With the beginning of development in Russia entrepreneurial activity associated with cooperative activities, privatization, small business development, entrepreneurship statistics began to take shape. Its main object is an enterprise or a separate individual who independently carries out its activities.
The tasks of statistics in the field of entrepreneurial activity are to analyze the activities of registered and actually operating business entities, their distribution by type of activity, organizational forms, sizes, where both indicators of the number of employees and the volume of output can act as drapery features.
Statistical information about entrepreneurial activity is based on a certain system of information sources, which includes lists of past state registration commercial organizations, individual entrepreneurs, farms.
Statistical analysis will help us to study more deeply the structure, development and formation of small business in the world economic economy.
In February 2012, Rosstat published the preliminary results of a comprehensive survey of small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs). For the first time, data were obtained on the number of actually operating micro, small and medium enterprises and individual entrepreneurs (IP). It turned out that it is significantly lower than the number of formally registered SMEs - by almost 1.5 million units (Table 1).
Table 1. - Key figures on the statistics of small and medium-sized businesses in Russia, according to the preliminary results of the continuous observation of Rosstat in 2011.
Number of enterprises of construction workers IPMicro-enterprises (legal entities)Small enterprises (legal entities)Medium-sized enterprises (legal entities)SMEs, total Number of registered, units 2.9 million 1.4 million 229 thousand .25.7 thousand 4.6 million Number of employees, units 1.9 million 1 million 227 thousand 25.7 thousand 3.2 million Number of employees, people 5.3 million 3.9 million 7.2 million 2.6 million 19 million*Revenue, RUB 4.5 trillion 5.7 trillion 13.3 trillion 7.3 trillion 30.8 trillion
For comparison, we present the key indicators of the SME sector in Russia and some EU countries, which we will consider in Table 2.
small business entrepreneurship russia
Table 2. - Main indicators of the SME sector: Russian Federation and some countries of the European Union, 2010
Some EU countries Russia Germany France Italy Great Britain Poland Netherlands Estonia 13.6 million 8.8 million 12.3 million 9.8 million 5.9 million 3.6 million 0.3 million Revenue, trln. EuroRevenue of the SME sector30.8 trillion. r.Eq 0.8 tr.eur2.21.91.92.20.50.80.02
The table shows that Russia has an advantage over other countries in terms of the number and employment of SMEs. This characterizes our country as a developing country striving for economic growth.
The main law of Russia, defining legislative framework activities of small enterprises is the law "On the development of small and medium-sized businesses in Russian Federation" dated July 24, 2007 No. 209-FZ. It sets limits for small enterprises on the average number of employees: up to one hundred people inclusive. Among small enterprises, micro enterprises stand out - up to fifteen people. capital in the amount of 25%.
Average size of companies: on average, 32 people work at a small enterprise, 4 people at a micro enterprise, and 101 people at an average enterprise. The annual revenue of a small enterprise, on average, is about 60 million rubles, micro enterprises - 5.6 million rubles, and medium - almost 283 million rubles.
The highest average annual revenue- almost 500 million rubles. per enterprise - for individual entrepreneurs, which, by the number of employees, can be classified as medium-sized enterprises, and the lowest - 1.4 million rubles. - for individual entrepreneurs with the scale of a micro-enterprise, where, on average, only 2 employees are employed.
The vast majority of existing MP-yur. 85.9% of persons are micro-enterprises with up to 15 employees. Exactly these small companies provide every third workplace and 43% of the revenue of the entire SME sector.
Almost all IP - 99.9% - fall within the SME sector. But about 100 individual entrepreneurs in terms of the number of employees can actually be attributed to large enterprises- they have from 251 to 800 employees. Approximately 40% of IEs worked in 2010 as employees at other individual entrepreneurs or in other companies.
Important for considering trends in the development of small business is to assess the share of small businesses in the sectors of the national economy of our country
Small businesses currently specialize in five main activities.
The first type is manufacturing industries, to which
worn by enterprises producing food products producing textile and clothing products, leather goods, wood products, leading publishing and printing activities, enterprises of the oil, chemical, metallurgical, machine-building industries, as well as other similar industries.
To this kind economic activity how construction is classified as small enterprises engaged in new construction, reconstruction, overhaul and current repairs of buildings and structures, including individual construction and repairs on orders from the population.
