Enterprises, being business entities, have their own financial resources and have the right to determine their financial policy.
The financial policy of an enterprise is a set of methods for managing the financial resources of an enterprise aimed at the formation, rational and efficient use of financial resources.
Enterprises must actually become truly financially stable, economic structures that effectively operate according to the laws of the market.
The purpose of developing the financial policy of an enterprise is to build an effective financial management system aimed at achieving the strategic and tactical goals of the enterprise.
The strategic objectives in the development of financial policy at the enterprise are:
capital structure optimization and provision financial stability enterprises;
profit maximization;
achieving transparency (not secrecy) financially economic activity, ensuring the investment attractiveness of the enterprise;
¦ the use of market mechanisms by the enterprise to attract financial resources(commercial loans, budget loans on a repayable basis, issuance of securities, etc.).
Tactical financial tasks are individual for each enterprise. They arise from strategic objectives, tax policy, opportunities to use the company's profits for the development of production, etc.
To help enterprises to develop financial policies have been prepared in due time Guidelines former Ministry of Economy Russian Federation 1.
The main areas of development of the financial policy of the enterprise include2:
analysis of the financial and economic state;
1 See: Reform of enterprises (organizations): Guidelines. M.: Os89, 1998.
2 See: ibid.
development of accounting policy;
development of credit policy;
management of working capital, accounts payable and receivable;
cost management (costs) and choice of depreciation policy;
dividend policy;
7) financial management. Let us characterize these directions in more detail.
1. An analysis of the financial and economic state is the basis on which the development of financial policy is built.
Attention is paid not only to methods financial analysis, but also the study of the results obtained and the development of management decisions.
The main components of the financial and economic analysis of the enterprise's activities is the analysis of financial statements, including horizontal, vertical, trend analysis of the balance sheet, the calculation of financial ratios.
The analysis of financial statements is the study of the absolute indicators presented in it in order to determine the composition of the property, the financial position of the enterprise, the sources of formation own funds, the amount of borrowed funds, estimates of the amount of proceeds from the sale of products (goods, works, services). Actual reporting indicators are compared with those planned by the enterprise.
Horizontal analysis consists in comparing financial statements at the end of the year with those at the beginning of the year and previous periods. Vertical analysis is carried out in order to identify specific gravity individual balance sheet items in the overall final indicator and subsequent comparison of the result with the data of the previous period. Trend analysis is based on the calculation of relative deviations of reporting indicators for a number of years from the level of the base year.
For analytical work when developing the financial policy of an enterprise, it is recommended to calculate:
a) liquidity indicators:
overall coverage ratio;
quick liquidity ratio;
liquidity ratio when raising funds;
b) indicators of financial stability:
the ratio of borrowed and own funds;
equity ratio;
¦ the coefficient of maneuverability of own working capital;
c) indicators of the intensity of resource use:
return on net assets based on net profit;
profitability of sold products;
d) indicators of business activity:
working capital turnover ratio;
equity turnover ratio.


2. Development of an accounting policy as a system of methods and techniques of conducting accounting at the enterprise. The accounting policy for all enterprises must be carried out in accordance with the Accounting Regulations "Accounting Policy of the Organization" (PBU 1/98), approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of December 9, 1998 No. 60n.
Based on the results of the analysis of the financial and economic state of the enterprise, options for certain provisions of the accounting policy are calculated, since the number and amount of taxes transferred to the budget and extra-budgetary funds, the balance sheet structure, and the value of a number of key financial and economic indicators directly depend on the decisions made in this part. When determining the accounting policy, the enterprise has a choice of methods for writing off raw materials and materials to production, options for writing off low-value and wearing items, methods for assessing work in progress, using accelerated depreciation, etc.
Development of credit policy of enterprises. For these purposes, the analysis of the structure of the balance sheet liabilities is carried out and the share of own and borrowed funds, their ratio is calculated, the lack of own funds is determined. Based on the calculation, the need for borrowed funds is established. Sometimes it is advisable for an enterprise to take out loans even if its own funds are sufficient, if the effect of attracting and using borrowed, credit funds can be higher than the interest rate. The credit policy of the enterprise provides for the choice of a credit institution, the size of the interest rate, the terms of repayment of the loan.
Management of working capital, receivables and payables. When developing financial policy, consider that this is the main problem of financial management. The efficiency of using both own and borrowed funds depends on the correct solution of this problem. The most important factor in improving the efficiency of the use of working capital, which is taken into account when developing the financial policy of an enterprise, is the turnover of working capital.
Cost management (costs) and choice of depreciation policy. To develop a section of financial policy devoted to the management of costs (costs) of production (at industrial enterprises) and distribution costs (at enterprises in the sphere of circulation), financial analysis data on the level of costs and profitability are used. Based on the analysis, measures are developed to optimize costs (variable, fixed and mixed) and achieve break-even operation of the enterprise.
