an arbitrary form. Refusal to give an explanation is not an obstacle to the application of a disciplinary sanction.
On the imposition of a disciplinary sanction, an order is issued signed by the head. The employee must be familiarized with the order against signature within 3 days from the date of its issuance. If the employee refuses to sign the specified order, an appropriate act is drawn up.
A disciplinary sanction is applied no later than one month from the day the misconduct was discovered. The specified period begins to run from the day when the person to whom the employee is subordinate at work (service) became aware of the misconduct, regardless of whether it is vested with the right to impose disciplinary sanctions. This does not take into account the time of illness of the employee, his stay on vacation, as well as the time required to take into account the opinion of the representative body of employees. The absence of an employee from work for other reasons, including in connection with the use of days off, does not interrupt the course of the specified period. All holidays provided by the employer in accordance with the current legislation, including annual (basic and additional) holidays, holidays in connection with studying at educational institutions, holidays without pay should be classified as leave interrupting the course of a month.
In addition, a disciplinary sanction cannot be applied later than six months from the date of the misconduct, and based on the results of an audit, financial and economic activity or an audit, no later than two years from the date of its commission. The above time limits do not include the time of criminal proceedings.
For each disciplinary offense, only one disciplinary sanction may be applied. As a disciplinary measure Labor Code calls:
Comment;
Rebuke;
Dismissal.
Only their employer can apply them to the employee, taking into account the severity of the misconduct committed, the circumstances under which it was committed, the previous behavior of the employee, his attitude to work.
The process of labor relations is far from always connected with working moments and production activities. In any work collective there may be situations in which there is a violation of labor legislation or industrial discipline. Such cases are mandatory regulated by law, in addition, there is a wide base of court cases and legal practice to resolve such disputes and cases.
Normative base
Since the issues of disciplinary responsibility are important for both parties of labor relations (employee and employer) and often determine the future fate of the employee, the legislator has necessarily strictly regulated the process of resolving such disputes, as well as the actions of both parties in the presence of violations.
The main act governing labor Relations on the territory of our country, is the Labor Code c (but in which case the employee has the right to terminate the employment contract, you can read). In this issue, the imperative principle is used, that is, both parties to the conflict must adhere to strictly regulated rules when this type of responsibility occurs.
In turn, the Labor Code gives the concept of disciplinary responsibility. Such is an event or a fact of action or inaction, in which the employee does not fulfill his official duties in accordance with the employment contract (contract).
Grounds and conditions for bringing to responsibility
The basis for bringing the employee to responsibility is the fact of violation of the labor schedule and non-fulfillment by the employee of his direct duties established by the employment contract. The employee is obliged to comply with labor legislation, as well as internal labor standards, daily routine and labor discipline, if they do not contradict federal law. Based on this, in case of violation of any norms and the fact of objective proof of such violations, the employee will be liable for a disciplinary nature. And about which ones are considered in criminal law, read our article.
The basis is most often a misconduct, that is, an active intentional action of an employee, however, cases of inaction in case of violation are not uncommon. to grounds according to labor law relate:
- non-fulfillment by the employee of his direct regulated duties approved by the employment contract (Article 81). This ground also includes repeated violation of labor discipline (this concept is regulated by internal regulations enterprises). When committing these offenses, the employee may be held liable for this type of liability. When a one-time misconduct is committed by the employer, this type of punishment may not be applied, but only an oral or written remark;
- gross violation of labor regulations. This concept includes several types of violations:
- Absence of an employee without good reason(illness, difficult life situation) during the working day for more than 4 hours in a row or throughout the day. This type of violation can be punished up to and including dismissal, however, if the employee provides written evidence of the good faith of the day off within a few days, the employer is not entitled to take any measures.
- Also, if the employee appears during working hours in a state of any intoxication whether it be alcohol, toxic substances or drugs and their precursors, the employee must also be penalized, and such punishment may lead to the dismissal of the employee .
- It is also a serious offense to divulge any secrets of the organization.(according to civil law, these include commercial, state, official secrets). In view of the fact that the disclosure of confidential information can cause significant harm not only to a private company, but also to the state, the employer is obliged to resort to punitive measures for the employee.
- non-compliance with orders labor inspectorate and consequently violation of labor standards(labor protection) entails both the imposition of a fine on the organization, and organizational conclusions in relation to a certain employee. Committing a criminal or administrative offense during work and at the workplace related to the performance of official duties; It is also worth paying attention to what exist and what they are.
- commission by an employee of actions discrediting his honor and dignity or immoral acts(this type of offense is common among civil servants, as well as among teachers educational institutions). These actions also attract sanctions from the management;
- commission of illegal actions by an employee whose job contract involves working with the money supply (values) in relation to these values (waste, loss of property).
You may also be interested in information about what are
On the video - a list of violations and prosecution:
Procedure for imposing a disciplinary sanction
In the event of an action suitable for the imposition of such a penalty, the employer must adhere to following algorithm actions:
- after a misconduct is discovered, the employer is obliged to ask the offending employee for a written explanation of his actions, as well as to stop this violation (if he appears in a state of intoxication, it is necessary to send the employee for examination to a medical institution and not allow him to perform any work. It is also worth paying attention to the fact that );
- after receiving an explanation from the employee, it is necessary to form special commission, which will include representatives of the board of the organization, personnel service, direct supervisors of the subordinate and representatives of the trade union. The commission, within 4 days, analyzes the case of violation of labor discipline and makes a decision on the application of a penalty or the removal of all claims from the employee;
- if the employee does not agree with the decision of the commission, he remains to appeal this decision through the judiciary. If the employee agrees with the decision of the commission on guilt, he is immediately sanctioned.
It will also be useful to know for what and in what case









Quality requirements
Peat resources Milling peat extraction
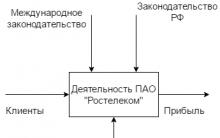
Closed Joint Stock Company Transtelecom
Setting up Wi-Fi equipment
Pasteurization drawer for the selection of "heads" during rectification