The next type of economic activity is wholesale and retail trade, repair vehicles, motorcycles, household products and items for personal use. In the future, this type of activity will be called briefly - trade.
Small enterprises of transport and communications include enterprises of land, water, air transport, as well as all types of telecommunication enterprises, postal and courier activities.
The scope of economic activity related to real estate transactions includes not only various real estate transactions, rental and related services, but also the rental of machinery and equipment without an operator and the rental of household and personal items, as well as a number of ancillary services. .
The sectoral structure of Russian small business has remained the same - trade and repair of motor vehicles and household products (38%), operations in real estate and services (21%), construction (11%) are in the lead. The share of SME-legal entities in the field of mining, production and distribution of electricity, gas and water is quite large (11%).
Figure 2.1.
The number of the main and largest segment of small business - trade and repair of household products decreased by 2.6 thousand enterprises, like most other sectors of small business. The growth in the number of small businesses in the 1st quarter of 2012 was mainly due to 8 thousand new enterprises in the field of real estate and services related to it and 3.5 thousand new housing and communal services enterprises, which were most likely created by the formal splitting of existing enterprises to optimize taxation .
Consider the birth and death rate of small enterprises in 2012.

Figure 2.2.
According to Rosstat for the 1st quarter of 2012, the birth rate of small enterprises (number of new enterprises per 1 thousand existing ones) is 22.3, which is 0.6 enterprises less than in 2011. And the mortality rate of small enterprises (the number of officially closed per 1 thousand existing ones) is 21.4, which is 5.1 enterprises more than in 2011. As can be seen from the graph of births and deaths of small businesses (2012 made on the basis of the 1st quarter), a critical moment will soon come for small businesses when more enterprises will close than open.
Thus, if the trend of the 1st quarter of 2012 on the birth and death of small businesses in 2012 continues, then no efforts to divide and sprout housing and communal services will not cover the reduction in the number of small businesses.
Another good news is that there are 15% more people employed in small business than last year (6.15 million compared to 5.262 million). If the number of small businesses, except for housing and communal services and real estate, is declining, where does this growth of almost 800,000 workers in small businesses come from? This increase could well have occurred due to the emergence of "small businesses" in the housing and utilities sector and real estate.
As for employment in the SME sector by industry - by the main type of activity of really operating enterprises and individual entrepreneurs, among SMEs
legal of persons, most jobs are provided by trade and repair enterprises (25%), real estate operations (21%), mining, production and distribution of water, electricity and gas (19%), as well as construction firms(13%). Agricultural enterprises provide 7% of all jobs.
Among individual entrepreneurs, in comparison with enterprises, even more workers are employed in the field of trade, repair and services - 57% of all jobs. The second and much smaller share of jobs - 9% - is noted in the field of transport and communications, 9% - in the field of mining, manufacturing, production and distribution of electricity, gas and water. 7% of all jobs are accounted for by individual entrepreneurs engaged in operations with real estate, and individual entrepreneurs in agriculture.
We can conclude that it is too early to talk seriously about small business in Russia as any significant factor in its development.
We have 238 thousand enterprises in 1 square. 2012, in the US for comparison, in 2011 there were more than 26 million. But our country does not stand still and is developing rapidly compared to some EU countries. Over the past 3 years, 124.5 billion rubles have been allocated to support small and medium-sized businesses in Russia, and in 2013-2015 it is planned to allocate 67.8 billion rubles to the regions from the federal budget. We hope that in a few years Russia will take its place in the global economy
Business statistics allows you to identify the most profitable industries and determine which direction needs to be developed more than others. Such information makes it possible to understand where and by whom to work and what specialty is better to get in order to be successful and wealthy.
