In the organization, the salary of employees is determined using a fork. AT staffing the maximum salary. How to get out of the situation if an employee appealed to the prosecutor's office with a complaint of salary discrepancy - read the article.
Question: In our institution, the salary of an employee when hiring is determined using a "fork", from and to. Those. his experience and education are taken into account. The staffing table includes the maximum salary, tk. we do not know which employee will come to work with us, with what experience and education. One employee turned to the prosecutor's office with the fact that his salary was incorrectly set, because. there is more in the staff list than he actually has, but with regards to the "fork", he is correct. Help get out of the situation.
Answer: In this case, we propose to make changes to the staffing table and set the employee a specific salary for the position (the same as indicated in his employment contract).
It is possible to establish a fork of salaries by position in the staffing table only in case of differences in the categories of professions or in the qualification category of employee positions (Article 143 of the Labor Code). Such positions should be reflected in column 3 "Position, rank, qualification class" of the staffing table (if you use a unified form).
That is, you can set a salary fork, for example, for milling operators of the second and sixth categories or a labor protection engineer of category I and a labor protection engineer of category II. These positions are divided into categories and categories, in connection with this, the salary of employees may differ.
The law obliges the employer to provide employees with equal pay for work of equal value (Article 22 of the Labor Code). In this regard, the establishment of a range of salaries for one profession or position that does not have gradations by category or category is discrimination in the sphere of labor (Article 3 of the Labor Code).
In this case, variation in the amount of remuneration is possible by establishing allowances depending on the employee’s labor skills, complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed by him, which you will reflect in columns 6-8 “Extras, rub.” staffing table (part 1 of article 132 of the Labor Code).
Similar explanations are given by Rostrud specialists in a letter dated April 27, 2011 No. 1111-6-1. The legitimacy of this position is confirmed by the courts. See, for example, the cassation ruling of the Supreme Court of the Udmurt Republic dated 08.08.2011 No. 33-2789/11, the appeal rulings of the Altai Regional Court dated 03.26.2014 No. 33-2530-14, the Yaroslavl Regional Court dated 05.05.2014 No. 33-2519/ 2014, decision of the Savelovsky District Court of Moscow dated 06/03/2015 No. 2-3726/2015.
It turns out that in this situation, we advise you to make changes to the staffing table and set the same salaries (a specific amount) for all employees with the same positions. And then, depending on the length of service of the employee, the level of education and other indicators, vary the amount of salary by setting allowances. Allowances also reflect in the staffing table.
Rationale
How to make a staffing table
Is it possible to set a salary fork in the staffing table by position
No.
Set a fork in the staffing table official salaries for a vacant position from the minimum to the maximum size is possible only in case of differences in the categories of professions or in the qualification category of employee positions (Article 143 of the Labor Code). Reflect such positions in column 3 “Position, rank, qualification class” of the staffing table. For example, millers of the second and sixth categories or a labor protection engineer of category I and a labor protection engineer of category II.
At the same time, the law obliges the employer to provide employees with equal pay for work of equal value (). In this regard, the establishment of a fork of salaries for one profession or position that does not have gradations by category or category is discrimination in the world of work ().
In this case, variation in the amount of remuneration is possible by establishing allowances depending on the employee’s labor skills, complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed by him, which you will reflect in columns 6-8 “Extras, rub.” staffing table (part 1 of article 132 of the Labor Code).
Similar explanations are given by Rostrud specialists in a letter dated April 27, 2011 No. 1111-6-1. The legitimacy of this position is confirmed by the courts. See, for example, the cassation ruling of the Supreme Court of the Udmurt Republic dated August 08, 2011 No. 33-2789 / 11, appeal rulings
Good afternoon! There are situations when, on the basis of a resume, you hire an employee, but it turns out that he overestimated his abilities, and you have to train him, and he receives a salary already as a highly qualified specialist. Is it possible to provide for a "fork" of salaries in the staffing table, minimum and maximum, and set at the discretion of the management and in accordance with the qualifications of the employee. How to draw up such a staffing table? And are there any recommendations for situations where a new employee is given a lower salary until he proves that he complies with job descriptions?
