Organizational potential of the enterprise
Organizational capacity- this is the total capabilities of the employees of the management apparatus, expressed in the volume and types of work that can be performed by the management of the enterprise.
The basis of organizational potential is the culture of the organization - the totality of managerial personnel, value systems, systems and procedures. This part of the organizational potential is subject to the strongest influence from the chosen strategy of the company Spivak V.A. Corporate culture. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2001.
An increase in organizational capacity can be achieved by improving the organizational structure of management.
In the early 1970s American scientist I. Ansoff put forward a number of new ideas regarding approaches to understanding and developing organizational management structures. He identified two approaches to the formation of organizational structures.
The first one is the structural approach. The main emphasis in it was placed on the internal structure of firms, the division of functions and the rationalization of management. The second is a dynamic approach. It focuses on the analysis of the firm's links with the environment in which it operates and with sources of resources. With a dynamic approach, the analysis of managerial problems is carried out in two stages. At the first stage, the firm is considered in conditions of stable external relations. Organizational problems are operational in nature. At the second stage, the impact on the organization of changes in the external environment is studied. The organizational problems arising from this are considered strategic. Ansoff believed that the main task of the top management of a modern firm is to solve strategic problems in a changing external environment.
The main strategy of firms in the conditions of constant external relations was the reduction of production costs and price competition. The result was a divisional structure. Ansoff viewed this kind of organizational structure as " functional structure repeated several times." Education multinational companies led to the need to bring marketing services closer to the national markets in which the company operates. It was divided and branches were formed in different countries. Ansoff called such a structure a multinational structure, a matrix of the branch-country type. Ansoff believed that the idea of a matrix is one of the main modern science on the formation of organizational structures.
The behavior of modern firms can be structured in three directions, i.e., three main strategies can be distinguished: achieving resource efficiency, ensuring competitiveness, and an active policy in the field of innovation. Depending on which strategy prevails, one or another type of structure is chosen. The use of several strategies requires the formation of matrices of various types or a reasonable combination different types structures within the same company. One of the latest forms of multinational structure is the product-market matrix, which attempts to combine market policy with the development of a firm's strategy. Having considered the evolution of organizational structures, Ansoff identified the main trends in their development. The main trend can be considered the awareness of managers of the fact that any organization is a complex collection of a large number of interrelated elements.
For companies that have separate structural divisions (enterprises, organizations, branches), organizational potential is important in achieving a sustainable financial condition. The organizational potential of a company depends mainly on whether the given company (legal entity) is a system or a conglomerate. An increase in organizational capacity can be achieved by improving the structure of the company and the structure of its activities (optimal diversification of activities). It is important that as a result of these improvements, the level of systemicity be increased and due to this, a synergistic effect (interconnection effect) is obtained, in which the total return on investment of the company is higher than the sum of the return indicators for each technological chain (group of enterprises) separately.
Improving the structure of the company and the structure of its activities is carried out according to the scheme:
1. Definition of the mission, goals and strategy of the company;
2. Structurization of technological chains for the production of final products;
3. Structuring the processes of life cycles of products / technologies of intermediate (according to technological chains of production) and final products;
4. Determination of the role of the (basic) enterprises operating in the company in the technological chains of production and life cycles of products / technologies and, possibly, their reconstruction;
5. Designing additions to the basic composition of enterprises due to:
- acquisition of operating enterprises of other companies;
- penetration into other companies (participation in them);
- formation of branches and representative offices, design and construction of new enterprises.
6. Integration of industries of various industry affiliations, various technological chains and product/technology life cycles.
The main sources (factors) of synergy in the designed system can be:
- the presence of unified elements in the design of manufactured products;
- the possibility of combining certain links of technological chains;
- the possibility of combining certain processes of product/technology life cycles (for example, design processes for unified product elements);
- the possibility of combining (combining) individual functions and management tasks, as well as technical, informational and regulatory management bases;
- mutual opening of channels of commercial and scientific and technical information, providing:
- accelerating the diffusion of innovations and best practices;
- savings from combining information banks;
- increasing protection from the reflexive impact of competitors due to more qualified screening (filtering) of external information;
- harmonization of intracompany standardization.
When assessing synergy, all these sources are concretized into synergy factors. It should be noted that the interaction can also lead to a negative effect of synergy, when 2 + 2
In foreign practice, the structure of the activities of many successfully operating firms is unsystematic: each type of activity is practically isolated from other types. These are conglomerate firms. The experience of US firms shows that synergistic firms and conglomerates perform roughly the same under favorable general conditions. But in tense situations and (or) in moments of recession, synergistic firms are more resilient and have top scores activities than conglomerates. Therefore, we can conclude that the higher the expected instability and stiffness of competition, the more success will depend on the presence of a positive effect of synergy (systematic activity).
Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation
Branch of the State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Kostroma State University"
them. ON THE. Nekrasov in the city of Kirovsk, Murmansk region.
Specialty: 080507 "Management of the organization"
Department: full-time
Abstract on the discipline "basics of management"
on the topic: "The potential of the organization"
Completed by a student
group 3 MEN
Nesterova E. S.
Checked by: A. M. Koptyaev
Introduction 3
1. The concept of "potential" 4
2. Law of synergy 5
3. Total potential 6
3.1. Production capacity 6
3.2. Labor potential 7
3.3. Innovation potential 8
3.4. Organizational capacity 10
Conclusion 12
References 13
Introduction
characteristic feature modern economy is not only the multitude of factors, both external and internal, influencing the organization, but also the dynamism of their change. Under such conditions, control system must respond quickly to all changes and ensure that the full potential of the organization is used to the maximum.
The issues of effective management of the organization's potential are especially relevant for Russian enterprises whose main problem is the lack of resources. If in a planned economy the main direction of growth was the accumulation of resources, then in a market economy the main task is to increase the utility of resources. Thus, the transition from a planned economy to a market one forced the leaders to reassess the potential of their enterprises and start looking for new opportunities to use the available resources. Increasing the return of the resources used is inextricably linked with an increase in production efficiency, which makes it possible to ensure the development of the enterprise and increase competitiveness.