Statistics by country
Business statistics in the world allows you to rank the countries in which the most favorable conditions for entrepreneurship are created. The data is presented in table:
| Country | Place in the world |
||||
| By the number of registered enterprises | Lending | For international trade | By the number of liquidated enterprises | ||
| New Zealand | 1 | 1 | 1 | 55 | 34 |
| Singapore | 2 | 6 | 20 | 41 | 29 |
| Denmark | 3 | 24 | 32 | 1 | 8 |
| Hong Kong | 4 | 3 | 20 | 42 | 28 |
| South Korea | 5 | 11 | 44 | 32 | 4 |
| Norway | 6 | 21 | 75 | 22 | 6 |
| Great Britain | 7 | 16 | 20 | 28 | 13 |
| USA | 8 | 51 | 2 | 35 | 5 |
| Sweden | 9 | 15 | 75 | 18 | 19 |
| Macedonia | 10 | 4 | 16 | 27 | 32 |
| Estonia | 12 | 14 | 32 | 17 | 42 |
| Latvia | 14 | 22 | 7 | 25 | 44 |
| Georgia | 16 | 8 | 7 | 54 | 106 |
| Germany | 17 | 114 | 32 | 38 | 3 |
| Lithuania | 21 | 29 | 32 | 19 | 66 |
| Canada | 22 | 2 | 7 | 46 | 15 |
| Kazakhstan | 35 | 45 | 75 | 119 | 37 |
| Belarus | 37 | 31 | 101 | 30 | 69 |
| Armenia | 38 | 9 | 20 | 48 | 78 |
| Russia | 40 | 26 | 44 | 140 | 51 |
| Azerbaijan | 65 | 5 | 118 | 83 | 86 |
| Kyrgyzstan | 75 | 30 | 32 | 79 | 130 |
| Ukraine | 80 | 20 | 20 | 115 | 150 |
| Uzbekistan | 87 | 25 | 44 | 165 | 77 |
| Tajikistan | 128 | 85 | 118 | 144 | 144 |
Small business indicators in the world
Business statistics allow us to conclude that small businesses make a big contribution to the state economy. Especially in leading countries. According to statistics, small business in the world is able to provide significant income, many jobs, and growth.
In the US, ½ of the working-age population works at MB enterprises. There are more than 20 million of them registered in America. Analytics show that every third family in the USA is related to business. More than 40% of GDP is accounted for by IBE.
Developed countries provide great support to small businesses and get a good return from it in the form of development of innovations, employment of the country.
The statistics of the Association of European Businesses shows that the IBE in the EU countries is developing very quickly. Small business abroad is at a higher level than in Russia. It is one of the components of economic development. Small business in Europe according to statistics is from 70% to 90% of all enterprises. More than half of the population of the EU country works in this area.
According to statistics, small business is developing most actively in Germany. The contribution of MB enterprises to the country's economy is almost ½ of everything. More than ½ of the able-bodied population is provided with jobs at the expense of small businesses. SMEs make up 99% of all enterprises in the country. Many of them entered the world market. More than 1,000 German small businesses have become world leaders.
Data for Russia
Business statistics in Russia over the past 10 years show the closure of more SB enterprises than were opened. In our country, only 4% of enterprises exist for more than 3 years. The rest die much earlier. Many close in the first year of their existence. Less than 20% of the total GDP is accounted for by small businesses in Russia. Statistics confirm these figures. Here, unlike in Europe and the United States, they do not provide adequate support to small business enterprises.
Business statistics in Russia show that over 5 years the number of enterprises has increased by an average of 4%. The number of closed business entities increased by 11%.
What are the business opening statistics according to Rosstat for 2016-2017? 3.5 million entrepreneurs were registered in our country. However, more than 7 million have ceased their activities. Business closure statistics are simply frightening.
Statistics of business incubators in Russia have identified the main reasons why they stop economic activity. The data is reflected in the diagram:
Below is a graph showing how the small business in Russia according to statistics from 2005 to 2015:
Business development statistics show a negative trend in our country. This happens for a number of reasons. The main problems of business according to statistics:
- high prices for raw materials;
- complex and frequently changing legislation;
- not stable exchange rate of the ruble;
- high lending rates in banks;
- in business;
- high taxes;
- large contributions to the FIU;
- . in business centers states that often such incidents lead to the closure of enterprises due to lack of money for restoration;
- sanctions from other countries;
- crisis, which reduced the demand for services and.
Business lending statistics show that 24% more loans were issued in 2016 than in 2015. New economic conditions forcing entrepreneurs to apply to banks more often. In 2016, banks issued more than 4 trillion. rub. for lending to small and medium businesses. Most often, entrepreneurs take loans in. The diagram shows business statistics by areas for 2013–2014:
As you can see, in Russia there are most enterprises that are engaged in. Their income for 2014 amounted to 15 trillion. rub. The second place belongs to companies that deal with real estate. Their income amounted to about 3 trillion. rub. The amount of capital of organizations providing medical and social services- 194.36 billion rubles. The diagram shows the number of IPs by:
Small business shows the lowest performance in Crimea.
