RF Krasnodar Territory
NCOU SPO "Legal College"
Kropotkin
COURSE WORK
on academic discipline: "Economics of the industry"
Topic: "calculation of the main indicators of a business plan"
Kropotkin
1. Theoretical part…………………………………………………………….
1.1. Characteristics of the enterprise and its development strategy……………… page
1.2. Description of products (services)………………………………………… page
1.3. Analysis of sales markets. Marketing strategy………………………… page
1.4. Organizational plan………………………………………………… page
1.5. Legal Plan………………………………………………………page
2. Practical part……………………………………………………………..
2.1. Calculation of the main indicators of the business plan………………………………..
2.1.1 Determination of labor costs for the development of software modules……
2.1.2. Valuation development……………………………………………
2.1.3. Determining the selling price of a software module……………………
2.2. Financial plan……………………………………………………………..
2.2.1. Calculation of break-even creation software product……………….
2.2.2. Discounting the results of designing a software product.
2.3. Project performance indicators………………………………………….
List of used literature. ……………………………………………
Summary
Any production, from the release of CDs and ending with the construction spaceships, needs a certain set of services. Thus, our company operates in the most dynamic area - the service sector.
We plan to provide wide range services such as:
Intermediary activity in the trade of consumer goods, electronic and other equipment, souvenirs;
Marketing and sale of products, goods and services of Russian and foreign companies;
Consulting activities and provision of consulting and information services;
Organization and holding of exhibitions, fairs, auctions;
Implementation complex services related to the organization and activities of offices;
Organization of individual and group tourism in Russia and abroad, including business, student and school tourism.
However, the main area of our activity is the development, implementation and service software, as well as the development and production of software technical means based on new information technologies. The industry is young enough to Russian market and therefore most companies lack professional software. Most companies use low-quality discs and pirated programs. Therefore, the need for this type of product is very high. UAB "Omega" is able to provide necessary programs for the fruitful functioning of various kinds of companies.
1. Theoretical part.
1.1. Characteristics of the enterprise and its development strategy.
Closed joint-stock company Omega has been registered in the register of business entities since 2005. The company is quite young, only 6 years old on the market, however, it is one of the few enterprises in the Krasnodar Territory that manufactures this type of product.
Software production is a science-intensive industry, so the project will be carried out by specialists in this field...
In the laboratory for the most complicated technique the specialists of our company will develop programs. The senior programmer will choose those that the market needs the most. Further, using the equipment of leading companies, the programs will be recorded on laser discs.
The software update database is constantly updated with information from various sources. Therefore, our company is constantly in step with technical progress and fully meets the needs of the market. It is possible to draw up special programs to meet the needs of regular and especially profitable customers.
The software will be sold in small wholesale lots through personal contracts with customers. This form is very convenient, as it does not require a special room for sales. Perhaps in the future JSC Omega will organize its own retail sale through a network of branches. It is planned to expand the company's activities throughout Russia, and in the future to master the markets of near and far abroad.
Our main activity is the production and sale of software. This industry requires highly qualified personnel, knowledge of market needs and quality of work. The project will be carried out on recently developed equipment using newly released technologies. To obtain the necessary information JSC "Omega" has numerous contacts with Russian partners.
1.2. Description of production (service).
JSC "Omega" produces programs and software and hardware. This production is necessary both for firms, and for private users. The software includes various programs in the field of financial and accounting reporting, production planning, legal registration. All programs are developed based on the needs of Russian clients, taking into account the uniqueness of the Russian market. At the same time, they are in no way inferior in terms of workmanship. Western counterparts. The materials for the production of our products are of high quality and reliability. By purchasing our programs, you can be sure that they will satisfy the requirements of even the most biased client. Information base is updated as technology develops and keeps up with technical progress.
Among the features of our products we would like to highlight the following:
High quality;
Compliance;
Use of the latest achievements of science and technology.
We believe that it may not be a novelty, but a rarity, our products will be on the market for a long time, since at the moment there are no companies in the Krasnodar Territory that use technical programs similar to ours. There are practically no companies on the market that are seriously engaged in this kind of activity. Firms tend to try to win at low costs by acquiring low quality materials. Therefore, their programs can not only improve, but also worsen the work of clients. In our production we use only high-quality materials, both domestic and western. At the same time, it should be noted that the raw materials and materials necessary for the implementation of the project are not purchased from China or Taiwan, but from the world leaders of the Western countries. Thus, UAB "Omega" compares favorably with all companies operating in the market. There are some factors of competitiveness:
Quality;
Price level;
exclusivity of the goods;
After-sales service;
The reputation of the firm.
1.3. Analysis of sales markets. Marketing strategy.
Market research has shown that there is a need for a software manufacturer. The goal of UAB Omega is to occupy this niche.
We are aware that sales will not come by themselves and must be won. Large customers will want to test the profitability of our products themselves. These trials can take anywhere from one to six months depending on the purchasing policies of the respective clients. The main goal of the first year production activities is to establish itself as a reliable supplier. Ultimately, we expect to be the primary supplier for most, if not all, major customers in this market.
Thanks to extensive connections in business world our company is already very popular. Our products will be of more interest to the buyer, since high-quality and "fresh" programs are not easy to find on the Russian market.
We expect to attract the interest of the buyer to the product due to:
Direct connections with the main buyers;
The highest quality of our products, friendly atmosphere of treatment, openness;
Personal contacts of our employees.
The focus is on increasing wholesale sales. The main consumers of our products are:
Large corporations in manufacturing, banking and other areas;
Medium and small firms;
Individual individuals;
Any customers wishing to purchase our products. Over the past few years, the market share held by software and hardware has steadily increased. However, in our country, production is not yet able to cover the entire consumer market.
The pre-sales were an essential part of our preparatory work and helped establish quite extensive relationships with major buyers in the region. We will be able to serve both large and small clients. Programming is big problem for many users, and our delivery will give us a comparative advantage in serving small but clearly profitable customers.
We plan to distribute our products in small wholesale lots. Clients will go to a cozy modern office and make deals on the spot. It is envisaged to develop special orders from regular customers according to their needs.
Our product does not need wide advertising, but it is planned to send several trial options large companies as promotional material. It is also necessary to give an announcement via networks and faxes to some firms. This will be enough to attract a large number of customers. The sales market in the future is expected to expand and move beyond the Krasnodar Territory. To do this, you need to send fax messages to companies in major cities and regions of the country.