All this gives grounds to talk about the need to study the potential of organizations, the impact on it of the external and internal environment and potential management.
Over the past two decades, a lot of work has appeared abroad and in Russia on the potential of organizations. Most authors consider the potential as a complex of resources and their effective use. At the same time, despite the fact that the term potential is used quite widely not only in management, but also in the economy, the essence of the organization's potential as a factor that ensures the existence and functioning of socio-economic systems has not yet been disclosed. The reasons influencing the change in the potential and its role in the life of the organization have not been studied either.
1. The concept of "potential".
Economic science has not yet developed a clear definition of the concept of "potential of an organization (firm, enterprise)".
The basic term for the concept of "potential" is the term "potency". Potency - (potential - strength) - a hidden opportunity, ability, strength that can manifest itself under certain conditions.
In the Russian Explanatory Dictionary, potential is understood as a set of means, opportunities in some area.
In the explanatory dictionary of S. I. Ozhegov and N. Yu. Shvedova, the following definition of potential is given: “... the degree of power in some respect, the totality of some means, opportunities ...”.
The Soviet Encyclopedic Dictionary gives the following definition: “Potential - sources, opportunities, means, reserves that can be used to solve any problem, achieve a specific goal; the possibilities of an individual, society, state in a certain area.
There are many similarities between the above interpretations of the term "potential". They talk about the totality of any opportunities in some area.
Turning to the explanatory dictionary, you can find out that “opportunity” is a favorable condition, circumstance, situation in which something can be done; internal resources, forces, abilities. And ability is natural giftedness, talent; skill, and also the ability to perform any action. That is, no distinction is made between capabilities and abilities in a particular context.
Summarizing the above, we can say that potential is a set of opportunities to achieve certain goals in any area (for example, in an organization). The potential of the organization is a product of strategic management.
2. Law of synergy.
Any organization is characterized by the following elements: productivity, interest, scientific potential, attitude to the external environment, microclimate in the team, personnel potential, technical potential, development prospects, image. They determine the potential of the organization, its ability to operate. The process of significant increase or decrease in capacity material system called synergy .
The law of synergy: for any organization there is such a set of elements in which its potential will always be either significantly greater than the simple sum of the potentials of its elements (people, computers), or significantly less.
The manager's task is to find such a set of elements in which synergy would be creative. It is rather difficult to design the conditions for achieving synergy in advance. It is also difficult to assess the possible increase in the overall capacity of the organization. The synergy effect has not yet been measured. However, the accumulation of statistical data on the impact of synergy is being carried out, and the simplest models of the conditions for its achievement are being formed.
There are a number of methods for successfully implementing the law of synergy. The method of "questions and answers" is the simplest in organizational execution, its implementation can be partially formalized using a computer by creating an information base of possible questions, answers and the consequences of their implementation. The “conference of ideas” method, which is based on the stimulation of the thinking process at the level of consciousness, is very promising. All methods should be aimed at strengthening the action of the law of synergy.
3. The total potential of the organization.
Organizations develop through their total potential, the potentials of their constituent units and other elements.
The overall potential of the organization includes:
Industrial;
Labor;
Innovative;
organizational potential.
Organizational management requires a variety of approaches and ways to use the overall potential of the organization.
3.1. Production potential.
This potential reflects readiness for stable production activities and includes:
Various activities;
Projects.
The production potential of the organization is determined by:
Equipment used (its capacity, capabilities);
applied technology;
The level of organization of production, etc.
Moreover, if the result of production is products (services), then in the context of production potential, not any product (service) is included in its composition. This is explained by the potential profitability inherent in the product. If the product is based on the latest technologies, using high quality materials, etc., then it is part of the production capacity, and will be in demand in the market. Products (services) are the result. At the beginning of the process, various resources enter the organization:
Logistics;
natural;
human;
Financial;
Informational.
3.2. human potential.
From an economic point of view, the main element of human potential is labor potential.
Labor potential is a personified labor force, considered in the aggregate of its quality characteristics. This concept allows, firstly, to assess the degree of use of the potential capabilities of both an individual employee and their totality, ensuring in practice the activation of the human factor, and, secondly, to ensure a qualitative (structural) balance in the development of personal and material factors of production.
It is necessary to distinguish between two levels of potential: the labor potential of the organization and the labor potential of the employee.
The labor potential of an employee (LPR) is the total ability of the physical and spiritual properties of an individual employee to achieve certain results of his production activity under given conditions, on the one hand, and the ability to improve in the labor process, to solve new problems arising as a result of changes in production, on the one hand. another.
The labor potential of an employee includes:
1) psychophysiological potential - the abilities and inclinations of a person, his state of health, performance, endurance, type of nervous system, etc.;
2) qualification potential - the volume, depth and versatility of general and special knowledge, labor skills and abilities, which determines the ability of an employee to work of a certain content and complexity;
3) personal potential - the level of civic consciousness and social maturity, the degree of assimilation by the employee of the norms of attitude to work, value orientations, interests, needs and demands in the field of work, based on the hierarchy of human needs.
The labor potential of an organization is, on the one hand, a set of
conditions that ensure the realization of the labor potential of an employee, on the other hand, a new quality that arises with a purposeful joint activities workers and groups.
3.3. Innovative potential.
Innovative capacity is the degree of readiness of an organization to perform the tasks necessary to achieve its goals (for example, the readiness of an organization to implement a project). Based on the results of the assessment of innovative potential, an innovative strategy of the organization is selected.
The innovative potential depends on the parameters of the organizational structures of management, the professional and qualification composition of industrial and production personnel, external conditions economic activity etc. Therefore, the assessment of innovative potential is a necessary component of the strategy development process.
The structure of the innovative potential covers those elements of the organization that determine its readiness for change: decentralization in decision-making, a low level of formalization and regulation of managerial work, the ability of organizational structures to flexibly rebuild according to changes in tasks and operating conditions. Centralized hierarchical organizational structures negatively affect the innovative potential, which contradict the creative nature of innovative activity: stable relations and management procedures actively resist any innovation.