Ukraine, Belarus and Abkhazia
What are the business statistics in Ukraine? This area is far from being at a high level today. total amount tax revenues from businesses in 2013 amounted to UAH 260 billion. According to statistics, not too large a percentage falls on large businesses. Large Enterprises are not major taxpayers. Because there are not many of them in the country. The largest tax revenues, according to statistics, come from small businesses. The IBA accounts for more than 200 billion hryvnias.
Small and medium business statistics brings to the first place in the number of jobs. More than 70% of the population works in small enterprises. Medium and small sell more products than large ones. Small business support statistics show that a lot has been done in the country since 2015. The period for registering enterprises was shortened. Now the procedure takes only 2 days. About 40% of the documents for opening an IP were canceled.
According to statistics, small business in Belarus is developing very slowly. Belarus is far behind other countries. In 2003, the number of IBEs was 2.5 per 1,000 population. In 2010, the figure rose to 7.2. In 2011, there were only 72 thousand small enterprises in the country. In recent years, the number of SMEs has increased by 13%.
Business contribution statistics show that small businesses in Belarus make a small contribution to the country's economy. Of the working-age population, only 13% are employed in the business sector. In developed countries, this figure sometimes reaches 70%. Entrepreneurial activity still remains unattractive for the population of the country.
What are the statistics of venture business in Belarus? This area is practically not developed. The main reasons are that investment is not developed in the Republic, there are no new technologies, there are few initiative people and the market is very small.
Business statistics in Abkhazia show that the most developed industries here are trade and
Industry indicators
Business statistics states that the success of an enterprise largely depends on the industry in which it operates. There are the most and least demanded areas of activity. In Russia, not better times going through p restaurant business. Statistics state that only last year 1.5% of establishments were closed. According to forecasts, in 2017 the figures will increase to 20%. Because of the crisis, Russians prefer to save money and visit restaurants and other similar establishments less often.
Statistics hotel business demonstrates a stable demand for such services. Over the past 15 years, the number of hotels and hotels has increased by 63%. The situation is worse with rest houses and sanatoriums. Most of these establishments have undergone reconstruction and renovation.
According to statistics, the entertainment business is in demand even in times of crisis. The chart shows which sectors of the entertainment industry are the most and least popular:
Network business statistics states that this area attracts a huge number of potential employees and buyers. The annual increase in profits of companies is 20-30%. The number of people working in this area is more than 100 million people.
In America, 20% of millionaires made their fortune in the network business. According to experts, network marketing in the future will be 70% of all enterprises.
The most successful industries and companies
Statistics profitable business demonstrates that there are goods and services that are in demand even in times of crisis. These are clothing, shoes, food, medicines, car repairs and household appliances. Statistics profitable businesses was published in . The rating looks like this:
- private auditors;
- manual therapists;
- specialized clinics;
- accounting services;
- private dentists;
- tax calculations;
- orthodontists;
- lawyers;
- small lending;
- private managers.
Statistics successful businesses states that individuals and companies that provide such services receive the largest net profit. And even times of crisis do not affect their income in any way.
The sharks of business according to statistics include billionaire Michel Ferrero. His company is one of the largest chocolate producers in Europe. In second place is Brad Hughes. His automatic lockers along the freeways have made a fortune of $5 billion. Third place goes to Ralph Lauren. He made his billions in horse polo shirts. In fourth place in the ranking is Jeff Bizos. He is the owner of the world's largest online store. Fifth place belongs to Ty Warner. He made billions from teddy bears.
conclusions
As business statistics show, Russia is far behind Western countries. But if the government takes certain steps and goes to meet the IP, then there will be much more enterprises, which will have a positive effect on the country's economy.
LEVEL OF DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL BUSINESS IN RUSSIA IN COMPARISON WITH DEVELOPED COUNTRIES
Tashtamirov Magomed Ruslanovich 1 , Kalaeva Zalina Zaynalbekovna 2
1 FGBOU VO "Chechen State University”, Senior Lecturer, Department of Banking
2 Chechen State University, 2nd year student of the Faculty of Economics and Finance
annotation
This article is devoted to the issues of conducting and developing small and medium-sized businesses. Various aspects of the organization of small and medium-sized businesses in Russia are revealed in comparison with other developed countries. A comparison is made of quantitative and quality characteristics small and medium business in the Russian Federation and European countries, USA, China and Japan. The most urgent and fundamental problems in the implementation of entrepreneurship by small and medium forms of management are identified. Without creating favorable conditions for doing business in the state, it is impossible to provide an impetus to economic growth and an increase in social welfare, as well as social stability.