Answer
Labor legislation obliges the employer to provide employees with equal pay for work of equal value (Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this regard, the establishment of a range of salaries for one profession or a position that does not have gradations by category or category is discrimination in the sphere of labor (Article 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Variation in the amount of remuneration in this case, depending on the labor skills of the employee, the complexity, quantity, quality and conditions of the work performed by him, reflected in the "Surcharges, rub." staffing ().
A similar position is held by Rostrud in.
Nina Kovyazina
2. Situation: Is it possible to set different salaries for employees holding the same position
Yes, you can, if the position provides for different categories.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation does not prohibit setting different salaries for employees holding the same position. It is only said that the salary should depend on the employee, the complexity of the work performed by him and the quality of labor (). However, personal salary setting cannot be arbitrary (). Therefore, if the organization sets different salaries for employees holding the same positions, job descriptions should establish different responsibilities for them. And in the staffing plan to provide various categories posts. For example, enter positions: payroll accountant, fixed asset accountant, salesperson, senior salesperson, etc.
Nina Kovyazina
Deputy Director of the Department of Education and Human Resources of the Ministry of Health of Russia
Current personnel changes
-
Inspectors from GIT are already working according to the new regulations. Find out in the Kadrovoe Delo magazine what rights employers and personnel officers have had since October 22 and for which mistakes they will no longer be able to punish you. -
There is not a single mention of the job description in the Labor Code. But personnel officers need this optional document. In the magazine "Personnel Business" you will find an up-to-date job description for a personnel officer, taking into account the requirements of the professional standard. -
Check your PVR for relevance. Due to changes in 2019, the provisions of your document may violate the law. If the GIT finds outdated wording, it will fine. What rules to remove from the PVTR, and what to add - read in the magazine "Personnel Business". -
In the magazine "Personnel Business" you will find an up-to-date plan on how to create a safe vacation schedule for 2020. The article contains all the innovations in laws and practice that must now be taken into account. For you - turnkey solutions situations that four out of five companies face when preparing a schedule. -
Get ready, the Ministry of Labor is changing the Labor Code again. There are six amendments in total. Find out how the amendments will affect your work and what to do now so that the changes are not taken by surprise, you will learn from the article.
In today's realities of life, when scientific and technical progress does not stand still, business develops and becomes mobile, it is becoming more and more difficult for us, specialists in personnel administration, to comply with the requirements of Russian legislation. This is especially evident in the preparation of the staffing table.
Fairness in staffing
The staffing table is normative document an enterprise that draws up the structure, staffing and number of the organization, indicating the amount of wages depending on the position held. For this document, a unified form T-3 is provided. 
Since 2013, unified forms have become optional for employers to maintain. However, Law No. 402-FZ "On Accounting" dated December 6, 2011 does not prohibit their use. However, it is still recommended, if possible, to use the unified forms in the work in order to avoid additional questions from the inspectors. But if you still decide to use your form of staffing, then it should be approved by order for the enterprise (for the main activity).
The document (staffing) in its form is quite simple and at the same time very useful, as it allows you to plan the quantitative and financial resources of the company. Nevertheless, when compiling this document, personnel officers face a rather difficult task - to comply with the requirement of Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and provide employees with equal pay for work of equal value. In practice, this means that there should not be different salaries for the same positions.
The legislator has established a fairly fair requirement for all employers, which is difficult to fulfill in practice. Firstly, now many employers use the “agreement” method with a future employee on wages even at the interview stage, depending on his education, experience and qualifications in general, regardless of the staffing table. So, the position of "secretary" can be as a person with experience and knowledge foreign languages With high salary, and a university graduate with no work experience and no knowledge of languages, with a much lower rate. Wages can also depend on the economic situation in the country and, so to speak, the "average temperature in the hospital" within the industry. In this case, the salary of a new employee may be higher than that of a long-time employee in the company; or, conversely, less. (This can happen, for example, during a crisis, when there are significantly fewer vacancies on the labor market than job seekers). It is not uncommon for an employer, without thinking about the consequences, to increase the salary not for the position, but simply for a specific employee, for example, fearing his transfer to a competitor.