Of the three main pricing targets that the firm can choose from (sales based, profit based, status quo), our business prefers the status quo targets because we are satisfied with the volume of sales, but an increase in relative profit is not justified by elasticity. demand for the product. But we are interested in stability and maintaining a favorable climate for our activities.
The pricing strategy is focused on avoiding a downturn in production and minimizing the impact of external forces such as competitors and channel participants.
1.4. Organizational plan.
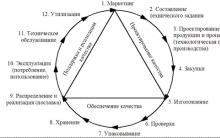
General structural scheme management of the enterprise determines the relationship that develops between its various divisions, aimed at fulfilling the mission and achieving the goals.
JSC "Omega" operates a centralized functional management structure, consisting of the following specialized departments:
1. Department technical control– 1 person (OTK).
2. Personnel department - 1 person. (head of personnel department).
3. Department accounting– 3 people (chief accountant, accountant of the 1st category, accountant of the 2nd category).
4. Planning and economic department - 1 person. (Leading economist).
5. Department of logistics and sales - 3 people. (head of department, supply engineer, sales engineer).
6. Production laboratory - 15 people. (Senior programmer, software engineers).
7. Management department - 3 people. (Director, Deputy Director for Commercial Affairs, Deputy Director for Production).
At the head of each subdivision (department) is a leader, endowed with certain powers, who manages subordinate employees.
According to the current staffing The company employs 27 people.
The management structure is formally defined, it is characterized by unity and clarity of command, the absence of conflicting commands, which is especially important at the lowest level of management, quick decision-making and quick response to any change. production process, coordination of actions of performers, full responsibility of the head for the results of the activities of his department.
An important step in adjusting the strategy of the enterprise is to communicate to all employees the mission and goals of the enterprise. With their knowledge, each employee of the company will strive to achieve the set goals and try to ensure that the work they perform is in line with the mission and strategy of Omega UAB. At the same time, employees must identify their well-being with the well-being of the entire enterprise. In accordance with this, management must protect the interests of workers at all levels, which will entail a sense of confidence, security and reliability. A factor in the prosperity of the enterprise is the cohesion of the team, so it is necessary to develop a sense of respect and mutual understanding by developing old traditions and laying new ones.
 |
||
Diagram 1 shows a diagram of the Omega personnel management structure.
As can be seen from the diagram, one of the simplest centralized functional structures management and reflects the most common stage of the division of managerial labor.
The powers of senior managers and heads of departments are organizationally assigned to official, or collective limited right and responsibility to use the resources of the organization, independently make decisions, give orders and carry out certain management actions of the organization.
Within the organization, the limits of authority are determined by the rules job descriptions set out in writing, but certain powers may be transferred orally. Powers are transferred by the top manager to the next one and further along the chain to other subordinates. The leader, endowed with authority, has the right to make decisions and act in certain matters without the consent of others, within the limits of the organization's instructions.
Director– manages, in accordance with the current legislation, the production, economic and financial and economic activities of the enterprise, bearing full responsibility for the consequences of decisions made, the safety and efficient use of the property of the enterprise, as well as the financial and economic results of its activities.
Deputy Director for Commercial Affairs- organizes the development of short-term and long-term forecasts for the development of the market, its capacity, takes part in the preparation of plans for export activities in various markets, adjusting plans taking into account sales of products and existing orders. Monitors the implementation of product sales indicators, the achievement of established profit indicators and other financial performance.
Deputy director for production- determines the technical policy and directions of the technical development of the enterprise in a market economy, the ways of reconstruction and technical re-equipment of production, the level of specifics and diversification of production in the future. Ensures timely and high-quality preparation of production, technical operation, repair and modernization of equipment, achievement High Quality products during their development and production.
Chief Accountant – carries out the organization of accounting of economic and financial activities and control over the economical use of material, labor and financial resources, the safety of the property of the enterprise. Leads the preparation and adoption of the chart of accounts, forms primary documents, provides rational organization accounting and reporting at the enterprise based on the maximum centralization of accounting and computing work and the use of modern technical means and information technologies, progressive forms and methods of accounting and control, the formation and timely presentation of complete and reliable accounting information about the activities of the enterprise, its property status, income and expenses, and also develops and implements measures aimed at strengthening financial discipline.
Sales Engineer- organizes the marketing of the company's products in accordance with the planned targets and concluded contracts, its shipment to consumers in the time and volume established by the implementation plan. Carries out the choice of channels of distribution, assessment of consumers and their needs for the goods of the enterprise. Provides participation of the department in the development of long-term and short-term plans for the development of the market, its capacity, production and sales, export activities in various markets, the harmonization of conditions and the conclusion of contracts for its supply, the development of estimated standard reserves finished products, planning its delivery to consumers, adjusting plans, taking into account the sale of products and existing orders.
supply engineer- receives, according to applications and other documents, inventory items (raw materials, materials, equipment, components, inventory, stationery, etc.). In accordance with the established procedure, it purchases inventory items, takes measures to improve the efficiency of the use of material resources, reduce the costs associated with their acquisition, delivery and storage.
Leading economist- does the work of implementing economic activity enterprise aimed at increasing the efficiency and profitability of production, the quality of products and the development of new types of products, achieving high end results with optimal use of material, labor and financial resources. Prepares initial data for the preparation of projects of economic, financial, production and commercial activities. Performs calculations for material, labor and financial costs necessary for the production and sale of products, advanced equipment and technology. Determines the economic efficiency of the organization of labor and production, the introduction of new equipment and technology, rationalization proposals and inventions.
Accountant 1st, 2nd category- performs work on maintaining accounting of property, liabilities and business transactions, participates in the development of measures aimed at maintaining financial discipline and rational use resources. Reflects on the accounts of accounting operations related to the movement of fixed assets, inventory and cash. Compiles accounting cost estimates for products, identifies sources of losses and unproductive costs, prepares proposals for their prevention. It calculates and transfers taxes and fees, payments to banking institutions, funds to finance capital investments, wages of workers and employees, other payments and payments, as well as deductions of funds for material incentives for employees of the enterprise.
1.5. legal plan.
Legal status firms - a closed joint stock company. This form of ownership is easy to implement and convenient in its structure. Closed Joint Stock Company CJSC "Omega" has an authorized capital of rubles. It is formed as a result of the investment of money by the sole founder. The Company issues 100 ordinary registered shares worth 1719.4 rubles each. The shareholder is the founder.
According to the form of ownership, the joint-stock company has a private form. JSC "Omega" is owned by the founder.