LEVEL OF DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL BUSINESS IN RUSSIA IN COMPARISON WITH THE DEVELOPED COUNTRIES
Tashtamirov Magomed Ruslanovich 1 , Kalaeva Zalina Zainalbekovna 2
1 Chechen State University, Senior Lecturer, Department banking
2 Chechen State University, Student faculty of economics and finance
Abstract
This article is devoted to questions of maintaining and developing of small and medium business. Various aspects of the organization in Russia of small and medium business in comparison to other developed countries reveal. Comparison of quantitative and qualitative characteristics of conducting small and medium business of the Russian Federation and the countries of Europe, USA, China and Japan is made. The most actual and fundamental problems in business implementation are determined by small and average forms of managing. Without creating favorable conditions of business in the state, it is impossible to provide a push to the economic growth and increase in public welfare, and also social stability.
Bibliographic link to the article:
Tashtamirov M.R., Kalaeva Z.Z. The level of development of small business in Russia in comparison with developed countries // Modern scientific research and innovation. 2015. No. 10 [ Electronic resource]..03.2019).
Business is a sphere of application of labor, capital, land and entrepreneurial resources. The term "business" and "entrepreneurship" are synonymous. At the heart of business (entrepreneurship) in economic activity is the constant search for solutions to the tasks with a focus on innovation, the ability to attract and use various resources. For the state, this is one of the most important elements of a market economy. Solving many economic problems (increase in revenues to the state budget, formation competitive environment, employment, etc.) depends on the level of development of small and medium-sized businesses.
A large contribution to the development of the Russian economy is made by small and medium-sized businesses. Large enterprises differ from small ones in that large enterprises, on the one hand, create new jobs, but on the other hand, they reduce a number of jobs by automating production, while small and medium-sized enterprises create thousands of times more jobs for people. This is a big plus, as unemployed people get new jobs, inflation problems are solved, the standard of living of the population is growing, and middle class as the guarantor of democracy. Accordingly, the development of small and medium-sized businesses is a priority in the development of the economy.
In countries such as China, USA, Japan and European Union(EU) small and medium business is developing much faster than in Russia. In these countries, the state gives great attention small and medium-sized businesses, supporting them with various programs and benefits, for example, in some EU countries, any business is exempt from paying taxes in the first 2 years, and the cost of credit resources is low compared to Russian business - 4% and 20-25%, respectively .
Table 1. Employment thresholds in enterprises in various countries.
Thus, the report of the International Labor Office notes that small and medium-sized enterprises have significant competitive advantages, require less capital investment compared to large enterprises. Small businesses, unlike large ones, tend to save and invest. Small enterprises have more motivation and goals to achieve certain success, and this has a positive effect on the activities of enterprises. The disadvantages of small enterprises include: the risk of an unstable position in the market, dependence on large enterprises, shortcomings in business management, difficulties in borrowing funds, and others.
So in Russia, the definition of small and medium-sized businesses does not correspond to definitions in other countries, for example: the USA, Europe, China, etc. Let's consider the structure of small and medium-sized enterprises in modern Russian business.
As of January 1, 2015, according to Rosstat, 4.9 million organizations were registered in Russia.
Table 2. Number of enterprises in Russia from 2012 to 2014
Based on the data in Table 2, it can be seen that the predominant number of enterprises are micro-enterprises. There is an increase in micro-enterprises from 2012 to 2013 by 68616 units. From 2012 to 2013 there is a reduction of small enterprises by 8532 units. And in 2014, the number of small businesses increased by 990 compared to 2013. For medium and large enterprises, from 2012 to 2013 there is a decrease by 2015 units, and in 2014 an increase in these enterprises by 680 units.
Rice. 1. Employment in small and medium-sized enterprises by country in 2013
According to this figure, it is determined that in countries such as Italy and China provides jobs for 80% of the population employed in the sector of small and medium-sized businesses, and in Russia this figure is about 30%.
