one of the forms of out-of-store sale of goods to the public by sending them on individual orders to postal parcels. The emergence of parcel shipping dates back to 1887, when the largest mail-order firms, Montgomery Ward and Sears, Roebuck & Co., were founded in the USA; the sales market in the first period of their activity was mainly agricultural. regions of the country. In pre-revolutionary Russia, the trade union arose at the beginning of the 20th century. The largest were the parcel departments at the department stores "Mur and Meriliz" (Moscow), "Alexander" (Petersburg), "Petrococci" (Odessa).
In the USSR, shopping malls organically complement the store chain in small urban and rural settlements in which it is not economically feasible to create trading network with a full range of products. Through P. t. implemented (1973) about 30% of all retail spare parts for motorcycles, scooters and bicycles, more than 5% of retail sales of books and about 3% of retail sales of records. In contrast to the structure of the turnover of a store chain, in the commodity turnover of retail stores the predominant part is accounted for by cultural, domestic and household goods (84%), while in the turnover of stores their share does not exceed 25%. The formation of the assortment of consumer goods is largely determined by the level of production of individual goods and the degree to which rational consumption norms have been achieved and the population is provided with goods (in the latter case, mainly durable goods). Along with this, the assortment of radio equipment is formed by replenishing it with goods of episodic and rare demand, which have a large number of varieties that are not interchangeable in consumption (radio components, photographic, sports, and stationery, etc.). Over 50% of parcels are sent to buyers by specialized and universal depots of the Postal Trade of the Ministry of Trade of the RSFSR, the main organization that carries out parcel posting in the USSR. In addition, P. t. The Kooppostyltorg organization, functioning in the system of the Centrosoyuz, carries out small-scale wholesale trade in supplying consumer cooperation stores (see Consumer cooperation) by sending them consumer goods by postal parcels.
P. t. develops in foreign socialist countries. In the GDR, for example, it is carried out through the "Mail Delivery House" (Versandhaus; Leipzig).
In the capitalist countries, retail shopping is regarded as an additional form of selling goods and, along with mail-order firms, it is carried out by large department stores. In the developed capitalist countries, mechanical engineering is produced by highly mechanized enterprises with a universal range of goods that use electronic computers to control technological processes. In 1973, the share of retail trade in retail trade in individual countries was: in the USA and Great Britain, ≈ 4; in the FRG, ≈ 5; in France, ≈ 1.2; in Italy, ≈ 0.5; Most large firms P. t. in Western Europe: "Neckermai", "Quelle" and "Otto Ferzand" (Germany); "La Redoubt" and "Galeries Lafayette" (France); in the USA, Sears, Roebuck & Co., Montgomery Ward, and others.
one of the forms of out-of-store sale of goods to the population by sending them to individual orders in postal parcels. The emergence of parcel shipping dates back to 1887, when the largest mail order firms, Montgomery Ward and Sears, Roebuck & Co., were founded in the USA; the sales market in the first period of their activity was mainly agricultural. regions of the country. In pre-revolutionary Russia, the trade union arose at the beginning of the 20th century. The largest were the parcel departments at the department stores "Mur and Meriliz" (Moscow), "Alexander" (Petersburg), "Petrococci" (Odessa).
In the USSR, retail trade organically complements the store chain in small urban and rural settlements, in which it is not economically feasible to create a trade network with a full range of goods. (1973) about 30% of all retail sales of spare parts for motorcycles, motor scooters, and bicycles, more than 5% of retail sales of books, and about 3% of retail sales of gramophone records are sold through retail trade (1973). In contrast to the structure of the turnover of a store chain, in the commodity turnover of retail stores the predominant part is accounted for by cultural, domestic and household goods (84%), while in the turnover of stores their share does not exceed 25%. The formation of the assortment of consumer goods is largely determined by the level of production of individual goods and the degree to which rational consumption norms have been achieved and the population is provided with goods (in the latter case, mainly durable goods). Along with this, the assortment of radio equipment is formed by replenishing it with goods of episodic and rare demand, which have a large number of varieties that are not interchangeable in consumption (radio components, photographic, sports, and stationery, etc.). Over 50% of parcels are sent to buyers by specialized and universal bases of the Postal Trade of the Ministry of Trade of the RSFSR, the main organization that carries out P. t. in the USSR. In addition, P. t. is carried out by parcel departments of the Gostiny Dvor department store (Leningrad), the Central Department Store of Voentorg (Moscow), the Book by Mail and Seeds by Mail stores. The Kooppostyltorg organization, functioning in the system of the Centrosoyuz, carries out small-scale wholesale trade in supplying consumer cooperation stores (see Consumer cooperation) by sending them consumer goods by postal parcels.