The organization's readiness for change involves a detailed assessment of the innovative potential, using the "resources - functions - projects" scheme. This scheme is used even at the stage of justification of an innovative project. It covers:
1. a description of the problem of enterprise development and the definition of tasks that are included in the problem solving program;
2. description of the environment for solving the problem (the state of the internal environment, environmental factors that affect innovative activity);
3. assessment of the resource potential in relation to a certain innovative task (providing the project with the resources necessary for its implementation);
4. assessing the ability of personnel to achieve certain performance results (resource support managerial functions);
5. assessment of the level of providing the project with the functions necessary for its implementation (functional support of the project);
definition integral assessment the potential of the organization, its readiness to solve an innovative task;
6. determination of the main activities necessary to achieve a certain potential for the implementation of an innovative project (Lapin E.V. Economic, 2002).
Another way to assess the innovative potential of an organization is the SWOT analysis, which makes it possible not only to assess the organization's ability to implement innovations, but also to determine how this ability is affected by the innovative climate of the external environment. The standard SWOT analysis methodology is conceptualized in terms of the innovative opportunities that the business environment and the potential of the organization itself can provide. During the analysis, fix:
1. strengths the potential of the company, which will ensure it the use of opportunities that have appeared in the external environment; this helps determine the appropriate strategy for their use;
2. weaknesses in the potential of the company, which deprive it of the chance to use new opportunities or create threats to its existence.
Due to the high innovative potential, the organization can quickly respond to changes in the external environment, conduct innovative search and implement organizational changes. Low potential does not provide such an opportunity; innovations under these conditions are rarely introduced and only when the company begins to feel difficulties in marketing its products. However, developing innovative solutions in response to a problem is inefficient. The innovative policy of the enterprise of the masses, to be the result of in-depth market research, constant monitoring of the actions of competitors, must resist the modern scientific and technological achievements in the relevant industry and the effective use of the intellectual and creative potential of employees. This will enable top management develop optimal innovative strategies that will shape strategic advantages enterprises in the long term (Lapin E.V. Economic, 2002).
3.4. organizational potential.
Organizational capacity - a connecting link for the implementation of management processes and part of the total potential of the organization. Elements of organizational potential are independent and serve as objects of study of management science. The elements of organizational capacity include:
Organizational structure of management;
Organizational system and management style;
leadership capacity;
Functional potential of the organization;
Organizational (corporate culture).
The organizational structure of management is a form of division and cooperation management activities within which there is a management process aimed at achieving the goals of the organization. The management structure is a set of elements, levels of management and links, the mechanism of functioning of which allows the organization to achieve its goals. The organizational structure is a reflection of the division of labor existing in the organization between departments, groups, employees.
The organizational system and management style consist of an object, subject, management process and social resources, and also include the accepted methods and methods of management.
Leadership capacity includes characteristics such as:
Qualification;
Professionalism;
Organization loyalty;
Learnability, etc.
The functional capability of an organization includes activities across all functions throughout the life cycle of a product, as well as production, distribution and consumption.
Organizational (corporate culture) - as part of the organizational potential, it is formed "at the exit" of the organization in the form of a system of rules and norms of social behavior (artifacts), accepted (basic) values and ideas, which contributes to the achievement of the organization's goals.
Conclusion
Organizational management requires a variety of approaches and ways to use the overall potential of the organization. The potential of the organization consists of the resources and sources of their replenishment that it has, its connections, position and the organizational system as a whole. The potential of the organization itself is a source of formation competitive advantage organization and that is why it needs constant development and improvement. The potential of the organization is strategic resource organization, which ensures its stability in inadequate conditions of the macro environment, allows you to neutralize the negative impact external factors. The potential of any organization has the greatest impact not only on the final results of any of its activities, but also on the limits of growth and structural development of the entire organization.
Bibliography
1. Lafta J.K. Theory of organization: Proc. allowance. - M.: TK Velby, Prospect Publishing House, 2003
2 Modern dictionary of foreign words. Approximately 20,000 words. - M: Rus. yaz., 1993. - 740 p.
3. Lopatsh V. A, Lopatina L. E. Russian explanatory dictionary / Ed. 7th, rev. and additional - M.: Rus. yaz., 2001. - 882 p.
4. Ozhegov S. I., Shvedova N. Yu. Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language: 80000 words and phraseological expressions / Russian Academy of Sciences. Institute of the Russian Language. V. V. Vinogradova / Ed. 4th, add. - M.: Azbukovnik, 1999. - 944 p.
5. Soviet encyclopedic dictionary. Ch. ed. A. M. Prokhorov / Ed. 4th. - M.: Sov. encyclopedia, 1987. - 1600 p.
6. Shafikov M. T. Potential: essence and structure // Social and humanitarian knowledge^ 2002, No I, p. 236-246
7. Lapin E.V. Economic potential of the enterprise: Monograph. - Sumy: ITD "University book", 2002
ORGANIZATIONAL CAPACITY OF THE ORGANIZATION / SUSTAINABLE FUNCTIONING / RESOURCE POTENTIALS/ PRODUCTIVITY / CONTROL TECHNOLOGY / ORGANIZATIONAL POTENTIAL OF AN ORGANIZATION/ SUSTAINABLE FUNCTIONING / RESOURCE POTENTIALS / PRODUCTIVITY / MANAGEMENT TECHNOLOGYannotation scientific article on economics and business, author of scientific work - Tretyakova Elena Petrovna, Kuvshinov Mikhail Sergeevich
The article presents the theoretical provisions that reveal the organizational potential as the ability of an organization to create a resource structure for the production of products and the maintenance of key values. By considering the properties, forms and functions of the organizational potential, the possibility of its use as a means of management has been established. sustainable functioning manufacturing organizations. To use the organizational potential in this capacity, the laws of its formation, functioning and development have been established, a model of the functioning of the organizational potential has been developed, the essence of organizational potential management has been determined, and an appropriate mechanism has been developed, including cycles of operational, tactical and strategic management using specialized technologies. Proposed and substantiated a set of productivity indicators for evaluation sustainability of functioning production organizations, as well as summary indicators of the status and effectiveness of organizational capacity. It has been established that the formation of the productivity of organizational potential occurs through education resource potentials organizations (industrial, financial, labor and market). The application of the above theoretical provisions makes it possible to ensure sustainable operation production organizations by harmonizing economic results with indicators and means of organizational activity that ensure their achievement.