The choice of depreciation policy is of great importance in the financial policy of the enterprise. In accordance with the current legislation, an enterprise has the right to apply accelerated depreciation, i.e., to accumulate funds for the replacement of equipment at an accelerated rate, while at the same time increasing costs (cost of production). The enterprise also has the right to conduct a revaluation of fixed assets, to determine the method of calculating depreciation.
6. The dividend policy of the enterprise is developed in joint-stock companies Oh, production cooperatives, consumer societies. When choosing it, you must keep in mind the following circumstances:
¦ payment of dividends ensures the protection of the interests of members of joint-stock companies and cooperatives;
¦ high payment of dividends reduces the share of profit directed to the development of the organization.
When developing a financial policy, one should evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of dividends, find best option payment of dividends, take into account the costs of long-term development of the enterprise.
7. Financial management of the enterprise. The modern financial management system of an enterprise is based on the territory of planning, regulation and regulation.
An essential element of sustainability production activities is the system financial planning, which consists of:
budget planning activities structural divisions enterprises;
free (comprehensive) budget planning of the enterprise1.
These processes include: formation of budgets and their structure; responsibility for the formation and execution of budgets; coordination, approval and control over the execution of budgets.
Budget planning of the activities of the structural divisions of the enterprise is necessary in order to strictly save financial resources, reduce unproductive costs, as well as improve the accuracy of planned indicators (for tax and financial planning purposes), greater flexibility in managing and controlling production costs.
1 See: Reform of enterprises (organizations). Guidelines. S. 64.
The benefits of budget planning are:
monthly planning of budgets of structural divisions gives more accurate indicators of the size and structure of costs and, accordingly, profit, which is important for tax planning (including payments to state trust funds);
within the framework of monthly budgets, structural subdivisions are given greater independence in spending the economy according to the budget of the wage fund, which increases the material interest of employees;
minimization of the number of control parameters of budgets allows to reduce non-productive expenses of working time of employees of the economic services of the enterprise;
budget planning makes it possible to implement the mode of saving the financial resources of the enterprise, which is especially important for overcoming the financial crisis.
At enterprises, it is advisable to create the following end-to-end system of budgets:
payroll budget;
budget for material costs;
energy consumption budget;
depreciation budget;
other expenses budget;
budget for repayment of credits and loans;
tax budget.
Payments to state trust funds and a part of tax deductions are connected with the budget of the wage fund.
The depreciation budget largely determines the investment policy of the enterprise. In addition, the actual depreciation charges accumulated in the depreciation fund, until they are spent for their intended purpose, can be used as working capital of the enterprise.
Miscellaneous budget allows you to save on the least important financial expenses.
The budget for the repayment of loans and borrowings makes it possible to perform operations to repay loans and borrowings in accordance with the payment schedule.
The tax budget includes taxes and obligatory payments to the federal, regional and local budgets, as well as in government trust funds. It is planned for the whole enterprise.
An approximate system of enterprise budgets is given in Table. 4.2.
Note. The consolidated budget in terms of cost composition is equal to the consolidated budget (page "Total") plus the credit and tax budgets.
The given system of budgets covers the entire phase of the financial calculations of the enterprise. Budgets are developed as a whole for the enterprise and for structural divisions. At the same time, it is recommended to be guided by the principle of decomposition, which consists in the fact that each budget of a lower level is a detailed budget of a higher level.
The consolidated budget is compiled on the basis of data from functional budgets and consists of revenue and expenditure parts. When forming the budget, priority areas of expenditure are determined, among which are: wages; costs for the purchase of materials, components, etc., necessary for the implementation of the production program; payments to state trust funds, taxes.
Drawing up the consolidated budget of the enterprise, as well as forecasting the bank interest rate and the solvency of customers, make it possible to determine the amount of profit necessary to ensure the solvency of the enterprise.
The consolidated budget of the enterprise consists of revenue and expenditure parts, the main articles of the consolidated budget are shown in Table. 4.3.


The revenue part of the budget is planned on the basis of the plan for sales (implementation) of products and financial receipts from other sources. In addition, balances on the company's accounts are taken into account.
The expenditure part of the consolidated budget is planned on the basis of: the schedule of tax payments; payroll budget; the schedule of payments to state trust funds, the budget of material costs, the schedule of repayment of loans and other budgetary expenses.
The essence of politics is the relationship between social groups, classes, nations regarding the establishment, retention, strengthening and implementation of state power.
The subjects of politics are individuals, classes, the elite, the state, parties, trade unions and other social communities. According to the chosen criterion, politics is distinguished: external and internal; economic, social, national, military, cultural; local, regional, national, international, world (global); strategic (long-term) and tactical (current).
An integral part of economic policy is financial policy, which, by its specific methods and methods, contributes to the achievement of goals and the fulfillment of the tasks set by economic policy. In the process of conducting financial policy, it is especially important to ensure its relationship with other constituent parts economic policy - credit, price, monetary.
Financial policy - the activities of the state for the purposeful use of finance.
The purpose of financial policy is the most complete mobilization and efficient use of financial resources necessary to meet the needs of society.