P. t. develops in foreign socialist countries. In the GDR, for example, it is carried out through the "Mail Delivery House" (Versandhaus; Leipzig).
In the capitalist countries, retail shopping is regarded as an additional form of selling goods and, along with mail-order firms, it is carried out by large department stores. In the developed capitalist countries, P. t. is produced by highly mechanized enterprises with a universal assortment of goods that use electronic computers to control technological processes. In 1973, the share of retail trade turnover in individual countries was 4 percent in the USA and Great Britain, 5 percent in the FRG, 1.2 percent in France, 0.5 percent in Italy, and 1 percent in Belgium and the Netherlands. The largest P. t. firms in Western Europe are Neckermai, Quelle, and Otto Ferzand (Germany); "La Redoubt" and "Galeries Lafayette" (France); in the USA - Sears, Roebuck & Co., Montgomery Ward, etc.
L. I. Mikhalev.
Page Links
- Direct link: http://site/bse/62362/;
- HTML-code of the link: What does mail order trade mean in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia;
- BB-code of the link: Definition of the concept of mail order trade in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia.
Catalog trade- the type of business most relevant for regional centers. The level of income of the population there is relatively high, but the opportunity to purchase for themselves such goods as clothing and footwear that meet the taste of the consumer is rather small. Since they bring to these cities mostly cheap consumer goods, and then at rather inflated prices. Therefore, for residents of these regions, buying goods from catalogs is a real opportunity to purchase really high-quality and original things.
Experts believe that catalog trading is one of the most promising areas of small business in the conditions of our country. After all, the multi-million population of the country is scattered over a vast territory, and the network of post offices is quite developed.
One of the main secrets of the success of such a business is to communicate with customers with understanding. It is necessary to explain to newly arrived customers as accessible and understandable as possible all the features and nuances of buying goods from catalogs.
Parcel trade - a form of sale of goods in which their sale is carried out using postal channels or telephone lines to collect orders and assist in the delivery of sold goods. Parcel trade is carried out on orders carried out in the form of postal items. The mail order system originated at a time when customers began to send their orders to manufacturers by mail. Later, sellers tried to stimulate the flow of orders from consumers by sending out catalogs, primarily to residents of rural areas.
In all the vast mass of buyers there is a special group who prefer not to spend part of their time on energetic trips in search of the right thing. These people find particular pleasure in the leisurely browsing of brightly and richly designed catalogs.
Catalog companies can be divided into two main groups: international and domestic operators.
Parcel trade organizers can be:
individual manufacturers of goods;
intermediaries specializing in this form of trade;
Stationary retail network
Retail trade network - is a collection of retailers and other trade units located in a certain area for the purpose of selling goods and serving customers, or under common management.
depending from the conditions in which the sale, retail trade may be stationary or non-stationary.
Fixed network located in specially equipped buildings and structures intended for sale and purchase.
The stationary retail network is represented by a retail network (shops) and a small retail network (pavilions, kiosks, stalls, vending machines).
Retail network is a set of trade enterprises interacting on the basis of a single coordination determined by external environment. This network includes specially equipped buildings (shops) that sell goods and services to customers for their personal, family and home use.
Small retail trade network includes pavilions, tents, stalls, kiosks. The small retail trade network has great flexibility, the ability to quickly deploy and get as close as possible to customers, its construction and operation does not require large expenditures.