Related Topics scientific papers on economics and business, author of scientific work - Tretyakova Elena Petrovna, Kuvshinov Mikhail Sergeevich
-
Diagnostic analysis of the organizational potential of an industrial enterprise
2016 / Tretyakova E.P. -
Development of a complementary technological approach to managing the organizational potential of production organizations
2018 / Tretyakova E.P. -
Overview of methods and problems of assessing the organizational potential of a company
2012 / Tretyakova E.P. -
The role of innovative potential in the system of managing the economic security of enterprises
2015 / Anisimov Yu.P., Zhuravlev Yu.V., Kuksova I.V. -
Organizational potential, organizational capital, company resources: the essence and correlation of concepts in management science
2013 / Tretyakova Elena Petrovna -
Increasing the competitiveness of construction enterprises on the basis of organizational and economic solutions for managing human resources
2017 / Emirbekova Jaminat Ramidinovna -
Tools for activating the intellectual potential of companies
2015 / Egoshina Olga Leonidovna -
Management of sustainable development of business structures based on the assessment of the effectiveness of the use of their resource potential
2014 / Okolnishnikova Irina Yuryevna, Shevrov Vlad Yuryevich -
Assessment of the resource potential of a trade organization is the most important condition for its competitiveness
2015 / Nikolaeva Tamara Ivanovna -
Development of a system for managing the labor potential of a manufacturing business in the context of implementing an import substitution strategy
2015 / Garanina Marina Petrovna
The article presents theoretical premises that consider organizational potential as the ability of an organization to create constructions of resources for manufacturing products and maintaining key values. The author argues a possibility of using organizational potential as a means of managing sustainability of an industrial enterprise based on its properties, forms and functions. In order to apply organizational potential in this capacity, the author describes the laws of its formation, functioning, and development; offers a model of organization potential functioning; determines the essence of organizational potential management, and develops an appropriate mechanism that includes cycles of operational, tactical, and strategic management with the help of specialized technologies. A set of indices of productivity for the assessment of sustainability organization and compound indices of the state and effectiveness of organizational potential are offered and grounded. It is proven that development of productivity of organizational potential is implemented through resource potentials of organization (production, financial, labor, and market). Application of the aforementioned theoretical assumptions provides sustainable functioning of an industrial enterprise by means of harmonizing economic results with indices and instruments of organizational activity, ensuring their achievement.
The text of the scientific work on the topic "Organizational potential as a means of managing the sustainable functioning of industrial organizations"
UDC 658.338 DOI: 10.14529/et170317
ORGANIZATIONAL CAPACITY AS A MEANS OF MANAGING THE SUSTAINABLE FUNCTIONING OF PRODUCTION ORGANIZATIONS
E.P. Tretyakova, M.S. pitchers
South Ural State University, Chelyabinsk, Russia
The article presents the theoretical provisions that reveal the organizational potential as the ability of an organization to create a resource structure for the production of products and the maintenance of key values. By considering the properties, forms and functions of the organizational potential, the possibility of its application as a means of managing the sustainable functioning of production organizations has been established. To use the organizational potential in this capacity, the laws of its formation, functioning and development have been established, a model of the functioning of the organizational potential has been developed, the essence of organizational potential management has been determined, and an appropriate mechanism has been developed, including cycles of operational, tactical and strategic management using specialized technologies. A set of productivity indicators for assessing the sustainability of the functioning of production organizations, as well as summary indicators of the state and effectiveness of organizational potential, has been proposed and justified. It has been established that the formation of the productivity of the organizational potential occurs through the formation of the resource potentials of the organization (production, financial, labor and market). The application of the above theoretical provisions makes it possible to ensure the sustainable functioning of production organizations by harmonizing economic results with the indicators and means of organizational activity that ensure their achievement.
Key words: organizational potential of the organization; sustainable functioning; resource potentials; productivity; control technology.
AT modern conditions the growing uncertainty of the business environment, the issues of maintaining the sustainable functioning of production organizations are of particular relevance. The traditional way of increasing profits by reducing costs does not always give the desired result, since in a competitive environment, reducing the costs of manufacturing organizations below a certain level is problematic. Therefore, the profitability of organizations is ensured by increasing income by expanding the range or constantly updating products, expanding the geography of sales, providing services, changing work with personnel, which requires the use of different forms of organizing activities, procedures and technologies for their creation.
Thus, the sustainable functioning of production organizations is achieved by organizational management that ensures that organizations are appropriate to their business environment through organizational activities. However, spontaneous organizational decisions may have a number of disadvantages, including fragmentation and imbalance, lack of a single direction of action, their possible inconsistency with the state of the business environment, the presence of hidden unused reserves of an organizational nature. The solution to these problems, in our opinion, is the directed formation and application of organizational potential as the ability of an organization to organize activities, which consists in the selection
re and combination of compatible components based on the developed order of construction and establishment of links between components to ensure the strength of the system being created. This gives reason to consider the essence of the organizational potential of the organization and explore the possibility of using it as a means of maintaining the sustainable functioning of production organizations. To do this, a number of tasks should be solved: to state the author's idea of the essence of organizational potential in comparison with the prevailing ideas; identify and reveal the functions and basic processes of organizational potential as a system; substantiate the author's view on the essence of organizational capacity management; build and justify an adequate mechanism for managing organizational capacity to maintain the sustainable functioning of organizations.
Basic concepts I. Ansoff, as the founder of the concept of organizational potential, called organizational potential the total capabilities of linear and functional managers, expressed in terms of the amount of work that can be performed by general management. As the concept of strategic management developed, ideas about the essence of organizational potential also changed. Modern authors give different interpretations of this concept: the order of placement of elements of the total potential in time and space; organization system
labor and production; the possibility of bringing all interrelated and interdependent resources of the organization in full compliance with the chosen strategy; reserves extracted by directional change in the organization. These definitions reflect only certain aspects of organizational potential and do not allow to fully reveal its nature. Therefore, based on modern management concepts, we have proposed the following definition: "The organizational potential of an organization is its ability to form a resource structure, united by a focus on producing products and maintaining key values" .