- development of scientifically based concepts for the development of finance;
- determination of the main directions for the use of finance for the future and the current period;
- implementation of practical actions aimed at achieving the set goals.
Financial policy receives legal registration in financial law. Financial right - a set of legal norms governing social relations arising in the process of formation, distribution and use of state and local government funds necessary for the implementation of their tasks.
Depending on the duration of the period and the nature of the tasks to be solved, financial policy is divided into financial strategy and financial tactics.
Financial strategy- a long-term course of financial policy, designed for the future and providing for the solution of large-scale tasks determined by the economic and social strategy, and concerning important major changes in the financial mechanism, the proportions of the distribution of financial resources.
Financial tactics is aimed at solving the problems of a particular stage in the development of society by changing the ways of organizing financial relations, regrouping financial resources. Financial tactics provides for solving the problems of the current period (within a year or less), is flexible and mobile.
Main types of financial policy the following: classical 1 , regulatory, neoconservative, planning and distribution, monetarist.
Classical financial policy based on the works of the classics of political economy A. Smith (1723-1790) and D. Ricardo (1772-1823), who believed that the wealth of a nation is created not in trade (here the monetary form of value changes to its commodity form), but in production. Production is based on natural laws, and therefore does not need state intervention through state funds. The state is a "night watchman" protecting the world, property and law and order, but by no means an economic entity. The state can be entrusted with the management of mail, communications, the construction of exorbitantly expensive railways, a few fiscal monopolies, but from everything,
From lat. sk^yush - exemplary, first-class.
that brings at least an average profit, the state must be removed. The dogma of exceptionally hard budgetary restrictions was proclaimed in the name of "healthy finances".
Regulatory financial policy is based on the economic theory of the English economist J. Keynes (1883-1946), who believed that the state should intervene in the economy and regulate its development. The main tool for intervention in the economy is government spending, while a budget deficit was allowed. The creation of some budget deficit was seen as a powerful means of stimulating economic activity. J. Keynes and his followers considered the problems of using a progressive income tax rate; application of the state credit; changing the financial management system through the allocation of separate services involved in budget planning and budget expenditures, their financing, control over the receipt of taxes, and public debt management; other options for “creating” budget deficits and “models” for the behavior of public finances.
neoconservative financial policy. In the 70s. 20th century the neoconservative strategy associated with the neoclassical direction of economic theory was taken as the basis of financial policy. This kind of economic theory does not propose to abandon state regulation, but limits state intervention in the economy and social area. The regulation of the economy is becoming multi-purpose. In addition to economic growth and employment, the state regulates money circulation, the exchange rate, social factors of the economy, and the restructuring of the economy. Under these conditions, financial policy is based on the need to reduce the volume of redistribution of national income through the financial system, reduce the budget deficit, and stimulate the growth of savings as a source of productive investment. An important role is assigned to taxes, the task is to reduce them and reduce the degree of progressiveness of taxation.
Planning and distribution financial policy aims to ensure the maximum concentration of financial resources from the state for their subsequent redistribution in accordance with the main directions of the state plan. The financial mechanism includes instruments by which all resources unused in accordance with the state plan are withdrawn from state enterprises, the population and local authorities. The planned and distributive financial policy showed its rather high efficiency in a period when the maximum concentration of financial resources was required to finance the emergency expenses of the state (during the war years, the restoration of the national economy, etc.). At the same time, the use of such a financial policy in other operating conditions that differ from the planned economy, or without emergency, can lead to negative consequences: a catastrophic shortage of cash, a decrease in the volume of consumer goods, a decline in production, an increase in import dependence, and an increase in the export of natural resources.
Monetarist financial policy relies on monetarism - the theory according to which the amount of money in circulation is a determining factor in the development of the economy. According to monetarists, money is the main sphere that determines the movement and development of production, therefore, in order to ensure the correspondence between the demand for money and their supply, it is necessary to pursue a course towards a gradual increase in money in circulation. When conducting a monetarist financial policy, the entire spectrum of economic activity of the state is reduced to financial sector, first of all, to the control of the state over the money supply, the issue of money, the amount of money in circulation and in stocks, the achievement of a balance in the state budget, mediation between business entities.
Importance of financial policy It is manifested in the fact that the correctly chosen financial policy:
- stimulates the growth of production, the rational distribution of productive forces throughout the country;
- increases the interest of the regions in the development of the economy, the use of local resources;
- contributes to the strengthening and development of economic ties with all countries of the world;
- leads to an increase in the material and cultural level of the population.
When developing financial policy, it is necessary to take into account: economic and financial opportunities of the state; domestic and international environment; domestic and foreign experience in financial construction; the history of the development of finance, the requirements of the globalization of financial processes.
The financial policy of tsarist Russia
The general concept of Russia's financial policy began to take shape in the middle of the 19th century. and by the beginning of the 20th century. has acquired a certain degree of maturity.
The initial principles in the concept of financial policy can be called the following: continuity, caution, budget balance, stability of the monetary system, centralization of funds.