The development of a small retail trade network does not require large investments, it allows using cheap materials for its construction. Many outlets are open 24/7.
The small retail trade network sells food and non-grocery goods simple range and everyday demand. It complements the network of stores during the period of seasonal trade in vegetables, fruits, flowers, drinks, and is also used as an independent trade in tobacco, confectionery, book and magazine products, newspapers, ice cream.
Pavilion - this is a closed, equipped building of light construction, having a trading floor and a room for storing inventory, designed for one or more jobs.
Kiosk - it is closed, equipped commercial equipment building without trading floor and premises for storage of goods, designed for one workplace, on the area of \u200b\u200bwhich the inventory is stored.
Tent - this is an easily erected prefabricated structure that does not have a trading floor and premises for storing goods, designed for one or more workplaces.
Stall - a building equipped with commercial equipment that does not have a trading floor and a room for storing goods, designed for one workplace of the seller.
A variety of small retail chains are vending machines("vending" - automatic trading) - are used to sell goods through automatic devices. They can be used for the sale of piece, packaged goods, drinks.
The advantage of trading through vending machines is a significant acceleration of the process of selling goods, reducing the cost of maintaining staff, and unlimited working hours.
Despite the undeniable advantages, trading through vending machines in the CIS countries is developing extremely slowly (including due to the withdrawal of metal coins from money circulation).
auction trading
Auctions are a kind of intermediary organizations that promote the circulation of goods. Unlike the stock exchange, auctions are not permanent, but periodically operating centers of intermediary trade in real goods with individual properties. Auctions are traded using the open auction method.
Types of auctions:
Open auction - an auction during which participants see the bids of all their opponents. A classic example is the English open auction.
Closed auction - an auction during which participants do not see the bids of their opponents and cannot change their bids. Applications are submitted in closed form (in envelopes) - each participant directly, without publicly disclosing, informs the auctioneer of the size of his bid. An example is the privatization auctions in Russia.
First price auction - a closed auction in which the winner is the participant with the highest price and it is this price that is payable. Typically, closed auctions are first-price auctions.
Second price auction - a closed auction in which the winner is the participant with the highest price, but he must pay the "second price", that is, the price of his closest competitor. Today it is not widely used.
A double auction is a generalized form of an auction, denoting a situation where more than one seller and more than one buyer participate in it, simultaneously reporting their bids to the auctioneer, who then determines the equilibrium price at which transactions are made between sellers and buyers whose bids were not worse than this price .
An English auction is the most common type of auction, which involves buyers bidding for an item at an increasing price in increments until there is only one auctioneer left - the winner. It is also called an upward auction.
Dutch auction - an auction in which bidding starts at a very high price and goes down until a buyer is found who is willing to buy at the advertised price. Usually this kind of reverse wholesale auction is used when it is necessary to sell several units of goods at the buyer's price. The Dutch auction is most often used for the sale of securities, flowers and second-hand goods, sales of construction in progress, and issuance of licenses.
Scandinavian auction - an online auction in which the starting price of bidding for all goods does not exceed 1 ruble. Bidding is carried out with a fixed predetermined price increase step, which usually does not exceed 25 kopecks. The ability to place a bet is paid. The winner of the auction is the participant who made the last bid before the end of the auction.
Organization and technique of auction trade
Typically, periodic auctions publish a bidding schedule or notify suppliers and traditional buyers in advance of the timing of the bidding.
Goods accepted from suppliers are either sorted immediately or undergo additional pre-sale refinement. Sorting is carried out according to the quality of goods. Goods of the same quality are sorted into batches (lots). A sample is taken from each lot. The number of goods in a lot depends on the customs in the trade of this type of goods.
mail order is one of the forms of sale of goods on the basis of pre-orders of buyers with the delivery of ordered products, as a rule, by means of the postal service.
Purpose of mail order business ambiguously. First of all, it is perceived as a means of satisfying the need for goods for which their stable supply is not provided in the local trading network. Thus, it eliminates the uneven development of a chain of stores in small settlements. However, by providing convenience and time savings for customers, mail order is becoming increasingly important to meet demand in a wide range goods and city dwellers. In addition, through the mail order business, not only the demand for consumer goods is satisfied, but also for industrial and technical goods.