2. Practical part.
2.1. Calculation of the main indicators of the business plan
The process of information processing can be divided into main stages. In accordance with this, the general formula for calculating labor costs in man-hours (man-hours) is as follows:
 (1)
(1)
where: - labor costs for preparing the task description, (man-hours);
Labor costs for studying the task description, (man-hours);
Labor costs for the development of an algorithm for solving the problem, (man-hours);
Labor costs for the development of the flowchart of the program, (man-hours);
Labor costs for the direct writing of the program, (man-hours);
Labor costs for debugging a program on a computer, (man-hours);
Labor costs for preparing documentation for the task, (man-hours).
The components of labor costs are determined through the conditional number of commands in program modules:
where: - estimated number of operators,
Program complexity coefficient, C = 1.26;
Coefficient of correction of the program during its development, P = 0.2;
n = 1, 2,… - the number of program corrections during its development,
Labor costs for preparing a task description
The labor costs for studying the description of the problem, taking into account the clarification, can be determined by the formula:
where: - the degree of preparedness of the performer to perform the work, \u003d 1.2
The coefficient of increase in costs by the complexity of the task, =1.4.
Labor costs for the development of an algorithm for solving the problem:
Ta = ![]() (4)
(4)
Labor costs for the development of the flowchart of the program:
![]() (5)
(5)
Labor costs for direct writing of the program:
![]() (6)
(6)
Labor costs for debugging a program on a computer:
![]() (7)
(7)
Labor costs for preparing documentation for the task:
Td = ![]() (8)
(8)
2.1.2. Development valuation
The cost of the project is determined as follows:
where: - assessment of the work of the developer of the software module, rub.;
Software debugging costs for the task, rub.;
The cost of computers and other technical means purchased for the development and operation of the software module, rubles;
Other expenses, rub.
The valuation of the work of theme developers can be determined by the formula: (10)
where: O - average wage designer of the 1st category per hour, (rubles/hour);
Labor intensity of design, (person * hour);
Percentage of additional salary,
Percentage of deductions for social needs, including: social and medical insurance, employment fund, Pension Fund, =26%;
Overhead percentage,
The average salary of a 10 grade designer per hour can be determined by the formula:
 (11)
(11)
where: - the average salary of a designer of the 1st category per month.
Number of working days in a month;
Discharge coefficient, \u003d 2.98;
The duration of the shift, = 8 hours.
The valuation of the use of computers during debugging is carried out according to the formula:
Debugging time on a computer, hours, which can be determined by the method of the number of commands and by the average computer time for programming a separate program in interactive mode in minutes per command in programming language codes:

![]() (13)
(13)
Where n is the number of program corrections during development,
o is the number of operands.
The cost of a machine-hour of computer operation, rubles, which can be determined based on the operating costs associated with the use computer science:
 (14)
(14)
where: - total annual costs of computer operation, rub.;
The actual fund of computer operation time for the same period, h.
Operating costs are calculated using the formula:
where: - the cost of labor for the maintenance personnel of the computer, rub./year;
The cost of renting a room for the placement of computer equipment, rubles / year;
Electricity costs, rub./year;
Depreciation costs (depreciation charges), rubles/year;
- cost of materials, rub./year;
Repair costs, rub./year.
Labor costs for computer maintenance personnel are calculated by categories: 
where: - labor costs of the category of operators,
Labor costs for the category of electronics engineers;
The labor costs of operators, and then electronics engineers, are calculated according to the formula:
where: - wages of workers of the i-th category.
Operator's monthly salary:
Electronic engineer monthly salary:
Number of employees of the i-th category:
The cost of renting a room per year for the placement of computer equipment is calculated by the formula:
where: S - room area,
Average rental rate, (rub*month/sq.m)
 Energy costs per computerized workplace per year is calculated by the formula:
Energy costs per computerized workplace per year is calculated by the formula:
where: M is the nameplate power of the computer, M = 0.5 (kW);
Valid annual fund of time, hours;
The price of one kWh of energy at the time of the calculation,
Coefficient of intensive use of power, = 0.8
The actual fund of computer operation time for the period (year) under consideration is calculated by the formula:
where: - the number of days in a year;
Number of days off in a week;
Quantity public holidays per year;
Shift ratio, i.e. number of computer work shifts;
The percentage of loss of working time associated with the prevention and repair of computers (15% -30%).
The remaining costs are determined based on the book value of the equipment: 
where: - computer acquisition price,
Coefficient characterizing additional expenses related to the delivery, installation and commissioning of equipment, 12% -13%.
Depreciation costs (depreciation charges):
where: - depreciation rate for renovation, = 12.5%.
Material costs:
where: - cost standard for information carriers, = 1% of
Repair costs:
![]() (24)
(24)
where: H p - repair cost standard, N p \u003d 2%.
Calculate the cost of a machine-hour of computer operation:
The cost of a computer is determined by the formula:
Where is the purchase price of a computer,
d - shipping costs (12% of).
Other costs (cost of paper, printer ink, stationery): Сn=1.3% SEVM
The cost of production of one copy of the software product is calculated by the formula:
 (27)
(27)
where - Cost estimate of the project,
The actual number of copies ordered by buyers.
 2.1.3. Determining the price of implementing a software module
2.1.3. Determining the price of implementing a software module
Potential buyers are several dozen enterprises. Estimated sales volume - 30 copies.
The selling price for a software product, taking into account the above information, is determined as follows:
Where - the level of profitability, \u003d 15-30%
Rate of deductions to the income tax budget, = 24%
Based on the estimated sales volumes, it is possible to calculate the selling price of one copy, taking into account the cost of replication (Ztir) and service maintenance(Zso):
3 shooting gallery = 100 rubles per copy
2.2. Financial plan
 2.2.1. Calculation of break-even of creating a software product
2.2.1. Calculation of break-even of creating a software product
Break-even analysis is one of the most important elements of financial information used in assessing the effectiveness of investments.
The purpose of the analysis is to determine the critical selling point. If the sales volume is less than the critical point, the enterprise operates at a loss; if the sales volume exceeds the critical point, the enterprise operates at a profit.
The break-even point (Q cr) is determined by the formula:
Where - semi-fixed costs for a software product are calculated by the formula:
Selling price of a software product unit.
PZ - conditionally variable costs for a software product, calculated by the formula:
PZ ed - conditionally variable costs per unit of the software product; calculated by the formula:
![]() (33)
(33)
Let's add 30% of the quantity to the break-even point to find the point of confident profitability, the point at which the release and introduction of products will bring tangible income.