The principle of succession was based on respect for traditions, for what was created by predecessors both in the field of financial theory and in practice.
Precautionary principle did not allow to make serious changes in financial policy even in extreme conditions, for example, during wars and revolutions. Everything was done in order not to destroy the financial system created in Russia by the beginning of the 20th century. with great effort and effort. This principle fully corresponded to the spirit of Russia, its fear of reforms, its conservatism. In addition to a certain benefit, this principle also brought obvious harm, expressed in restraining economic development.
The principle of budgetary balance. The Russian budget made it possible to carry out the minimum necessary expenditures, which supported the existing system of economic relations. Budget revenues for each new fiscal year calculated on a deliberately low scale. The difference between real and projected revenues was budget balances, which, accumulating, formed the so-called “free cash of the state treasury” and served as an indicator of the well-being of Russian finances. As noted by S.Yu. Witte in his report to the State Council on the state list of incomes and expenditures for 1901: “The system according to which the state should not concentrate reserve funds at its disposal is not applicable to the finances of Russia. This system would lead to a breakdown in the state economy, would make it difficult to provide government assistance to the population in cases of disaster, and would be a step towards the political weakening of the Fatherland.
The principle of stability of the monetary system. Its implementation was carried out through the correspondence of the paper money supply to the gold reserve. The issuance of non-gold-backed banknotes was severely limited.
The principle of centralization of funds. The state budget of Russia received up to 85% of all funds, while in England - 54%, Prussia - 68%. As a result of such a financial policy in Russia, by the beginning of the 20th century. a certain financial stabilization was achieved, ensuring its economic growth in a short period of time.
Financial policy in the USSR
The construction of socialist finance began only after the end of the Civil War. The economic conditions were the most difficult: a devastated country, a complete decline in the economy. The main tasks of this period were the revival of the economy, the restoration of industry and Agriculture, public sector support. Therefore, the new financial policy was built on completely different principles. Economic and political conditions dictated the need for maximum concentration of financial resources in the hands of the state.
To solve the tasks set, we developed financial methods development of the country's economy, which had no analogues in history and is directly opposite to market methods of development. If in a market economy the growth of the production sector is paid for from the funds received from the sale of consumer goods, and the scale of the economy expands as the consumer sector expands, then in the Soviet-type economy, funds for the development of production were formed directly in the sector of material production through the distribution and redistribution of the created national income ( without a stage of buying and selling in the market), and consumption grew following the increase in the possibilities of the economy.
Money circulation was understood only as the movement of cash. The sphere of cash movement reflected the distribution of cash incomes of the population, and non-cash - the distribution of means of production. Banknotes had different security. The cash ruble was provided with a relatively small amount of consumer goods and services, non-cash - with a set of means of production intended for distribution. Such a system implied the establishment of strict distinctions between the spheres of action of cash and non-cash money: it was impossible to mix, and even more so convert cash (“labor”) money into non-cash (“accountable”) money.
The main national fund was the state budget, which occupied a central position in the country's financial system, served as the main distribution mechanism, through which funds were redistributed within material production (intersectoral redistribution), financing was provided for most of the organizations in the non-productive sphere, national income was distributed between the republics, regions , districts, etc.
The developed financial policy allowed the country's economy to achieve significant success in a short time with limited material, labor and financial resources.
Already by 1930, the state sector became dominant in industry. Collective farms and state farms became the main producers of agricultural products. wholesale and retail almost completely concentrated in the hands of the state and consumer cooperatives. Tax reform 1930-1931 provided a significant reduction in the number of taxes and payments, simplified the methods of their calculation and the procedure for transferring them to the budget. Minister of Finance of the USSR A.G. Zverev wrote: “During 1938-1940, the production of the industry as a whole increased almost 1.5 times, the production of means of production - more than 1.5 times, and the growth of engineering was 76 percent. Every 10 hours (on average) we have a new industrial enterprise" one .
A very high degree of concentration and centralization of resources was achieved through the state budget of the country. During the years of the Great Patriotic War(1941 - 1945) expenditures of the state budget of the USSR amounted to 1146.8 billion rubles, of which 582.4 billion rubles. was directed to cover military expenses (50.8%). In the expenditure side of the budget, the largest share of funds for defense was achieved in 1943 - 59.5%. This can be considered the limit of military spending, since, in addition to defense, funds are needed for the national economy, socio-cultural events, administration, and for other purposes. In the first post-war decades high level concentration and centralization of resources in the country's budget remained.
Zverev A.G. Minister's Notes. M.: Politizdat, 1973. S. 212.
State in post-war years carries out a number of activities, including those related to the improvement of profit distribution methods, leaving the tax system unchanged. However, these efforts were not successful. The tasks of transferring the economy to intensive development methods and “embedding” market mechanisms turned out to be unresolved. The economy, by inertia, continued to develop largely on an extensive basis, focused on the involvement in production of additional labor and material resources. As a result, a gap was formed between social needs and the achieved level of production, between effective demand and its material coverage.