Table 3. The scale of development of small businesses in foreign countries and in Russia
As can be seen from Table 3, small enterprises in Russia have the lowest development rates in comparison with the developed countries of the EU, the USA and China. Having the third place in terms of the number of economically active population among these countries, in Russia only 21.4% are employed in small businesses, the lowest figure. Only in terms of the institutional provision of the population with small enterprises, Russia is ahead of China, however, the reason is the huge population of China. The United States is the most prosperous country in the form of small enterprises, as a result, having the most favorable climate for the implementation of small businesses, the availability of financial resources, support from the state, etc.
The low quantitative and qualitative indicators of the development of small enterprises in Russia are caused by internal reasons.
Small and medium enterprises constantly face various difficulties. The most common problems in Russia for small and medium-sized businesses:
- Administrative: complex legislation, difficulties in registering as a legal entity or individual entrepreneur, control by various state bodies, etc.)
- Tax: no tax holidays, high taxes for small and medium businesses
- Insufficient support from the state
- Monopolism
- Unavailability of loans: high interest rates, refusal to issue a loan
- Lack of qualified specialists
Reasons hindering the development of entrepreneurship:
Analyzing the business environment that has developed in the country, we can identify a number of reasons due to which the development of small and medium-sized businesses “slows down”:
- Difficult financial and economic situation in the country: inflation, disruption of economic ties, low payment discipline, high level interest rates, weak legal protection of enterprises.
- Low level of organizational, economic and legal knowledge of enterprises, lack of business ethics, culture of management both in business and in the public sector.
- The weakness of the mechanism of state support for small and medium-sized businesses.
The current economic situation has a negative impact on small and medium-sized businesses in all areas. The level of inflation and rising prices for all factors of production put enterprises on the verge of bankruptcy. These include domestic enterprises that are engaged in the production of goods, the provision of services to the population, consuming raw materials, materials, the price of which is growing.
Analyzing foreign and domestic experience in the development of entrepreneurship, one can indicate the advantages of small business:
- Faster adaptation to local business conditions;
- Greater freedom of action for small businesses;
- Low operating costs
- More opportunities to realize your ideas;
- Low initial capital requirement
The author believes that despite the current difficult political situation in Russia, small and medium-sized businesses are developing, but problems persist. Today, for the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation, the availability and accessibility of financial resources plays a significant role. In March 2015, President V.V. Putin has developed a set of financial support measures for small and medium-sized businesses in Russia. To stabilize the development of business in our country, an anti-crisis fund will be created in the amount of about 234 billion rubles.
Barriers to business development: complex legislation, inspection and control of enterprises by various authorities, difficulties in obtaining loans and high interest rates, inflation, low level of knowledge of entrepreneurs, weak state support, etc.
http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_52144/
22.12.2015 00:52
In Russia, there are significantly more small businesses dying than new ones appearing. The share of small and medium-sized businesses in GDP in our country accounts for about 20%, while abroad, only for small businesses, this figure reaches 50%.
In developed countries, support for small enterprises is considered a strategically important task for economic development.
According to statistics, only 3.4% of small businesses in Russia live for more than three years, the rest are closed earlier.
The growth rate of the number of registered individual entrepreneurs in our country remains low - annually their number increases by 4%, while the number of individual entrepreneurs who have ceased their activities increases by 11%. According to the Federal Tax Service, as of April 2015, 3.5 million individual entrepreneurs were registered in the USRIP, and 7.7 million people have ceased their activities for the entire time.
The main reasons for this negative trend are administrative and economic barriers. Firstly, this is a rather complex and voluminous legislation, which, moreover, changes very often. At the same time, there is no full-fledged information about the ongoing changes, and it is expensive to use the services of professional lawyers in small businesses. As a result, entrepreneurs often make mistakes and violate the law, resulting in high fines.
Constantly rising prices for raw materials as a result of fluctuations in the ruble exchange rate and high interest rates on loans are one of the main economic reasons for the underdevelopment of this business segment.
Finally, with the development of opportunities for earning money on the Internet, for many people, the desire to register an enterprise has completely disappeared, because. in this case, it is easier to evade taxes. The last straw for many enterprises was the growth of deductions in Pension Fund more than twice.
Recall that from January 1, 2013, contributions to the Pension Fund of Russia with individual entrepreneurs amounted to 32,479.2 rubles, regardless of the income received. Later, in 2014, they were reduced to 20,727.53 rubles. But as a result of this measure, more than half a million entrepreneurs closed in the country, and new ones were in no hurry to register.