Net profit
2.3. Project performance indicators
Based on the data obtained, it is necessary to build a dependence model for the indicators of creating a software product:


Figure 1 Dependency model of software product indicators
Having the calculation data of the table for the total annual costs of the designed product, it is necessary to evaluate the economic efficiency of the projected event.
To do this, define:
Net present value (NPV) of the project;
Profitability index (ID) of the project;
Payback period of the project;
Determine the discount rate using the formula:
where: i – percentage of inflation;
The amount of discounted net cash receipts for the period in question;
The volume of investments in the amount equal to the cost of sales
The results obtained are recorded in the table:
Table 3
Calculation of NPV and ID for the project
| The name of indicators |
Quarters |
||||||
| Discount coefficient |
|||||||
| Net cash receipts, rub. |
|||||||
| Discounted net receipts, rub. |
|||||||
| Investments, rub. |
|||||||
| The amount of discounted net cash receipts, rub. |
|||||||
The yield index is 0.16.
It is necessary to find the payback period of the project using the formula:
T ok \u003d t-  (35)
(35)
where: t is the project implementation period at which the difference between the net present value of investment and the amount of investment takes a negative value.
Net present value relative to investment for period t,
Net present value relative to investments for period t+1.
 Based on the table, we find: t = 5
Based on the table, we find: t = 5
By substituting the data obtained into the formula, determine the payback point:
So, the payback point will come in 6 periods after the start of sales.
Based on the data obtained, we will build a schedule of return on investment
List of used literature.
1. Vlasova V.P. Business plan of the investment project. Teaching aid. - Kropotkin, Law College, 1997.
2. Goremykin V.A. Business plan: Development methodology. - M .: "Os-89", 2008.
graduate work
1.3 Methods for assessing the economic efficiency of business planning
In the business plan, without fail, an assessment of the project is given. This assessment can be presented as a separate section of the business plan or included in the financial plan.
In order to evaluate the effectiveness of a business plan, it is necessary to adhere to the approaches that are described later in this chapter. thesis.
Let's consider a cash flow estimate.
To assess the commercial effectiveness of an investment project, it is necessary to calculate the value of the cash flow based on forecast data.
Net cash flow is the amount of cash required by the project during the investment phase, or the cash that is released from the project, which is the operating phase.
The net cash flow is calculated based on the data of the forecast cash flow statement. The net cash flow of the project is formed in different ways, based on the point of view of which project participant the analysis of the effectiveness of this project is carried out.
The net cash flow for total investment costs, which is usually reported as NCF, should reflect the project's flows from the perspective of the organization that implements it, or from the perspective of all project participants. Use this show to evaluate overall performance. The attractiveness of the project for individual participants in this case is not taken into account.
A company's NCF is calculated using the following formula:
NCF of the company = OFP + PC * SNP + FDI, where (1)
ODP - operating cash flows that do not include interest on loans;
PC - interest on loans;
SNP - profit tax rate, which at the time of calculation is officially established;
IDP - investment cash flows.
Next, consider the net cash flow for equity, which are commonly referred to as NCF eigen. This indicator carries information about the flow based on the position of shareholders or owners of the company. This indicator makes it possible to assess the effectiveness of the project based on the fact that shareholders or owners do not always finance all investment costs, and also based on the fact that not all income goes to the shareholder and they can freely dispose of it, since some of these income, without fail, must go to repay bank loans.
Based on the above, we give a formula that allows you to calculate the NCF eigen.
NCF own \u003d ODP + IDP + PC - VD, (2)
where, ODP - operating cash flows;
PC - credit receipts;
VD - funds spent on the payment of the main credit debt.
Next, consider the calculation of such an indicator as net cash flow for land capital. This indicator is designated as the NCF of the bank. This indicator provides information about the flow of the project based on the position of the bank or banks that finance this project. This indicator describes how the project is able to recoup the funds that are invested in it.
This indicator is calculated using the formula:
Bank NCF \u003d ODP + PC * SNP + IDP + PAK - VD, (3)
where ODP - operating cash flows that do not take into account interest on loans;
PC - interest paid on loans;
SNP - profit tax rate, legally established at the current time;
IDP - investment cash flows;
PAK - inflow of capital from shareholders;
PD - dividend payments.
When calculating such an indicator as net cash flow, those investments and expenses of investors that were made by them before the project began to be implemented are not taken into account in the calculation process, i.e. costs incurred prior to the start of the billing period are not included in the calculation. Instead, the opportunity cost of the assets that are contributed to the project is taken into account. The principle of determining this opportunity cost is described below.
In the event that in order for the project to be implemented, some assets are contributed, which can be represented by buildings, equipment, construction in progress, having a market value at which they could be submitted, if they were not used in project, the cost of these assets should be taken into account when calculating the NCF of the company and NCF own. But this cost is not taken into account when calculating the bank's NCF. The cost of these assets is included in the calculation as a loss of profit, which is considered as an opportunity for an alternative use of these assets or an investment project in progress. In order to take into account the opportunity cost, a number of approaches are proposed, which are listed below:
In the event that the assets transferred to the project have a value in the market and can be realized within a reasonable time, then the opportunity cost takes into account the lost profit that could be from the sale of these assets. In order to determine this lost profit, it is necessary to take into account the price for which the property could have been sold and deduct from this price the costs that would have been incurred in connection with the sale. This may include pre-sale preparation, distribution and dismantling costs, etc. In case it is necessary, given price can be discounted to the point at which the property begins to be used in the project considered in the business plan. In the event that the sale price of an asset depends on the moment when the property is sold, then this moment in the calculation must be taken such that the amount of lost profit that is subject to discounting is at the maximum level;
In the event that it is impossible to sell the described assets for one reason or another, which may be the following: strategic considerations, lack of demand for a particular type of asset, etc., but options for the alternative use of these assets are known, then it is recommended to use an assessment as an alternative cost value by income methods, which is performed for certain options for the alternative use of assets;
In the event that the property can be rented out, the opportunity cost taken into account is the discounted amount of rental payments received from the lease of the property. From these payments it is necessary to deduct the cost of capital repairs of the leased property, as well as other costs that, according to the lease agreement, the lessor would have to bear. The income and expenses described above should be taken into account only for the period in which the property is used in the implementation of the project in question;
In the event that an asset is not subject to sale on the open market, and there are no payments for its alternative use, then it is reasonable to take its opportunity cost equal to zero.
The main performance indicators, the calculation of which is required in the investment project, are:
Net present value of the project;
Internal rate of return;
Discounted payback period.