For the first time in 1989, the state budget was in deficit. It was already impossible not to recognize the serious deformation of all parts of finance - state, sectoral, regional.
By 1992, a change in political orientation had taken place in the country. The state proclaimed a course towards a market economy, which required a radical restructuring of the entire economy in general and finance in particular. Importance in this process had denationalization and the emergence of economic entities of various organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership. On site state enterprises there were cooperatives, partnerships, etc. Structural transformations caused a significant decline in production, the collapse of entire industries, and hence unemployment, social and political instability, inflation and other negative aspects of the transition period. Under these conditions, financial policy was unstable, often changed under the influence of the current moment.
Topic. Financial policy of the Russian Federation.
Financial policy: concept, goals and objectives of formation
financial mechanism
Characteristics of the main directions of financial policy
1. Financial policy: concept, goals and objectives of formation
Financial policy is a special area of state activity aimed at mobilizing financial resources, their rational distribution and efficient use for the state to carry out its functions.
It should be noted that financial policy is not limited to the principles outlined above. Financial relations in the state is a dynamic, developing system. The following are important for its functioning: ♦ financial regulation and stimulation of production; ♦ financing of scientific and technological progress; ♦ insurance protection of social production. Among the levers of state financial regulation, the main role belongs to taxes, customs duties, and tariffs. With their help, the level of profitability and the amount of cash savings of enterprises are regulated. The system of tax incentives contributes to the accelerated development of priority sectors, the renewal of fixed assets.
determination of the main directions, goals and objectives of financial policy.
formation of a financial mechanism.
financial management.
The main objectives of the financial policy are:
providing financial resources for programs implemented by the state;
establishing a rational distribution and use of resources;
achievement of financial stability and financial independence of the state;
creation favorable conditions for the functioning of business entities;
formation of the level of income, ensuring the normal reproduction of the population.
In the Russian Federation, the priority in the development of financial policy belongs to the President of the Russian Federation, who in his messages determines the main directions of the economy for the planned year and the future. (3 years)
The Government of the Russian Federation acts within the framework of this message and develops the main directions for the development of the economy and ensuring social stability. They are developing the necessary legislative acts for the implementation of financial policy.
The basis of financial policy is the strategic directions that determine the long-term and medium-term prospects for the use of finance.
At the same time, the state selects the current tactical goals and objectives of use, financial relations. When developing a financial policy, the peculiarities of the historical development of society are taken into account. It must take into account the specifics of the external and internal situation, the real economic and financial potential of the country.
Objectives of financial policy:
Fiscal policy is concerned with balancing government revenues and expenditures. (Laffer Curve)
Regulation of tax processes is carried out with the help of economic instruments. Regulation can be done spontaneously or consciously. Regulation is now a mandatory element of financial policy. Taxes, state credit, budget appropriations, etc. act as regulatory instruments.
Types of financial policy:
The policy of economic growth. It is a system of financial measures aimed at increasing GNP and increasing employment. This policy includes an increase in government spending, and a reduction in the tax burden. This policy is applied during the economic crisis. In the long term, this policy may lead to an increase in inflation. (Income goes down and Expenses goes up).
stabilization policy. It is characterized by limiting government spending and taxes, providing conditions for the formation of a balanced budget. (Expense = Income).
Business policy restriction policy. It is aimed at reducing the real volume of GNP. It is associated with a decrease in government spending and an increase in the tax burden. This policy is applied when a crisis has occurred (Expenditures decrease and Revenues increase).
2. Financial mechanism.
An important component of financial policy is the establishment of a financial mechanism.
The financial mechanism is a system established by the state: forms, types and methods of organizing financial relations.
The financial mechanism is the most dynamic part of the financial policy, its changes occur in connection with the solution of the tactical tasks of the state.
The financial mechanism is divided into:
Directive (direct impact) - is developed for relations in which the state is directly involved.
Regulatory (indirect impact) - associated with the financial relations of enterprises.
System of financial policy instruments:
Legal - regulatory legal acts, the adoption of state programs, the conclusion of international agreements.
Administrative - the procedure for registration, obtaining a license, quotas, application of state sanctions, administration of administrative measures, management of state property.
Economic instruments:
I.gr. Active-structural - this is state support, investment discounts, the use of real estate on preferential terms, public investment, public procurement.
II.gr. Fiscal-structural - these are special tax regimes, tax incentives, budget allocations, depreciation policy.
III.gr. Monetary - associated with the regulation of the money supply, interest rates, operations in the securities market and foreign exchange.
IV.gr. Instruments of antimonopoly policy, land regulation.
Characteristics of the main directions of financial policy
The financial policy includes eight main areas:
Tax policy should be based on a compromise between the interests of the state and taxpayers. Taxes should ensure that the budget receives such a volume of resources that is sufficient for the state to fulfill its functions and obligations.
budget policy provides :
determination of the share of GDP mobilized to the budget;
establishing optimal relationships between federal and regional authorities;
optimization of budget expenditures;
distribution of budget expenditures between budgets different levels;
public debt management;
determination of sources of financing the budget deficit.