Parcel trade organizers different: separate manufacturing enterprises; resellers specialized in mail order business; large retail stores. However, they can perform various functions. Manufacturers can use this form of trade to supply those who bought their goods, components, spare parts, including for warranty and post-warranty service. Retailers can sell products that they have in stock. The entire list of goods offered by catalogs can be delivered to buyers by specialists in wholesale trade intermediaries.
At the same time, it is possible to cooperate with the activities of mail order enterprises with large department stores and specialized stores.
Example J.1. One of the leaders in the field of mail order business is the famous German company Quelle. The colorful catalog of this company includes you-i boxes of names of various consumer goods. The company has created a network of stores that complement specialized mail order businesses. In addition to promoting mail order services widely, these stores also attract additional customers in local markets.
In the practice of mail order trade, a certain assortment of goods has developed. It has the following requirements:
based on the fact that everyday goods are purchased by buyers in a stationary retail trade network, the range of mail-order trade should include goods of periodic demand purchased at intervals of one month to one year, and goods of episodic demand;
since goods of a complex assortment, characterized by a large number of assortment features (name, model, article of material, finish, color, size, height, etc.), most often require personal selection, in the assortment of mail order trade should, first of all, go goods of a simple assortment;
due to the fact that goods with a low price level usually belong to everyday goods, the basis of the mail-order trade turnover is goods with an average price level; goods may also be sold high prices, but a simple assortment.
All of these requirements are met by the following groups of goods: clothing and footwear; haberdashery goods; Perfumes and cosmetics; jewelry; household and cultural goods; seeds and plants; individual products(for example, baby food). It is these consumer goods that form the basis of the parcel trade turnover. As for goods for industrial purposes, as already noted, these are spare parts, components, etc. When forming the assortment, it is necessary to take into account, on the one hand, the presence of customer demand, and on the other hand, economic
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Characteristics of out-of-store forms of sale of goods. Features of the organization of markets in the Republic of Belarus. The concept of selling goods in the markets and their types. Trading in the markets in the conditions of economic transformation. Prices for the main types of goods and products.
term paper, added 03/25/2018
Socio-economic significance of the methods of selling goods. Organization of trade in enterprises. Organization commercial activities for non-store sale of goods at enterprises. Organization of e-commerce and exhibition activities.
term paper, added 02/07/2012
Improving the retail trade of medicinal products in pharmacies. The requirement for information on the packaging (label) and other pharmacy products. Rules of sale, exchange and return certain types goods. Analysis of the design of the trading floor.
term paper, added 06/05/2014
Principles of operation, classification and requirements for commercial refrigeration equipment. Out-of-shop forms of trade service. The study of the rules for the sale of certain types of goods. Atmosphere and information system shopping facility. Organization of labor in trade.
term paper, added 06/04/2015
Retail trade enterprises in the conditions of the functioning of a market economy as an independent link in trade and services. Forms and methods of the retail network for the sale of goods. Analysis and evaluation of the effectiveness of retail trade on the example of Euroset LLC.
term paper, added 09/25/2008
The concept, composition, features of urban economy. The role of the sphere of trade in a market economy. Analysis of the sphere of trade on an example municipality- the city of Osinniki and determining the directions of measures to improve its functioning.
term paper, added 11/08/2011
Analysis of methods, application features modern technologies and new forms of trade in commercial activities. Influence study scientific and technological progress for the development of commercial activities. Distinctive features wholesale, retail sale of goods.
term paper, added 04/16/2010





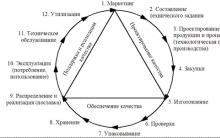



Layout of the house, plans of houses and cottages
Small Business - Home Production Ideas
History of JANOME. Sewing machines. Janome, Veritas, Pfaff Sewing machine janome manufacturer country
Working with the tattis system
Properties of copper and its application