The net present value of the project (NetPresentValue, NPV) is calculated using the following formula:
i - project year number,
T is the number of years in the project,
NCF i - net cash flow of the i-th year of the project,
d - discount rate.
The internal rate of return (InternalRateofReturn, IRR) is maximum cost project capital, which maintains its economic efficiency.
IRR is defined as the discount rate at which the project's NPV becomes zero. The project is considered effective if the IRR of the project is higher than the discount rate set for this project.
As a rule, the nominal discount rate is first determined for the project (the principles for its selection are given below), and, if necessary, the real rate is calculated on its basis. The formula for calculating the real rate d R looks like this:
where d H is the nominal discount rate, i-inflation.
It is permissible to use a simplified formula: d R \u003d d H - i.
When calculating performance indicators in terms of borrowed capital, the following value should be used as the discount rate:
d bank \u003d R cr * (1-t) (9)
where: R kr is the estimated interest rate on the loan, t is the income tax rate.
The adjustment for the value (1-t) takes into account the impact of the tax deduction of interest on the loan on the results of the project. This is an approximate calculation scheme that does not take into account the intricacies of calculating the amount of the tax deduction (such as limiting the amount of interest included in the deduction).
At the end of the first chapter of the thesis, the following conclusions can be drawn.
Any major investment projects are carried out according to one plan or another. The plan is a program document that includes a set of indicators and tasks that are balanced in terms of resources, the timing of their implementation, and are also distributed among the executors who are responsible for them.
Intra-company activities fall into the following categories:
Development of a strategy or concept for the development of the company with the specification of individual areas of activity;
Development and implementation of projects to create new products or services;
Assessment of internal technical and production potential, as well as identification of possible reserves;
Preparation and implementation of measures for the introduction of new technologies, as well as the acquisition of the necessary equipment;
Recruitment of new or retraining of existing employees or specialists;
Control over the financial performance of the organization;
Implementation of measures that would reduce the degree of risk for the organization;
Implementation of activities that contribute to the formation of a favorable image of the organization;
A set of measures to prevent possible bankruptcy and exit from the crisis.
Attracting investments for the implementation of planned projects;
Justifications that could contribute to the inclusion of the project in state or regional programs and the receipt of funds from centralized sources;
Obtaining credits and loans from banks;
Ensuring the successful sale of the company's shares when entering the stock exchange;
Organizational and financial justification for the creation of joint ventures with the use of external capital or the creation of other forms of joint activity.
Creating a business plan takes place in several stages. In a business plan, the following, most common sections can be distinguished:
Business concept (summary);
Description of the enterprise and industry;
Characteristics of services and products;
Market research and analysis;
Competition and competitive advantage;
Marketing plan;
Production plan;
Organizational plan;
Financial plan;
Financial strategy;
Potential risks.
To evaluate the effectiveness of the activities described in the business plan, I use a number of indicators that allow us to evaluate certain activities planned for implementation.
Risk analysis and assessment in the business planning system
In order to assess the probability of certain losses due to the development of events according to an unforeseen option, one should, first of all, know all types of losses associated with entrepreneurship ...
Analysis of financial economic activity enterprises LLC "Rezontorg"
Finance is a set of economic monetary relations arising in the process of production and sale of products, including the formation and use of cash income ...
Analysis of the economic efficiency of the technology for the production of the main products at CJSC Elektroizolit
The term "efficiency" is universal. It is used in all spheres of human activity: economics, politics, science, technology, culture, etc. In a semantic sense, efficiency is associated, firstly ...
Business planning
The business plan acts as Objective assessment own entrepreneurial activity firms and at the same time essential tool design and investment solutions in accordance with market needs...
Diagnostics of economic activity and development of a business plan to improve the efficiency of LLC "ContactStroyService"
Methodology for Determining Indicators of Absolute and Relative Efficiency of Capital Investments
Today, there are several main approaches or methods for determining the performance indicators of capital investments. The income method is based on the assumption that...
Organization of production at the enterprise on the example of OJSC "Tverstekloplastik"
The planning methodology is understood as a set of methods, techniques for developing, substantiating and analyzing forecasts, programs and plans, a system for calculating planned indicators, their interconnection ...
Evaluation of the efficiency of the enterprise LLC "Regionstroy", Bryansk
Economic efficiency is the most important socio-economic category, which is characterized by the properties of dynamism and historicity...
Assessment of the economic efficiency of an investment project, taking into account the risk factor
Static methods for assessing the economic efficiency of investments are simple methods ...
Indicators to assess the effectiveness of the economic activity of the enterprise
The calculation of indicators for assessing the efficiency of activities and the level of economic security was made on the basis of the data of the annual balance sheet of CJSC " Trading house". Data on break-even ratios are given ...
Development of a business plan for OAO Trest "Mordopromstroy" to master the technology of frame-monolithic housing construction
Development and calculation of a business plan for organizing the technical development of a construction company
The word "business" means any occupation, a business that generates income. A person doing business is a businessman, that is, a businessman, merchant, entrepreneur ...
Statistical Study of Efficiency industrial production
The system of production efficiency indicators should provide a comprehensive assessment of the use of all enterprise resources and contain all general economic indicators. Very important...
Economic expertise. Theoretical basis business planning
The success of any business primarily depends on how well the business area is chosen, the market situation is correctly assessed, the strategy is chosen and the tactics for its implementation are developed. In doing so, it is necessary to take into account...
- 1. Net present value (net present value, net present value)
- 2. Profitability index
- 3. Internal rate of return
- 4. Payback period
Net Present Value - NPV
This indicator is based on a comparison of the discounted value of cash receipts for the forecast period.
Under the cash receipts is understood the sum of net profit and depreciation.
R i = P ri + A i
where R i - element of the cash flow in the i-th period of time;
P ri - net profit in the i-th period of time;
A i - the amount of depreciation in the i-th period t.
When calculating the net present value, the current annuity function F 4 - with an even distribution of income over the years, or the function F 3 applied to each element of the investment income stream, summarized over the forecast period, is applied.
PV i - present value of cash receipts in the i-th period of time /
IC - start-up investment
The use of this model assumes that the following conditions are met:
- - it is considered that the investments have been made in full and in full;
- - investments are valued at their cost at the time of settlement;
- - the process of return begins after the completion of the investment.
If the analysis is carried out before the start of investment, then the amount of investment costs should also be brought to the present moment.
The NPV calculation model in this case is as follows:

where IC t - investment costs in period t (t=1,n 1)
R i -income in period i (i = 1,n 2)
n 1 - duration of the investment period
n 2 - the duration of the return period
If NPV >0, then the project is effective and should be accepted.