As a result, we see the so-called "fork" of salaries for one position. This is a direct violation of the law, namely Article 22 Labor Code Russian Federation. For this violation, a fine may be imposed in accordance with Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. In this case, an obligation will be imposed to eliminate the discrepancy. This can be done in several ways, but in any case, you will have to fix it.
Many believe that you can avoid a fine if you sign different job descriptions with each employee by position. You can also try. But this will in no way protect the employer from the risk of litigation with the employee with all the ensuing consequences. Of course, you can try purely theoretically, but in fact the job description should reflect the duties of the position, even based on the title of the document. It turns out that for each position - one job description, reflecting the labor function of the position.
You can try to fix the responsibilities not job description but directly in the contract itself. But this means that with each employee you need to conclude an individual, not a template labor contract. This is labor-intensive and does not provide a 100% guarantee of protection against risks. . According to the legal dictionary, a position is a primary structural unit of the staffing table of a state or non-state organization established in a certain order, which determines the content and scope of powers, the amount of pay and place in hierarchical structure organization of the person replacing it (Big Legal Dictionary. - M .: Infra. M.A.Ya. Sukharev, V.E. Kurtskikh, A.Ya. Sukhareva, 2003). Ultimately, whatever one may say, we still come to the conclusion that, according to all concepts and definitions, employees working in the same position should perform equal duties and receive equal pay. Therefore, this trick is rather doubtful.
How to avoid "forks"?
Every personnel officer thinks about how to avoid this unpleasant “fork” of salaries, registering a new employee in a position similar to the one in which another employee has been working for a long time, but with a different salary, or changing the salary of a working employee. We don't have a lot of options here, but we do have them!
When you want to comply with the requirements of the law and at the same time “get” that same employee for “other” money, the first and most obvious option is to establish personal allowance. Non-state companies are given more freedom here. It can be like a bonus for performing special important works as well as high qualifications. There are many options - it all depends on the imagination of the employer (within reason). This is especially true when an employee is hired for the period of absence of the main employee, for example, during parental leave. There are frequent cases when only a more “expensive” employee can be found as a replacement (this is especially true for those companies that do not comply with the requirements of Article 134 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation on wage indexation). In this case, it is necessary to increase the salary for the position in accordance with the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but many employers avoid this by providing the same salary as the “retired” employee, while setting a personal allowance.
For example, provide elevated level remuneration to an employee with higher qualifications at equal salaries for the position can be a well-built motivation system based on personal contribution to the work and on the results achieved. This is a difficult but doable task.
When we have yet to register an employee, options can be found, but what to do when the company has long had the practice of registering employees for equal positions at different salaries. There are also options here, but not so many.
Position salaries can be equalized by increasing the salaries of employees with lower salaries to the highest positions. This option, of course, is not the most profitable for the employer in terms of financial costs, but it most closely complies with the requirements of the law.
When solving the problem of complying with the requirements of Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation in relation to the staffing table, you can also consider the option of renaming posts. Here everything depends on the imagination and knowledge of the industry of the personnel specialist. One can also help qualification guide, which is undoubtedly outdated by now, but is still able to “throw” a couple of ideas to the personnel officer. It remains only not to forget to appropriately arrange the transfers of employees to new positions and make entries in work books.
 The most difficult and labor-intensive option is to conduct a certification of employees in order to assign a rank to the position. This option is a whole process of work on the description of positions and categories, based on indicators for the level of education, the amount of special knowledge, work experience in this or a similar position, as well as positions that allow you to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to perform the work provided for by the current positions. At the same time, for each professional qualification group employees should have their own special indicators and evaluation criteria. It is important not to forget that the process and scheme for appraisal of employees should be written in local regulations companies. After the certification of employees, it will be possible to revise the remuneration system and equalize salaries for positions within the categories.
The most difficult and labor-intensive option is to conduct a certification of employees in order to assign a rank to the position. This option is a whole process of work on the description of positions and categories, based on indicators for the level of education, the amount of special knowledge, work experience in this or a similar position, as well as positions that allow you to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to perform the work provided for by the current positions. At the same time, for each professional qualification group employees should have their own special indicators and evaluation criteria. It is important not to forget that the process and scheme for appraisal of employees should be written in local regulations companies. After the certification of employees, it will be possible to revise the remuneration system and equalize salaries for positions within the categories.