2015 met entrepreneurs with sanctions, declining demand for goods and services, and rising prices. Contributions to the pension fund have grown, now they amount to 22261.38 rubles + 1% of the proceeds, if it is more than 300 thousand rubles. However, on January 1, the so-called law on tax holidays, Federal Law No. 477 of December 29, 2014 “On Amendments to Article 346 and Chapter 26 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” came into force. According to the document, individual entrepreneurs, who open their own business in the industrial, social and scientific fields, can be exempt from taxes for two tax periods. In addition, Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 27, 2015 No. 98-r “On the plan of priority measures to ensure sustainable economic development and social stability in 2015” was adopted, which also provides for a number of tax benefits for small and medium-sized businesses. This noticeably motivated many, and as a result, since January, the number of registered individual entrepreneurs began to increase sharply - by 14% compared to December 2014.

True, the number of those who ceased their activities, unfortunately, also increased.
The introduced amendments to the legislation are designed to stimulate production. In Russia, small business is still mainly engaged in trade, in 2014 the total number of enterprises in this area increased by 2% and amounted to 813,593.

In terms of turnover in small businesses, the first place is also occupied by wholesale and retail- more than 15 trillion rubles in 2014. In second place are enterprises engaged in real estate transactions - almost 3 trillion rubles.
The share of small enterprises in the field of manufacturing is 2456.84 billion rubles in terms of capital, health care and social services - 194.36 billion rubles.
Registration of individual entrepreneurs in general from January 2014 to April 2015 increases monthly by an average of 2%, i.e. for 50 thousand entrepreneurs.

At the same time, the registration of farms is increasing much faster - by more than 3% to 2 thousand farms per month on average, while the main peak just falls on the beginning of 2015.
An interesting fact is that it was in the direction of agriculture and forestry that in 2014 the largest number of small and micro enterprises decreased by 6614 to 55990. thousand rubles. At the same time, the main forces will be thrown into the economy of the south of Russia and in particular the North Caucasian federal district(the total number of individual entrepreneurs and farms in the region has already fallen by 5% compared to April 2014).

Significant funds will also be allocated to support farms in the Siberian Federal District.
Despite the growth of newly registered enterprises, it is practically impossible for the state to keep the existing ones. Only in 2014-March 2015, the activities of 647 thousand individual entrepreneurs and 21928 farms were terminated.
On average, 43,000 individual entrepreneurs terminate their activities every month - this is less than the number of those who register, however reduction is coming at a faster rate, even taking into account benefits (on average, the number of individual entrepreneurs decreases by 5% every month, while the number of new ones grows by only 2%). The main reason is the decision to terminate activities, in total for April 2015 this decision over 5 million individual entrepreneurs have been terminated for all the time.

The dynamics of the closure of farms also confirms this trend. On average, 1,462 farms stop their work every month, and the growth rate of such enterprises is also 5%.
The high cost of compound feed, great difficulties with the sale of products and low profits still force farmers to close. For many enterprises, the problem of selling products is acute, since they are located far from cities and large towns, it is difficult to bring fresh products, or it is associated with high costs.
The quantity has also changed foreign citizens operating in Russia. So, since the beginning of 2015, their number began to decline by an average of 1.5%.

At the same time, the reduction is now affecting almost all regions that account for the largest part of such enterprises - Krasnodar Territory, Moscow Region, Moscow, Rostov Region, etc.

statistics in the field of entrepreneurial activity are the analysis of the activities of registered and actually operating business entities, their distribution by form of ownership, types of activity, legal, organizational forms, sizes, where both indicators of the number of employees and the volume of output can act as grouping signs.
Statistical information about entrepreneurial activity is based on a certain system of information sources, which includes lists of state-registered commercial organizations, individual entrepreneurs, and farms.
In its economic essence, entrepreneurship refers to such a type of activity that aims to earn income from its own or borrowed funds, as well as through indirect participation in such activities (investment in its capital).
The main stimulus and the main statistical indicator in this kind of activity is profit as a form of income that remains after deducting the costs and wages of employees from the proceeds. Profit is the property of the entrepreneur and is spent by him at his own discretion.