If NPV< 0, то проект убыточен и его следует отвергнуть.
If NPV = 0, the project is neither unprofitable nor profitable, and additional information should be attracted to evaluate it.
Example. The enterprise is considering a business plan for the acquisition of new equipment, the cost of acquiring it is 20 million rubles. The term of operation is 4 years. Depreciation is accrued evenly at 25% per year. The proceeds from the liquidation of equipment at the end of its useful life cover the costs of its dismantling. Current expenses by years (net of depreciation) are carried out as follows: 4900 rubles. in the first year of operation, and then increase annually by 4%. The income tax rate is 24%. The interest rate for the loan is 15%. The sales proceeds are forecasted by years: 14,300 thousand rubles, 18,000 thousand rubles, 12,700 thousand rubles, 15,100 thousand rubles.
Calculation of cash receipts, thousand rubles
4918 thousand rubles > 0, therefore, the project is profitable
Profitability Index - PI
The NPV measure has a significant drawback, which is that after calculating the NPV for alternative projects, it may be found that although the net present values of alternative projects are close or the same, they require significantly different investments. For example, an alternative to the considered one is a project in which the sum of the given cash flows by periods is 4988 thousand rubles, and the initial investment is 70 thousand rubles.
To compare alternative projects in business planning, the indicator of return on investment is used.
For the first project PI = 8344 + 1107 + 6824 + 8487 / 20000 = 1,25
(1+0,15) 1 (1+0,15) 2 (1+0,15) 3 (1+0,15) 4
For the second project PI = PV= 4988 = 71,3
If PI< 1 проект убыточен
If PI > 1 the project is profitable
If PI = 1, the project is neither profitable nor unprofitable, and additional information should be involved to evaluate the project.
Internal rate of return - IRR
Borrowed capital is provided by the investor to the borrower for a fee in the form of an interest payment. An increase in the interest rate, as a rule, leads to a decrease in the profitability of the project. It is natural to ask the question: what is the rate of interest at which the project is neither profitable nor unprofitable?
The internal rate of return IRR is the interest rate for a loan at which NPV(r) = 0. That is, in order to determine the internal rate of return, it is necessary to solve the following equation:

This equation is solved using approximate calculation methods. Let r 1 ,r 2 be different interest rates, and r 1< r 2
IRR = r 1 + NPV(r1)(r 2 - r 1)
NPV(r 1) - NPV(r 2)
The values of r 1 and r 2 are chosen such that NPV(r 1)>0; NPV(r2)<0, то есть функция NPV(r) на интервале (r 1 ; r 2) меняет знак с плюса на минус.
Example
Table 6
Calculating the internal rate of return
r 1 \u003d 0.1 r 2 \u003d 0.15
|
Net cash flow, rub. |
1 ( 1+r 1) i |
1 (1+r2) i |
|||
r 1 \u003d 0.1 NPV (r 1) \u003d 152,560 rubles.
r 2 \u003d 0.15 NPV (r 2) \u003d - 131,280 rubles.
IRR=0.1+ 152 560 (0.15 - 0.1) = 0.121 or 12.1%
152 560 + 131 280
The smaller the interval (r 1 ; r 2), the more accurately the calculated IRR.
Let C be the price of borrowed capital. If IRR >C, then the project will be profitable. If IRR Example: the internal rate of return of the business project is 18%. The investor offers a loan at 20% per annum. This offer is not profitable. Payback period of the project - P The payback period of the project is the minimum time interval during which the investments are covered by cash receipts from the project. where P - payback period; Average annual discounted net cash flow. In our example, with r = 0.1 = 272 700 + 371 700 + 540 720 + 532 740 + 434 700
= 430 512 P= 2000 000
= 4.64 years. When using performance criteria, it should be taken into account that they can give conflicting results when comparing alternative projects. For example, a project that gives a large NPV value may turn out to be the worst according to the PI criterion. The IRR criterion, as a rule, is not used to compare alternative projects. The payback period does not give an idea of the cost parameters of the project. Test questions: 7. How is the value of the profitability index interpreted ... Probability allows you to predict random events, it gives them a quantitative qualitative assessment. At the same time, the level of uncertainty and the degree of risk are reduced. The uncertainty of the economic situation, which gives rise to risk, is largely determined by the counteraction factor. Countermeasures include: The entrepreneur, in the course of his actions, must choose a strategy that will allow him to reduce the degree of opposition, which, in turn, will reduce the degree of risk. The mathematical apparatus for choosing a strategy in conflict situations, when opposing interests collide, is provided by game theory. It allows the entrepreneur to determine a reasonable minimum degree of risk. Therefore, the risk has a quantitatively defined probability of loss, which is based on statistical data and can be calculated with a fairly high degree of accuracy. To quantify the magnitude of the risk, it is necessary to know all the possible consequences of any individual action and the likelihood of the consequences themselves. In relation to economic problems, the methods of probability theory are reduced to determining the values of the probability of occurrence of events and to choosing the most preferable event from possible events, based on the largest value of the mathematical expectation. In other words, the mathematical expectation of an event is equal to the absolute value of this event, multiplied by the probability of its occurrence. For example: There are two options for investing capital. The statistics available for similar provisions show that when investing in event “A”, making a profit in the amount of 25 thousand rubles. has a probability of 0.6, and in the project "B" profit in the amount of 30 thousand rubles. has a probability of 0.4. Then the mathematical expectation of profit on the project "A" is: The probability of an event occurring can be determined in an objective or subjective way. The objective method is based on calculating the frequency with which a given event occurs. For example, if it is known that when investing in an event, a profit in the amount of 25 thousand rubles. was received in 120 cases out of 200, then the probability of obtaining such a profit is 0.6 P = 120/200 = 0.6 The subjective method is based on various qualitative assumptions. Such assumptions may include: When the probability is determined subjectively, then different people can set its different value for the same event. The magnitude of the risk is measured by three main criteria: The mean expected value is the magnitude of the event that is associated with the uncertainty of the situation. The mean expected value is a weighted average of all possible outcomes, where the probability of each outcome is used as the frequency or weight of the corresponding value. The mean expected value measures the outcome we expect on average. Example: It is known that when investing in