Money-credit policy has the following elements:
emission policy;
national currency stabilization policy;
credit policy.
Monetary policy is implemented by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Price policy - regulation of prices and tariffs for monopoly goods and services. The pricing policy pursues the following goals:
regulation of prices for all goods and services within the country;
compensation of low domestic prices due to high external ones:
subsidizing prices in order to reduce them and conquer new sales markets (including external ones).
Customs policy is a part pricing policy, because customs fees and duties have a direct impact on the price of goods and services. It has the peculiarities of influencing the national economy, restricting or expanding access to the domestic market for imported goods and services, and restraining or encouraging the export of goods and services from the country.
Social politics includes:
development of a mechanism for the protection of the poorest segments of the population;
implementation of the pension reform, ensuring the formation of a multi-level pension system with sustainable financing;
regulation of forced migration.
Investment policy suggests:
creation of conditions for organized accumulation and investment of accumulation savings;
development of mortgage lending;
attracting foreign direct investment, etc.
International finance policy:
integration of Russia into the world financial system;
recognition of Russia as a country with a market economy;
joining international organizations (including the World Trade Organization);
settlement of external debt;
increasing the stability of the ruble exchange rate.
Politics - "the art of managing" the state, community, interstate relations) - the field of activity associated with relations between social groups, the essence of which is to determine the forms, tasks, content of the state. As applied to economic science: Policy is a set of measures and actions aimed at achieving a predetermined result.
The financial policy of the state is a set of measures and actions of the state aimed at using finance to strengthen its potential (economic, political, military, environmental, social).
An object management - all kinds of financial relations.
Subjects management - financial apparatus - organizational structures that carry out management functions.
Target government controlled finance - to provide:
- the relative balance of economic interests of the state of legal entities and individuals;
- deficit-free budget;
- stability of the national currency as a fundamental element of economic relations.
Methods state regulation include:
direct administrative impact:
- licensing of entrepreneurial activity;
- financial subsidies and subsidies for production;
- implementation of a system of measures of social guarantees and financial protection in relation to low-income segments of the population;
- application of financial sanctions against violators of financial discipline.
Indirect methods:
- formation of a competitive market environment, limiting the monopolization of the market;
- ensuring the stable functioning of settlement and payment relations in the financial sector;
- conducting an effective customs policy;
- assistance to the development of the insurance business;
- promoting the development of the capital market.
Components of financial policy
Monetary policy is a set of measures in the field of monetary circulation aimed at curbing inflation and equalizing the country's balance of payments.
Main directions:
- analysis and forecasting of the economic situation in conjunction with budget indicators;
- economically justified amount of money supply in circulation;
- methods of regulation of monetary circulation;
- achieving the convertibility of the ruble.
Credit policy- a set of economic methods and legal norms aimed at managing credit capital. Main methods:
- determination of the volume of loans provided by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation to commercial banks;
- calculation of the discount rate on loans of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- establishment of norms for required reserves placed by commercial banks with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
Since the main subject of monetary and credit policy is the Central Bank and the control levers affect both credit and monetary policy, they often talk about monetary policy. The content of monetary policy was considered in more detail in paragraph 1.8 "Monetary Policy".
budget policy- activities of the administrative apparatus for the preparation and execution of the budget of the country and regions. The main condition of the budget policy is the balance of budgets of different levels. Budget policy is closely related to tax policy.
Tax policy- system of measures of the state in the field of taxation. It is expressed in determining the volume of the tax burden on citizens and business entities and is enshrined in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Monetary policy- activities of the management apparatus for the regulation of foreign exchange operations and the management of foreign exchange resources. The area of activity is the foreign exchange market - the market of foreign freely convertible currency and the market of precious metals and stones.
Events:
- establishing the procedure for foreign exchange settlements in export-import transactions;
- establishing the procedure for exchanging the national currency for a foreign one;
- a system of measures to regulate the rate of hard currency (freely convertible currency) in relation to the national one;
- regulation of the balance of payments.
Functions of the financial management apparatus
President in accordance with the Constitution and federal laws defines the main provisions of the internal and foreign policy states, in accordance with which the financial policy of the country is built. The President issues decrees and orders on the formation and execution of the budget, off-budget funds, monetary policy, organization of settlements, regulation of foreign exchange and other financial relations, formation of financial and credit system bodies, and exercises control through the Main Control Department.
The Federal Assembly - the Parliament of the Russian Federation - is a representative and legislative body. The Federal Assembly consists of two chambers - the Federation Council and the State Duma. Considers and approves the federal budget and the report on its execution, laws on taxes, fees, non-tax payments, sets the maximum size of the state internal and external debt, adopts financial legislation (Budget Code, Tax Code, laws, etc.).
The Ministry of Finance is a federal executive body and ensures the implementation of a unified financial, budgetary, tax and currency policy in the country. Issues instructions, regulations, guidelines on the organization of financial activities. The functions of the Ministry of Finance at the regional level are performed by financial departments.