As an analysis of the literature has shown, the key values of the vast majority of Russian production organizations are aimed at maintaining sustainable functioning, which determines the purpose, main function organizational capacity of these organizations.
To substantiate the organizational potential as a means of managing the sustainable functioning of production organizations, we will clarify some concepts. According to the provisions of the resource approach, the ability of an organization to perform certain activities is expressed in procedures and algorithms of actions, and most importantly, in the principles and means of their creation. In the theory of organization, stability is the ability of a system to function in states close to equilibrium, under conditions of external and internal influences. Functioning in a general sense is defined as the process of performing a function determined by the purpose of the system, while maintaining the achieved level of organization and the main parameters of the organization. Concretizing the definition, a group of MSTU researchers proposed to consider the sustainable functioning of an organization as the ability to maintain or increase the volume of sales of products, works or services for a long time with various changes in infrastructure and with fluctuations in consumer demand.
Considering that, according to modern scientific views, the products of an organization are considered not only goods and services, but also knowledge, corporate culture, patterns of behavior in the business environment, etc., sustainable functioning will be understood as the preservation of the main processes and acceptable parameters of the organization in combination with adaptation to changes in the business environment due to the flexibility of supporting processes. In this regard, we believe that for an organization, as an economic system, sustainable functioning should be expressed in terms of profitability and compliance with the state of the business environment.
The concept of "value" is used by us in
the meaning of "priorities and standards of managerial activity", which are the criteria for the rationality of decisions made. We believe that in the conditions of uncertainty and dynamism of the business environment, it is the values that become stable strategic guidelines for the organization, and the goals are the means of measuring and controlling them.
According to the author's view, organizational resources form the basis of organizational potential, which, according to the homogeneity of components, can be grouped into the following groups: intellectual property, management system, corporate culture, information technology, external relations. The formation of organizational potential, as an ability, is carried out by searching, selecting and reusing a combination of organizational resources, subject to the conditions arising from the principles of building systems: value orientation, complementarity and interaction of organizational resources among themselves.
The essence of organizational potential as a system
We believe that the organizational potential in the process of formation takes on different forms: a system of organizational resources, a model of the organization's behavior and a quantitative expression of organizational potential (Fig. 1).
A behavior model is a dynamic form of organizational potential, a set of principles and methods of interaction between members of an organization and with objects of the business environment regarding the attraction, combination and use of resources. We consider the indicator of its state as a quantitative expression of the organizational potential. The sequence of occurrence and structural differences of these forms allow us to call them morphological forms.
Based on the author's definition of organizational potential, its functions can be distinguished: structuring, integrating, stabilizing, communicative, adaptive and developing. The structuring function consists in the selection and specialization of the monetary, material and property, labor and external resources involved in the production. information resources. This makes it possible to ensure their complementarity as a condition for interaction and integration in the course of product creation. Through the communicative function, links are established between the participants of the organization, as well as between the organization and the business environment. Thanks to the stabilizing function, a certain order of resource usage is maintained. The adaptive function ensures the current compliance of the organization with the state of the business environment, and the developing function ensures the strategic
Organizational Resources Conditions Organizational
Intellectual property -G> Correspondence of organizational resources with the key values of the organization Complementarity of organizational resources Interaction of organizational resources / System \ / organizational \ \ resources /
Control system
/ / Model \\ 1 / behavior \ ] 1 \ organization / 1
Corporate culture -( >
Information Technology\/-*-\/ Y Indicator of the state of \ \niya organizational/ \ potential / potential
External links
Rice. 1. Formation of the organizational capacity of the organization
compliance of the organization with the business environment through the restructuring of organizational capacity.
The management of the organizational potential of an organization should be based on the laws of its functioning and development, taking into account the influence of the business environment. We understand the functioning of the organizational potential as a process of its interaction with the resources involved in production, as a result of which products of a material and intangible nature are formed, which have a commercial and non-commercial nature (Fig. 2).
Marketable products give the organization a market and economic result. Organizational potential, as non-commercial products, is an organizational result, otherwise the ability of an organization to involve resources in a new economic turnover. This means that the impact of organizational capacity on the economic and market performance of the organization is the result of both single and multiple transformations. To develop a mechanism for managing organizational potential, let's consider the process of functioning in more detail. At the selection stage, the organizational potential acts as a kind of “filter”, with the help of which resources are selected based on criteria defined by the organization’s key values.
The structuring stage is characterized by a more active interaction of organizational potential with selected resources through the methods of differentiation, specialization, hierarchization, decomposition, integration, combination, shaping, formalization using rules and documents. As a result of structuring, the resource potentials of the organization (financial, production, labor and market) are formed. Resource potentials are the specific abilities of an organization
tion to the production of products in demand by the market with the help, respectively, of monetary, material and property, human and external information resources. Resource potentials, in our opinion, consist of components that are heterogeneous in material composition and role in production: structured resources, methods, tools, procedures and technologies for managing them. The formation of resource potentials proceeds through the mechanisms of selection and repetition of successful experience or through the mechanism of imitation. Selection includes consideration and analysis alternative ways combining the organizational potential with the resources involved by the organization, assessing their compatibility and regulating the best option selected according to the established criteria. The simulation identifies, tests and selects industry-specific organizational forms, structure, technology.
The stage of transformation consists in the transformation of resource potentials into products of material and intangible nature.
The development of organizational capacity, according to systemic ideas, is associated with its life cycle. The life cycle of organizational potential is the period of time during which an acceptable level of profitability and compliance of the organization with the state of the business environment is ensured. The introduction of the concept of "life cycle" is due to the way the organizational capacity is formed. The stages of the life cycle are traditional: origin, growth, maturity and extinction. Inception means the selection of organizational potential components empirically. In the course of harmonization of components, the organizational potential grows, at the stage of maturity it stabilizes at the maximum level due to complementarity
Rice. 2. Model of the process of functioning of the organizational potential of the organization of the enterprise
components and the fit of the organization to the business environment. Fading occurs when the organizational potential of the business environment does not match due to the structural shifts that have arisen in it.