event "A" out of 120 cases, a profit of 25 thousand rubles. was received in 48 cases, a profit of 20 thousand rubles. in 36 cases, a profit of 30 thousand rubles. in 36 cases. The average expected value is determined by: Calculation of the probability of the event "A" - profit of 25 thousand rubles. "B" - profit of 30 thousand rubles. "C" - profit of 30 thousand rubles. P (A) \u003d 48/120 \u003d 0.4; P (B) \u003d 36/120 \u003d 0.3; P(C) = 36/120 = 0.3 P(A) + P(B) + P(C) = 1 Рr - expected profit. Pr = PrA * P(A) + PrB * P(B) + PrC * P(C) РrА, РrВ, РrС - profit from activities A, B, C, respectively. Pr \u003d 25 * 0.4 + 20 * 0.3 + 30 * 0.3 \u003d 25 thousand rubles. The average value is a generalized quantitative characteristic and does not allow making a decision in favor of any option for investing capital. To make a final decision, it is necessary to measure the variability of indicators. The volatility of a likely outcome is the degree to which the expected value deviates from the mean. In practice, two criteria are usually applied for this: Variance, which is the weighted average of the squares of the deviation of the indicator values from the expected average. where is the dispersion; - expected value for each case; Average expected value; Number of observation cases. 2. Standard deviation is defined as follows: The standard deviation is a named value and has the same dimension as the variable attribute. Dispersion and standard deviation are commonly used as a measure of absolute variability. The coefficient of variation is calculated as the ratio of the root mean square to the arithmetic mean and shows the degree of deviation of the obtained values from the mean. where is the coefficient of variation; The average expected value of the feature. The coefficient of variation is a relative value, it varies in the range from 0 to 100%. The higher the value of this coefficient, the stronger the volatility. The following qualitative scale has been established, which allows interpreting various values of the coefficient of variation: Example: The use of volatility estimates in a comparative analysis of two business projects. Calculation of volatility estimates. Project "A": 25; (X - X) = 25 - 25 = 0 variance = 1800/ (48+36+36) = 1800/120 = 15 standard deviation = v15 ? ±3.9 units V = (±3.9/25)*100% = 15.5% According to the project "A", the assessment of volatility is moderate. Project "B": Variance = (3000 + 1000) / (30 + 50 + 100) = 22.2 standard deviation = 4.7; V = (±4.7/ 30)*100% = 15.7% Conclusion: the coefficient of variation calculated according to the statistical data on capital investment in the project "A" is 0.2% less than the same indicator for the project "B". Therefore, we can conclude that project "A" is somewhat less risky than project "B". Test questions: Literature: Mastering the basics of economic literacy is a mandatory task for every novice businessman who is aimed at building a stable and promising enterprise. Drawing up a plan for the implementation of a planned business undertaking is an understandable and necessary measure for everyone. One of the stages of obtaining information about the extent to which the planned business undertaking meets the expectations assigned to it is the evaluation of the effectiveness of the business project. Building a business rarely starts from scratch. Usually the founder has the initial capital, there is an idea that can become profitable, and there are associates who are willing to make intellectual and labor efforts to achieve their goals. In the post-Soviet mentality, the formulation of business goals and their assessment of viability, until recently, was something not entirely mandatory. This is due to a number of reasons, the essence of which boils down to one thing: you will spend time and money on making forecasts, but there are no guarantees that the forecasts will come true. There is, of course, some truth in this assessment of the situation. However, who, if not an entrepreneur, should try to raise the level of domestic business processes, improve their own professionalism and force the state machine to meet modern socio-economic demands? In this regard, the evaluation of the effectiveness of their own business projects should be carried out primarily by the entrepreneur himself and on his individual initiative. The initial data for conducting a comprehensive analysis can be ordered from specialized specialists. One of the most informative analytical studies of the aspects of the effectiveness of a planned entrepreneurial undertaking is the analysis and comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness of a business project. The essence of the approach is that the project is analyzed in several directions: Conclusions for each of these areas are the basis for the formation of both short-term and long-term strategies of the enterprise. Despite the fact that in the process of its development, a business needs to solve many different tasks, the most important indicator of the effectiveness of an undertaking is its economic efficiency. The calculation of the economic efficiency of a business project should give an idea of the main points: In order to make all the necessary calculations, the entrepreneur must have information about the following aspects of future activities: These indicators are used as benchmarks for the effectiveness of a particular business. It is under them that all internal economic processes related to the cost part and the level of sales are regulated. The need for additional research in terms of the possibility of achieving the goals is that such research allows you to adjust the main economic indicators. This allows the businessman to get a more detailed picture of the conditions under which the project will be implemented: It is difficult to argue that all of the above aspects can significantly affect the development of a business, both in a positive way and vice versa, so it is imperative to be aware of them and take them into account. Ideally, the formalized conclusions of the evaluation of the effectiveness of a business project should become part of the business plan. A business plan may be needed not only as a route map for the implementation of the project, but also as the main part of the presentation of your business to those structures on which the receipt of the necessary resources for the development of the business depends. The main criteria for evaluating business projects by third-party (budgetary, investment, etc.) organizations are as follows: These are the so-called external criteria, the evaluation of which allows the tender or investment commission to carry out a preliminary selection. In addition, low-cost and low-cost business ventures are evaluated according to these aspects. They are designed not so much to solve the economic problems of the country and the region as social ones: to provide jobs and support regional small businesses. Projects of large companies for investing and using investments are evaluated by professional experts who take into account all the individual features of the entrepreneurial project proposed for consideration.