* * *
Thus, for non-compliance with labor legislation, Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses provides for fines that can be imposed for each specific fact of violation. In the event that there are many discrepancies in salaries in the position in the staffing table, a fairly significant monetary penalty can be expected. So is it worth breaking?
Agree that, in principle, in a company where information on wages is transparent and fairly distributed among employees, everyone works easier, better, longer and with pleasure!
The meaning of the VSOTRK system is that the collective ore payment fund, which is a specific fixed percentage of the enterprise's profit, is distributed on the basis of consolidated wage rate, which is determined for each employee. It is obvious that the composite wage rate should reflect stable differences in the qualifications of workers, as well as in the value and significance of their work for a given enterprise. At the same time, it is assumed that the differences in the qualifications and significance of the work of workers have already been reflected in the existing at the enterprise tariff rates and salaries. Then initial composite wage rates :
where - respectively, the average wage i-th employee and the minimum average wage for the enterprise for the period preceding the transition to the VSOTRK system (six months, a year).
Then, the entire range of initial composite wage rates must be broken down into 8–15 qualification groups. At the same time, it is desirable that employees performing similar duties and bearing equal responsibility enter the same qualification group or neighboring categories (it is advisable to classify unqualified personnel in one group). This implies the main condition for the application of the VSOTRK system at the enterprise - the presence of a significant differentiation in wages (8 or more times), which makes it possible to identify a sufficient number of qualification groups.
Each qualification group has its own range of "fork" ratios in wages. The established intervals of wage coefficients reflect possible individual differences in the labor contribution of an employee within a particular qualification group. The average value of the “fork” is taken as the base coefficient of the ratios in pay, which is then adjusted taking into account the labor contribution of the employee, as well as the results of the activities of his unit and the enterprise as a whole. To do this, for each profession (specialty), it is necessary to develop indicators of increase and decrease:
where - the actual coefficient of the ratio in the wages of the i-th employee;
- the average value of the "fork" ratios in wages;
– total values of increasing and decreasing indicators.
At a small enterprise, it is allowed to single out criteria that are uniform for all categories of workers, correcting the basic coefficient of pay ratios. At the same time, the increasing indicators should ideally be, as it were, a “mirror” reflection of the decreasing ones.
|
Positions |
salary, rub. |
Coefficient pay ratios |
|
CEO |
||
|
Chief Engineer |
||
|
Head of Operations |
||
|
Operations Master |
||
|
Head of auxiliary production |
||
|
Auxiliary production mechanic |
||
|
Head of the Marketing Department |
||
|
Marketing manager |
||
|
Chief Accountant |
||
|
Programmer |
||
|
Head of Human Resources |
||
|
Security guard |
||
|
Dispatcher |
||
|
Secretary |
||
|
glass cutter |
||
|
Builder |
||
|
An electrician |
||
|
Driver |
||
The range of differentiation in remuneration is 10.46 times, that is, the differentiation can be considered significant, which makes it possible to apply the VSOTRK system.
We distribute the employees of the enterprise into similar categories:
We break the range of ratios in wages (1.00–10.46) into “forks”. The amplitude of the "fork" of the ratios in wages at this enterprise is the same for the first seven qualification groups and is + 0.45, while for the eighth qualification group, which included senior managers, the amplitude is + 1.55. Therefore, the corrective (increasing and decreasing) coefficients of the first seven categories will differ from the coefficients of the eighth group.
For example, a foreman, whose work experience at the enterprise is 4 years, at the end of the month has the following personal performance results: no claims from the management; obtaining savings on operating costs. At the same time, the company did not fulfill the plan for the volume of product sales.