Development of a mechanism for managing the organizational potential of the organization
We propose to understand the management of the organizational potential of a production organization (OPPO) as a set of processes of direct and indirect impact on the organizational potential that ensure the sustainable functioning of the organization. Depending on the scale and complexity of tasks, the processes of operational, tactical and strategic management can be distinguished. We propose to consider operational management as the preservation of organizational capacity by monitoring its state and functioning. Tactical management, in our opinion, should additionally provide for the possibility of regulating and correcting the state and application of organizational potential. Strategic is the process of managing the life cycle of organizational capacity, in which we distinguish 3 phases: building, maintaining and transforming organizational capacity (Fig. 3).
We believe that each phase of the life cycle is autonomous, has a particular result, includes a number of stages, is characterized by a balanced toolkit and a certain composition of participants. The building phase consists of creating value
but-oriented structure of organizational potential and bringing its characteristics to the desired level. Building organizational capacity is carried out taking into account the state of the business environment and the results of the previous activities of the organization. The result of this phase is the formed organizational potential that meets the key values of the organization. The maintenance phase consists in maintaining the structure and productivity of the organizational potential by monitoring, analyzing, regulating (correcting) its state and applying it. The transformation phase means the formation of a new structure of organizational capacity based on the new core values of the organization, which is the beginning of the next life cycle.
Strategic management begins with an analysis of the business environment and the development of core values. We consider market, economic and organizational values to be the key ones. Market value consists in the organization's compliance with the state of the business environment, economic value in profitability. Organizational values reflect priorities in the management of attracted resources. Considering the key values as strategic guidelines of the organization, we can formulate the requirements for the complex of their meters: perspective orientation; effectiveness; sensitivity to changes in the business environment; the clarity of the content of indicators; ease of calculation
Rice. 3. Model of the process of strategic management of the organizational potential of a production organization
and the availability of information; the ability to track indicators online. Based on these requirements, we consider sales growth and market capitalization as indicators of market value. As indicators of economic value, we offer profit before taxes and net cash flow.
Sales growth reflects an organization's ability to create and retain customers for a product. The high importance of sales growth is noted by foreign and domestic scientists, based on the results of empirical research. Some see sales growth as a substitute for value added. Others believe that growth in sales precedes the growth of assets and the number of employees, which is subsequently accompanied by an increase in market share and profits. But everyone agrees that rapid growth can cause financial difficulties and even bankruptcy. Therefore, one of the strategic objectives is to ensure a balanced and sustainable growth in sales, allowing you to maintain profitability and financial policy organizations . Market capitalization reflects the response of investors to the behavior of the organization in the market. Profit and net cash flow characterize the organization's ability to use the demand for products in their economic interests. All these indicators are called indicators of productivity. Organizational meters
values and effectiveness of organizational potential management, we offer summary indicators: a composite resource index (CIR), which reflects the state of organizational potential, and a composite process index (CIP), which reflects the results of its application.
The nature, scale of management tasks and the requirements for the efficiency of their implementation determine the format of control. Operational management should include monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of organizational capacity management through performance indicators. In the context of tactical management, we propose to use additionally consolidated indices of organizational potential and indicators of the organization's resource potentials for control. The formation of composite indices is proposed to be carried out on the basis of the indicator method. In the course of strategic management, it is required to expand the range of benchmarks by including, along with indicators, private indicators that characterize the state and effectiveness of the use of organizational potential, which are selected on the basis of the organization's key values.
Rice. 4. The mechanism for managing the organizational potential of a production organization
Based on the previously obtained results, we believe that organizational potential management should be carried out with the help of management technologies, since, due to the complementarity of the components, it is the technologies that make it possible to ensure the reliability and cost-effectiveness of the result. For strategic management, we propose to use technologies specialized in the phases of organizational potential life cycle management (technologies for building, maintaining, transforming). The building technology is aimed at building organizational capacity in accordance with the core values of the organization. Maintenance technology should ensure the preservation of organizational capacity by monitoring, analyzing, regulating and correcting its state and functioning in accordance with the basic values of productivity indicators, therefore it is also proposed as a tactical management tool. Regulation is defined as the elimination of deviations in the state and functioning of organizational capacity that exceed acceptable limits. Correction is considered as the improvement of the components of the organizational potential while maintaining the key values of the organization. The technology of transformation is aimed at restructuring the organizational capacity in accordance with the new core values of the organization.
Given the dominance of sales growth among productivity indicators, we believe that an organization operates sustainably if there is an increase or maintenance of profit before taxes, net cash flow and market capitalization at a given level of sales growth. The acceptable level of variability in performance indicators is determined by the management of the organization.
Conclusion
In modern economic conditions one of the dominants in the management of production organizations is the maintenance of sustainable functioning. A rational way to solve this problem, according to the authors, is to create a value-oriented organizational potential and use it as a means of managing the sustainable functioning of a production organization.
To substantiate this assumption, the author's idea of organizational potential has been developed in the light of modern concepts of strategic management, the patterns of its formation, functioning and
development. On this basis, the essence of organizational potential management is determined, a management mechanism and specialized management technologies are proposed.
We believe that the developed theoretical provisions make it possible to create a methodology for measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of organizational capacity management, which makes it possible to link the economic results of organizations with organizational performance indicators and prove the possibility of using organizational capacity as a means of managing the sustainable functioning of production organizations.
Literature
1. Christensen, K.M. Organizational response to the challenge of "disruptive" technologies / K.M. Christensen, M. Overdorf // Russian Journal of Management. - 2004. - No. 4. - S. 97-112.
2. Ansoff, I. Strategic management / I. Ansoff. -M.: Economics, 1989. - 519 p.
3. Pavlova, A.V. Organizational potential in the management of the firm / A.V. Pavlova. - Kazan: Kazan state. un-t im. IN AND. Ulyanov-Lenina, 2003. - 135 p.
4. Zhigunova, O.A. Theory and methodology of analysis and forecasting of the economic potential of the enterprise: monograph / O.A. Zhigunov. -M.: Publishing House "Finance and Credit", 2010. - 140 p.
5. Fedorova, N.N. Organizational structure and controlling system at the enterprise /N. N. Fedorova, V.V. Zolotov // Director's consultant. - 2003. - No. 3. - S. 8-15.