With the help of economic calculations, the most important financial characteristics are predicted, which are used as criteria for evaluating business plans: net profit, the volume and maturity of the loan, the payback period of the project, the forecast of income by months. In the process of economic analysis of the business plan, the following cash flow indicators were considered: 1) receipt of funds: capital investment plan, Revenue from the sale of services; 2) spending money: Fixed costs (current costs), Variable costs (business expenses), A single tax on imputed income. The difference between cash inflow and outflow at each calculation step is the net cash flow for the project. The period of investment investments is characterized by a slight excess of cash receipts over expenditure. This is due to the fact that during this period large investments are made in fixed capital, as a result of which the implementation of a business plan requires the attraction of financial resources. Borrowed funds were considered as a source of financing. The expenditure of funds includes financial costs (interest). The economic viability of the business plan is ensured in the case of a non-negative balance of cash accumulation over the entire life of the project. Three options for the cash flow statement were considered in accordance with the developed scenarios: 1) realistic (growth will average 20%); 2) pessimistic (there will be no increase in income); 3) optimistic (as a result of the project implementation, revenues will grow by an average of 40% per month). Calculations to justify the economic efficiency and viability of the business plan were carried out taking into account the characteristics of a particular object. A period of 1.5 years was taken as the life of the project. This period was considered with a breakdown by months for a more detailed study of the initial period during which capital investments are made and the loan is repaid. The need to consider project income for 1.5 years is due to the fact that the repayment of the main body of the loan occurs one year after the initiation of the project and it is necessary to determine the period during which the organization will accumulate the necessary funds to repay the loan. The rate of inflation is taken equal to the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia, and it is assumed that the rate of inflation is constant, since the dynamics of prices for products and resources make it possible to speak about the homogeneity of inflation. The results of economic calculations of the business plan are reflected in table. 1--4, applications 1-3 and in fig. 4, 5. Investment plan This section presents the planned work at different stages of the business plan implementation and the financial resources required to implement the project. Table 1 The cost of capital works on the project In today's market conditions, the expansion of the organization is unthinkable without appropriate advertising support. Due to the fact that the Molodezhnoye express cafe has been operating for a relatively long time and profitably, has regular customers and is quite well known in the market, it can be assumed that significant investments in advertising will not be required, however, a small advertising campaign should be carried out, as it will give a new impetus to development organizations. Advertising costs are presented in table. 2. table 2 Costs associated with increasing the firm's market share Definition of loan interest The monthly interest payment on the loan provided can be calculated using the formula where S is the amount of the loan provided, r -- interest rate. Since it is planned to take a loan in the amount of 500,000 rubles. and at 13%, we get X \u003d 500,000 x 0.13: 12 \u003d 4375 (rubles). Table 3 The cost of wages for employees of the express cafe "Molodezhnoye" (rubles / month) Fixed and variable costs of the organization Fixed costs - these are costs, the size of which practically does not change, regardless of the received turnover. The composition of fixed costs is given in table. 4. Table 4 Fixed costs of the express cafe "Molodezhnoye" (rub.) Variable costs are costs whose value depends on the volume of services provided by the organization. When determining the actual size of variable costs, very often they proceed from the indicator of marginal profit: Marginal profit = Income - Fixed costs. Rice. 4. The third scenario - optimistic - growth of monthly income by an average of 40%. Rice. 5. The first scenario - realistic - growth of monthly income by 20% after the implementation of the project. The second scenario is the pessimistic one - there will be no increase in visitors and income. The third scenario - optimistic - monthly income growth by an average of 40% If it is impossible to directly determine the value of marginal profit (due to the lack of accounting in accordance with applicable law), it is recommended to use the average value for the industry. The calculation of variable costs was based on the assumption that the marginal profit of Molodezhnoye LLC is 22.5% (average for organizations in this industry whose performance parameters are similar to those under consideration). It can be seen from the calculations (Appendix 1) that the organization initiating the project is able to repay the loan in full 10 months after receiving the loan. Let's analyze the picture presented in the figures. Considering the data in Fig. 4, pay attention to the following. The scatter (value of deviations) of potential income schedules under the three scenarios is much less than the scatter of project liquidity schedules. This is due to the so-called multiplier effect of the accumulation of financial resources, i.e. income growth by 1% means the possibility of growth of capital investments already by several percent without loss of financial stability. Only the pessimistic scenario assumes a negative liquidity of the organization in the second year of the project (Appendix 2). The other two options, including the optimistic one (Appendix 3), guarantee the sustainable operation of the organization at the current interest rate of borrowed financial resources. The graph in fig. 4 reflects the method of capital expenditure that provides the maximum burden on the finances of the organization. If capital investments are made not for three months, but longer, then the liquidity of the project being developed will increase several times. This indicates a certain margin of safety for this business idea. Analyzing fig. 5, you need to pay attention to the sharp drop in the liquidity of the organization in the 12th month of the first year of the project, which is due to the payment of the main body of the loan during this period. According to the realistic scenario of the proposed development of events, Molodezhnoye LLC has a certain margin of safety throughout the entire project implementation period, i.e. the level of liquidity meets all the necessary requirements, and fluctuations in the level of cash financial resources do not affect the state of the organization in the long run. If it is not possible to achieve income growth, then it is supposed to reach the level of profitability only after three six months from the moment the project was initiated. However, this development of events ensures profitability (albeit somewhat less) in the long run. In any case, the organization should achieve the development of events according to the third scenario (income growth by 40% per month), which will lead to a sharp jump in business profitability and will allow in the future to do without borrowing funds, for development there will be enough own financial resources. Project implementation efficiency indicators (Integral indicators) The main integral indicators of project efficiency are: 2) net present value, or net present value (NPV); 3) internal rate of return, or marginal efficiency of investments (return on investment ratio) (IRR). To determine these indicators, discounted amounts of receipts and payments are used. The amount of income includes income from the operation of the express cafe "Molodyozhnoye". The amount of payments includes fixed costs (see Table 4), variable costs, taxes (single tax on imputed income), interest payments on the loan. For this business plan, all three project performance indicators are calculated in accordance with the assumed realistic scenario (the cash flow statement for this option is given in Appendix 1). The discount factor in all three options is the same and is taken equal to the discount rate of the Bank of Russia (13% per annum). Obviously, if the expected revenues correspond to the pessimistic scenario, the main integral indicators will be lower, and if the optimistic scenario, they will be higher than those given in this business plan. The discounted amount of receipts, reduced to the present level, is 6,694,215 rubles, and the discounted amount of payments, also reduced to the present level, is 167,273 rubles. The profitability index, or discounted income ratio (PI), for effective projects should not be less than one. This index is determined by the ratio of the discounted amount of receipts to the discounted amount of payments: Net present value, or net present value (NPV), is defined as the difference between the discounted amount of receipts and the discounted amount of payments. This indicator is an estimate of the present value of future income. For effective projects, NPV must be positive. In our case NPV= 62 344 rub. Internal rate of return, or marginal efficiency of investments (return on investment ratio) (IRR). A discount rate is calculated for which the present value of the net proceeds from the project is equal to the present value of the investment. For this project, the IRR indicator is determined using MS EXCEL computer spreadsheets using discounted amounts adjusted for the future period: the internal rate of return of the project is 41.75%, i.е. margin of profitability of the developed project is over 28.75% per annum.


![]()
Who evaluates and how
A complex approach
Economic analysis

Assessment of additional factors

Expected Result
Key factors for evaluating business performance: Video


![]()








Layout of the house, plans of houses and cottages
Small Business - Home Production Ideas
History of JANOME. Sewing machines. Janome, Veritas, Pfaff Sewing machine janome manufacturer country
Working with the tattis system
Properties of copper and its application