Functions of the Ministry of Finance:
- coordination of budgetary and monetary policy;
- development of the draft federal budget and ensuring its execution;
- management of the public debt of the Russian Federation, including the preparation of issues of government securities, the development of government borrowing programs;
- implementation of state financial control;
- licensing of activities of financial institutions;
- acquisition of precious metals and stones to the state fund;
- methodical management of accounting of enterprises (except for banks);
- concentration of financial resources on priority areas of socio-economic development of the Russian Federation.
The Federal Tax Service (FTS) is a federal executive body and controls the correct calculation, completeness and timeliness of taxes, fees and other payments to budget funds. Monthly submits to the financial authorities and bodies of the federal treasury information on the amounts of tax and other payments actually received.
The Federal Agency for State Property Management (Rosimushchestvo) is a federal executive body and organizes the management of state property in order to generate non-tax income - rent, income from privatization, income from enterprises owned by the state, etc. The block of shares of enterprises belongs to the state in this federal agency.
Federal customs Service(FTS of Russia) is a federal executive body and controls the receipt of customs duties, carries out inspections of economic entities on obligations to pay customs duties.
The Central Bank of the Russian Federation or the Bank of Russia is a federal executive body - it is a bank of banks, an intermediary between the state and the rest of the economy, regulates credit flows in the state, organizes and controls the activities of commercial banks. Organizes through its divisions (settlement and cash centers) the movement of funds through the interbank system. Does not conduct transactions with enterprises and the public, its clients are commercial banks and other credit institutions, as well as government organizations. The activities of the Central Bank of Russia are regulated by the Law of the Russian Federation "On the Central Bank of Russia (Bank of Russia)" of 1995.
The main goal of the activity of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation is to strengthen the positions of the ruble both within the country and abroad.
Functions of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation:
- in accordance with the legislation of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, it pursues a unified monetary policy aimed at ensuring the stability of the ruble;
- issue of cash and organization of their circulation;
- lending to commercial banks;
- establishment of rules for conducting banking operations, accounting and reporting of commercial banks;
- implementation of currency control;
- establishment of rules for non-cash payments on the territory of the Russian Federation;
- analysis and forecast of the state of the Russian economy. Instruments used by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in its activities:
- discount rate;
- required reserves - part of the resources of commercial banks deposited in an interest-free account with the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- transactions in the stock market - purchase and sale of government bonds;
- licensing of banking activities;
- foreign exchange interventions - purposeful operations of the Central Bank for the purchase and sale of foreign currency to limit the dynamics of the national currency.
Federal Treasury is a federal executive body and performs the following functions:
- organization and control of execution of the federal budget;
- cash services for the execution of budgets budget system RF (management of budget revenues and expenditures on the accounts of the Federal Treasury in the Central Bank, based on the principle of unity of the cash desk);
- preliminary and current control for conducting operations with federal budget funds;
- keeping records of operations on cash execution of the federal budget;
- service of the external debt of the Russian Federation jointly by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
- short-term forecasting and cash planning of federal budget funds and their operational management;
- providing the Ministry of Finance with operational information and reporting on the execution of the federal budget and the consolidated budget of the Russian Federation.
Accounts Chamber created by the Federal Assembly and performs the following functions:
- supervises the implementation of financial legislation,
- exercises control over the execution of revenue and expenditure items of the federal budget and extra-budgetary funds in terms of volume, structure and purpose,
- determines the efficiency and feasibility of spending public funds and use of federal property,
- conducts financial expertise of projects for the expenditure part of the federal budget, federal non-budgetary bodies,
- supervises the execution of the federal budget, regularly provides the Council of Federations and State Duma information on the execution of the federal budget.
Financial policy is a fundamental element in the financial management system. Based on the definition of finance as specific value relations for the formation, distribution, redistribution and use of the gross social product, the state, when organizing these relations, determines the main goals and objectives facing society and, accordingly, the financial system.
At all times, the main goal of financial relations, which determine their necessity among other social relations, is to ensure the continuity of the reproductive process and, above all, the reproduction of productive forces as necessary condition life, existence and development of both the individual and society as a whole. The reproduction process is a combination of various social needs, the degree of satisfaction of which depends primarily on financial capabilities, that is, on the available financial resources and on the financial potential of the state.
Therefore, the second main and enduring goal of financial relations is their organization, which would be aimed at ensuring the growth of social wealth. Achieving this goal is possible only with the effectiveness of specific forms of distribution, redistribution and use of available financial resources and the financial potential of the state. A general indicator of the effectiveness of the financial mechanism is the growth rate of the gross domestic product and national income - the main source of growth in the welfare of society.
Financial policy is an independent sphere of activity of the state in the field of financial relations. This activity is aimed at providing appropriate financial resources for the implementation of a particular state program of economic and social development.
Financial policy is the definition of goals, objectives and main directions (concepts) for the development of national finances in the context of the country's overall geopolitical and socio-economic strategy, as well as the implementation of practical measures to mobilize financial resources, distribute them and use them effectively to achieve the set long-term, medium-term and short-term goals .