6. Simon, H.A. Organizations and Markets? / H.A. Simon // Journal of Economic Perspectives. -1991. - No. 5. - P. 84-113.
7. Tretyakova, E.P. Methodology for the formation of the organizational potential of the company /E.P. Tretyakov. - Chelyabinsk: Publishing Center of SUSU, 2012. - 150 p.
8. Strategic management of the organizational and economic sustainability of the firm: logistic-oriented business design / ed. A.A. Kolobova, I.N. Omelchenko. - M.: Publishing House of MSTU, 2001. - 599 p.
9. Laptev Yu.V. Strategies for the growth of Russian MNEs: testing by the crisis / Yu.V. Laptev // Bulletin of St. Petersburg University. -2010. - Ser. 8, no. 2. - S. 3-23.
10. Litovchenko, S. Top managers Russian companies outlined the key management tasks of the near future / S. Litovchenko, A. Dynin // Management of growth: ideas and technologies: collection of articles. articles. - M.: Alpina Publisher, 2002. - 280 p.
11. Yudanov, A. History and theory large enterprise(view from Russia) /A. Yudanov // World economy and international relations. -2001. - No. 7. - S. 23-33.
12. Tees, D.J. The dynamic capabilities of the firm and strategic management/ D.J. Tees, G. Pisano, E. Shuen // Bulletin of St. Petersburg State University. - 2003. - Ser. 8, no. 4. - S. 133-185.
13. Theory of organization: a textbook for universities / ed. V.G. Aliyev. - M.: Economics, 2003. - 431 p.
14. Kleiner, G.B. Enterprise strategy / G.B. Kleiner. - M.: Publishing House "Delo" ANKh, 2008. -568 p.
15. Galukhina Ya.S. Russian big business in 2000-2005: the main directions of transformation and development / Ya.S. Galukhina, Ya.Sh. Pappe //Problems of forecasting. - 2006. - No. 3. - S. 23-41.
16. Shirokova, G.V. Growth factors of Russian entrepreneurial firms: results of empirical analysis / G.V. Shirokova, A.I. Sha-
Talov // Bulletin of St. Petersburg University. - 2009. - Ser. S, no. 2. - S. 3-31.
17 Shetty, Y.K. New Look at Corporate Goals. /Y.K. Shetty // California Management Review. -1979. - V. 22, No. 2. - P. 71-79.
1S. Palepu, K. Business Analysis and Valuation. Using Financial Statements // K. Palepu, P. Healy, V. Bernard. - South Western College Publishing. Thompson Learning, 2000. - 325 p.
19. Higgins, R.C. Analysis for Financial Management /R.C. Higgins. - Irwin McGraw-Hill, 2001. - 4S0 p.
20. Tretyakova, E.P. Management technologies as a way to formalize organizational processes / E.P. Tretyakova // Bulletin of ISTU. -2013. - No. 1. - S. 206-211.
Tretyakova Elena Petrovna, Candidate of Technical Sciences, Associate Professor, Associate Professor of the Marketing Department, South Ural State University (Chelyabinsk), [email protected]
Kuvshinov Mikhail Sergeevich, Doctor of Economics, Associate Professor, Professor of the Department of Finance, Money Circulation and Credit, South Ural State University (Chelyabinsk), [email protected]
DOI: 10.14529/em170317
ORGANIZATIONAL POTENTIAL AS A MEANS OF MANAGING SUSTAINABLE FUNCTIONING OF INDUSTRIAL ORGANIZATIONS
E.P. Tretyakova, M.S. Kuvshinov
South Ural State University, Chelyabinsk, Russian Federation
The article presents theoretical premises that consider organizational potential as the ability of an organization to create constructions of resources for manufacturing products and maintaining key values. The author argues a possibility of using organizational potential as a means of managing sustainability of an industrial enterprise based on its properties, forms and functions. In order to apply organizational potential in this capacity, the author describes the laws of its formation, functioning, and development; offers a model of organization potential functioning; determines the essence of organizational potential management, and develops an appropriate mechanism that includes cycles of operational, tactical, and strategic management with the help of specialized technologies. A set of indices of productivity for the assessment of sustainability organization and compound indices of the state and effectiveness of organizational potential are offered and grounded. It is proven that development of productivity of organizational potential is implemented through resource potentials of organization (production, financial, labor, and market). Application of the aforementioned theoretical assumptions provides sustainable functioning of an industrial enterprise by means of harmonizing economic results with indices and instruments of organizational activity, ensuring their achievement.
Keywords: organizational potential of an organization; sustainable functioning; resource potentials; productivity; management technology.
1. Kristensen K.M., Overdorf M. . Rossiyskiy zhurnal management, 2004, no. 4, pp. 97-112. (in Russian)
2. Ansoff I. Strategicheskoe upravlenie. Moscow, 1989. 519 p.
3. Pavlova A.V. Organizatsionnyy potentsial v upravlenii deyatel "nost" yu firmy. Kazan", 2003. 135 p.
4. Zhigunova O.A. Teoriya i metodologiya analiza i prognozirovaniya ekonomicheskogo potentsiala predpriyatiya. Moscow, 2010. 140 p.
5. Fedorova N.N., Zolotov V.V. . Konsul "tant direktora, 2003, no. 3, pp. 8-15. (in Russ.)
6. Simon H.A. Organizations and Markets? Journal of Economic Perspectives, 1991, no. 5, pp. 84-113. (in Russian)
7. Tret "yakova E.P. Metodologiya formirovaniya organizatsionnogo potentsiala kompanii. Chelyabinsk, 2012. 150 p.
8. Kolobov A.A., Omel "chenko I.N. (Eds.) Strategicheskoe upravlenie organizatsionno-ekonomicheskoy ustoychivost"yu firmy: logistikoorientirovannoe proektirovanie biznesa. Moscow, 2001. 599 p.
9. Laptev Yu.V. . Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta, 2010, ser. 8, iss. 2, pp. 3-23. (in Russian)
10. Litovchenko S., Dynin A. Top-managery rossiyskikh kompaniy oboznachili klyuchevye upravlencheskie zadachi blizhayshego budushchego. Moscow, 2002. 280 p.