The master is included in the qualification group with a range of “fork” ratios in wages of 3.73–4.63. The mean fork for this skill group is 4.18. Then the total wage rate for the master will be:
|
Pay ratio brackets by groups |
||||||||
|
1. Unqualified personnel |
||||||||
|
2. Workers |
||||||||
|
3. Employees |
||||||||
|
4. Specialists |
||||||||
|
5. Leading experts |
||||||||
|
6. Leaders subdivisions, departments |
||||||||
|
7. Senior leaders |
||||||||
|
Increasing / decreasing the base factor indicators in wages |
significance |
For groups |
For group 8 (top managers) |
|
1. Fulfillment / non-fulfillment by the enterprise of the plan for the volume of sales |
0,18 | 0,62 | |
|
2. High-quality and timely execution official duties, lack of complaints and claims from the management / Violation labor discipline, poor quality and untimely performance of official duties |
0,14 | 0,47 | |
|
3. Obtaining ongoing cost savings / Application material damage enterprise, allowing marriage through one's own fault |
0,10 | 0,38 | |
|
4. Work experience in the specialty at this enterprise 3 years or more / less than 3 years |
0,03 |
n is the number of employees participating in distribution of the payroll.Publications
Oganesyan A.S., Oganesyan I.A. Remuneration of employees of enterprises
Tatulov B.E. Analysis of personnel motivation systems in Russia and abroad Braude A.M. Implementation of a financial structure: using marginal analysis in the development of a wage system
Lityagin A. Optimization of personnel remuneration. Tips for top managers
Danilova E. Tariff systems Related sections and other sites |
- Volgin, N., Val E. VILAR: motivational basis effective labor// Man and labor. - 2000. - No. 4. – P. 75–79.
- Volkova N.V. Personnel policy for securing young specialists at the enterprise (on the example of graduates of economic specialties of higher educational institutions) // Dis. … cand. economy Sciences: 06.08.00. - Biysk, 2005. - 169 p. ( pp. 38–42)
- Volkova N.V. Assessment of personnel competitiveness as component flexible wage systems // Problems of increasing the competitiveness of labor resources: materials of the interregional scientific and practical conference. - Biysk: Printing House, 2002. - S. 75–78.
- Mazmanova B.G. Pay management: textbook. allowance. - M. : Finance and statistics, 2001. - 368 p. ( pp. 244–314)
- Milyaeva L.G., Volkova N.V., Makarova O.M. Flexible Systems wages: types, principles of construction, application experience // International scientific and practical conference“Science and practice of organization of production and management” (Organization - 2001): collection of scientific reports / Alt. state tech. un-t im. I.I. Polzunov. - Barnaul: AltGTU Publishing House, 2001. - S. 147–151.
- Milyaeva L., Koinash G. Another variant of the tariff-free wage system // Man and Labor. - 2001. - No. 4. – P. 49–53.
Methods for selecting specialists and rules for maintaining documentation. HR strategy and subtleties labor law. As a HR worker, you know firsthand how many skills and knowledge this profession requires.
We also know how complex and multifaceted the tasks of a human resources specialist are. We understand how important it is to receive specialized information in time and in full. We are aware of how difficult it can sometimes be to interpret laws and apply them in practice.
To help you, we have created the official website of the magazine "Handbook of Personnel Officer" - a portal where all the most important professional information is collected.
Registration on Pro-personal.ru is:
About staffing and personnel office work- everyday.
Operative information about changes in the labor legislation.
Rostrud clarifications, expert comments, analysis of judicial practice.
practical advice, step by step instructions for all key processes.
The project team consists of experienced experts in the field of personnel management and labor legislation. The result of their work is materials that facilitate the work of personnel specialists at all stages: from the formation of staff to the preparation of reports and interaction with the State Inspectorate.
We strive to create an information space where professional personnel officers will find everything they need to effective work. AT electronic version magazine you will find not only useful articles, but also many services that will greatly facilitate your work. Among them:
Calculators of pension payments, other benefits.
Production calendars with the function of calculating the norms of working hours.
Dispensary schedules.
Use the free demo access to evaluate the information content and practical value of the materials in practice.
Register to use the opportunities of the personnel portal as efficiently as possible.









Quality requirements
Peat resources Milling peat extraction
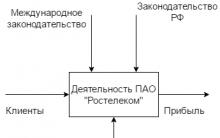
Closed Joint Stock Company Transtelecom
Setting up Wi-Fi equipment
Pasteurization drawer for the selection of "heads" during rectification