The most important place among these activities belongs to the legal and organizational regulation of the forms and norms of financial relations - the development of legislation, accounting policies, organizational structure financial management.
The effectiveness of financial policy is the higher, the more it takes into account the needs of social development, the interests of all strata and groups of society, specific historical
conditions and features of life.
To no lesser extent, the success of politics depends on the qualitative development of a mechanism for coordinating and realizing the interests of various strata of society and the objective possibilities available to the state, i.e. mechanism for the conscious use of comprehensive, sometimes even opposing factors influencing the course of financial policy implementation, taking into account changes in social structure society, in the state of social consciousness and psychology.
The financial policy should be directed, first of all, to the formation of the maximum possible amount of financial resources, since they are the material basis of any transformations. Therefore, in order to determine and formulate financial policy, reliable information about financial position states.
Types and main directions of financial policy
When developing financial policy, it is fundamental that the distribution and redistribution of financial
financial resources lies:
1) the choice of subjects of distribution relations, i.e. owners and distributors of financial resources;
2) determining the degree of centralization of financial resources at the disposal of the state, depending on the functions of the state and the degree of independence legal entities and the population in meeting their needs;
3) determination of priority public needs and measures to meet them and, accordingly, priority areas for the use of financial resources;
4) choice of sources and methods of formation of financial resources.
As a rule, as a part of financial policy, budgetary and monetary policy are singled out as relatively independent.
Fiscal policy is defined by the state as:
Sources of formation of state budget revenues;
Priority directions of budget expenditures;
Permissible limits of budget imbalance;
Sources of financing the budget deficit;
The principles of the relationship between the individual links of the budget system.
In turn, as part of the budget policy, they acquire relative independence:
Tax policy;
Investment policy;
Public debt management policy;
The policy of fiscal federalism.
Tax policy determines the choice of the composition of taxes, the size of their rates, benefits and sanctions for each type of tax. At the same time, a measure of a confiscation or incentive orientation is established both for the tax system as a whole and for a separate tax.
Monetary policy is understood as ensuring the stability of monetary circulation through the management of emissions, regulation of inflation and the exchange rate of the national currency; ensuring the timeliness and continuity of settlements in the national economy and in various parts of the financial system through the regulation and regulation of the banking system; activity management financial market through the regulation of the issue and placement of state and corporate securities and the regulation of their turnover (purchase and sale rates), through a proactive increase or decrease in the refinancing rate by the Central Bank.21
In monetary policy, relative independence is acquired by:
Issuing policy;
Price policy;
Monetary policy;
Credit policy;
Interest policy;
Investment policy;
Customs policy.
It should be noted that if in the practice of budgetary relations, investments are understood as financing the growth and modernization of fixed assets, then in banking practice, investments are understood as the formation of a portfolio of securities.
International financial policy is becoming increasingly important at the end of the 20th century. It is based on the management of monetary and financial and credit relations in the field of international relations associated both with the international division of labor, with the formation and repayment of public debt, and with participation in the activities international organizations, including international financial institutions. The financial policy of such international financial organizations as the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) and others (for example, the London Club of Creditors, the Paris Club creditors).
The international financial policy of individual states, as a rule, is aimed at developing the productive forces of their country, and, accordingly, each state tries to take its weighty place in the world. international markets raw materials, goods, labor and capital.
The state protects its interests through customs and foreign exchange policy, the features of which are determined by the degree of the state's interest in expanding or reducing its exports or imports. In accordance with this, a system of customs payments or a specific customs regime is applied. The main goal of the customs and foreign exchange policy is to preserve and increase the gold and foreign exchange reserves of the state.
The state protects its interests and contributes to the growth of the authority of the country, participating in the activities of international organizations, taking part in the formation of financial funds of these organizations and in the financing of joint programs.
The financial policy of international financial organizations is aimed at providing financial assistance to states experiencing financial crisis or experiencing financial difficulties. Assistance is usually provided in the form of loans or in the form of restructuring existing external public debt.
Assistance from international financial organizations is not provided free of charge and is accompanied by a number of economic or political conditions that are not always beneficial for the borrowing country.
During the period of evolutionary development public life and a stable state structure, the internal and external financial policy of the state solves one main task - ensuring the preservation and strengthening of the system of social relations existing in the state.
During the period of revolutionary changes, political forces interested in changing the existing system pursue a policy aimed at destroying the existing system and forming new system public relations. It is difficult to overestimate the role of financial policy in critical periods in the life of society, since, first of all, there is a development
a radical redistribution of social wealth and the financial system is being rebuilt.









Quality requirements
Peat resources Milling peat extraction
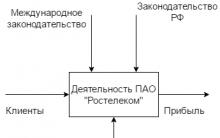
Closed Joint Stock Company Transtelecom
Setting up Wi-Fi equipment
Pasteurization drawer for the selection of "heads" during rectification