11. Yudanov A. . Mirovaya ekonomika i mezhdunarodnye otnosheniya, 2001, no. 7, pp. 23-33. (in Russian)
12. Tis D. J., Pisano G., Shuen E. Dynamic capabilities and strategic management. Strategic Management Journal, 1997, vol. 18, no. 7, pp. 509-534. DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0266(199708)18:7<509::AID-SMJ882>3.0.CO;2-Z
13. Aliev V.G. (Ed.) Teoriya organizatsii. Moscow, 2003. 431 p.
14. Kleyner G.B. Strategiyapredpriyatiya. Moscow, 2008. 568 p.
15. Galukhina Ya.S., Pappe Ya.Sh. . Problemyprognozirovaniya, 2006, no. 3, pp. 23-41. (in Russian)
16. Shirokova G.V., Shatalov A.I. . Vestnik Sankt-Peterburgskogo universiteta, 2009, ser. 8, iss. 2, pp. 3-31. (in Russian)
17 Shetty Y.K. New Look at Corporate Goals. California Management Review, 1979, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 71-79. DOI:10.2307/41165322
18. Palepu K., Healy P., Bernard V. Business Analysis and Valuation. Using Financial Statements. Southwestern College Publishing. Thompson Learning, 2000. 325 p.
19. Higgins R.C. Analysis for Financial Management. Irwin McGraw-Hill, 2001. 480 p.
20. Tret "yakova E.P. . VestnikIrGTU, 2013, no. 1, pp. 206-211. (in Russ.)
Elena P. Tretyakova, Candidate of Sciences (Engineering), Associate Professor of the Marketing Department, South Ural State University, Chelyabinsk, [email protected]
Mikhail S. Kuvshinov, Doctor of Sciences (Economics), Associate Professor, Professor of the Department of Finance, Money Circulation and Credit, South Ural State University, Chelyabinsk, [email protected]
Received b June 2017
CITATION SAMPLE
Tretyakova, E.P. Organizational potential as a means of managing the sustainable functioning of industrial organizations / E.P. Tretyakova, M.S. Kuvshinov // Bulletin of SUSU. Series "Economics and Management". - 2017. - V. 11, No. 3. - S. 126-134. BO!: 10.14529/et170317
Tretyakova E.P., Kuvshinov M.S. Organizational Potential as a Means of Managing Sustainable Functioning of Industrial Organizations. Bulletin of the South Ural State University. Ser. Economics and Management, 2017, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 126-134. (in Russ.). DOI: 10.14529/em170317
Theory of organizational potential. In the early 1970s, the American scientist Igor Ansoff put forward a number of new ideas regarding approaches to understanding and developing organizational management structures. He considers an industrial organization as a certain system that interacts with sources of resources and the external environment (sales markets, competitors, government, etc.).
Based on this, two historical approaches to the formation of organizational structures stand out.
The first of these - the structural approach - was characteristic of the period before the Second World War. The main emphasis in it was placed on the internal structure of firms, the division of functions and the rationalization of management. At its core, the approach was static, since it did not take into account the dynamics of changes in organizational structures under the influence of external factors.
The second, dynamic approach was most widely used in the post-war period. It focuses on the analysis of the firm's links with the environment in which it operates and with sources of resources. The dynamic approach is illustrated by the model of the firm presented in fig. 3.
Within the framework of this approach, the analysis of managerial problems is carried out in two stages. On the first one, the firm is considered in conditions of stable external relations (static aspect). The organizational problems that arise in this case are of an operational nature.
At the second stage, the impact on the organization of changes in the external environment (dynamic aspect) is studied. Organizational problems arising in connection with this, Ansoff calls strategic.
Ansoff believes that the main task of the top management of a modern firm is to solve strategic problems in a changing external environment. One of the main theses of the dynamic approach is the existence of a close relationship between the nature of external relationships and the behavior of the firm, on the one hand, and its internal organization- with another.
Ansoff emphasizes that any organization is a complex collection of a large number of interrelated elements.
The most important of them are: leaders, structure, information, systems and procedures, technological processes, values, organizational potential. A large set of these elements represents organizational capacity.
It is most expedient to start changing the organizational potential with people, with managers. This is followed by a change in the value system operating in the company, the restructuring of information flows, other elements.
It is believed that the basis of organizational potential is the so-called culture of the organization (the totality of managerial personnel, value systems, systems and procedures).
This part of the organizational capacity is most affected by the chosen strategy of the firm. There are cases when a small change in strategy may require a radical restructuring of the culture of the organization and when a change in strategy requires little or no change in the culture of the organization, and, consequently, organizational capacity. However, most often, changes in strategy are associated with certain changes in organizational capacity. The very nature of the transition essentially depends on the specific conditions. Within the framework of the theory under consideration, the influence of the product life cycle on the strategy for changing organizational capacity is revealed.
The theory outlined above is applicable only to organizations that are sensitive to all changes in the external environment. For each specific case, the optimal frequency of organizational restructuring should be established. The process of change itself is determined by external conditions. Experiments have been carried out when several possible management structures are worked out in advance in an organization and one of the options is selected depending on the conditions. Moreover, the choice of one or another variant can be carried out on a computer using formal methods.
The company management model (Table 2) shows that, depending on external conditions and the nature of the problems being solved, top management should focus on quite specific points indicated in the matrix.
Table 2 - The model of top management of the firm
|
Sustainable external conditions (operational issues) |
Changing external conditions (strategic issues) |
|
|
Type of activity Character Problems |
Making a profit (realization of potential) |
Building strategic capacity |
|
Implementation of the market strategy |
Strategic Capacity Development (1) |
|
|
Interior |
Economical use of resources |
Organizational Capacity Development (2) |
Note: Aggregates (1) and (2) represent the full potential.









Quality requirements
Peat resources Milling peat extraction
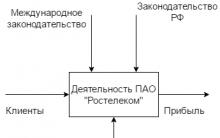
Closed Joint Stock Company Transtelecom
Setting up Wi-Fi equipment
Pasteurization drawer for the selection of "heads" during rectification