Entrepreneurial profit- this is a special kind of income, which, on the one hand, is accompanied by commercial risk, on the other hand, is a reward for commercial success (initiative and activity in the implementation of new ideas, high quality products or services).
The legislation of the Russian Federation provides quite wide economic rights entrepreneurial activities (along with economic obligations):
formation of a production program, independent choice of suppliers and consumers of their products;
setting prices for their products within the limits provided for by law and contractual obligations;
attraction on a contractual basis and use of financial resources, property and certain property rights of citizens and legal entities;
disposal of profits in accordance with the law, the charter of the enterprise and contractual obligations;
opening settlement and other accounts in any bank for keeping funds and carrying out all types of settlement, credit and cash transactions;
independent establishment of forms, systems and amounts of remuneration of employees (at the same time, the maximum amount of remuneration is not limited);
issuance and acquisition of shares and other securities.
Duties include:
timely submission of a declaration of income and payment of taxes and other mandatory payments and fees in accordance with the law;
fulfillment of contractual obligations;
timely application for bankruptcy of the enterprise in case of impossibility of fulfilling obligations to creditors;
full responsibility for compliance with settlement discipline, etc.
In the context of the formation of a market economy, the development of medium and small businesses, small businesses is of particular importance. It is small enterprises that are able to quickly and economically solve the problems of economic restructuring, since they do not require large start-up investments, guarantee a high rate of resource turnover, and quickly respond to changes in market conditions.
Currently, in developed countries, small and medium-sized firms consistently create up to 50-60% of GDP. In table. 20.1 shows the share of small and medium-sized enterprises at the beginning of the 90s (in terms of the share of those employed in industry and the share in total sales).
Table 20.1
Share of small and medium enterprises
| Country | Share of employed in small and medium-sized industrial enterprises, % | Sales of small and medium-sized enterprises in total sales, % |
| Japan | 79,9 | 61,4 |
| Canada | 75,0 | 64,6 |
| USA | 62,0 | 53,8 |
| Italy | 53,4 | 45,1 |
| Great Britain | 53,2 | 43,8 |
| France | 47,0 | 37,4 |
| Germany | 43,2 | 33,0 |
Source: The importance and role of small and medium-sized enterprises in home economies // Small and medium-sized: Transnat, corporation, Role, impact a. policy implication / Un conf. On trade a. development. - N.Y.; UN, 1993, P. 21-22.
In Russia, the small business boom occurred in 1990-1994. and at the beginning of 1998. In Table. 20.2 reflects the dynamics of small business development in Russia.
Table 20.2
Dynamics of small business development in Russia
| years | 1993 | 1994 | 1995 | 1996 | 1997 | Beginning 1998 | Beginning 2001 |
| Number of enterprises | 560 | 865 | 869,9 | 840 | 877,3 | OK. 1 million | 850 |
| Man, million | 7,2 | 11,2 | 11,66 | 10,92 | 11,4 | 13 | 11,1 |
| GDP, % | 6,6 | 10,4 | 10,7 | 10,1 | 10,5 | 12 | 10,2 |
The table is based on sources: 1. Small business. Revival of entrepreneurship in Russia. M .: State Committee of the Russian Federation for the Support and Development of Small Business, 1997. 2. Interfax of January 3, 1998. 3. NG of February 23, 2001.
The largest number of small businesses are concentrated in the field of trade and Catering(30%), 26% - in construction, 23% - in industry.
As for the development of small business in the printing industry, in percentage terms, its share in the industry is relatively small (about 0.14%), but it is quite consistent with the place and role of the printing industry in the modern Russian economy. For comparison: in Germany, printing enterprises of small and medium-sized businesses account for 1.8% of the total industry.
According to sources involved in statistical analysis in the printing industry, by the beginning of 1998, about 3,000 enterprises were engaged in printing activities. Of these, the sector of mixed ownership accounted for 33.3%, and private sector - 14,5%.
Small-scale printing is engaged in the production of small-printed, advertising, small-circulation book and magazine products. According to statistics, in developed countries there is one small printing production unit for every 5 thousand inhabitants. If we proceed from this norm, then we can calculate that there should be at least 29.6 thousand such “points” in Russia, and about 2.5 thousand in Moscow (compare with 3 thousand small printing enterprises in Russia).
According to estimates by domestic statisticians, 2.5-3.5 million small firms are needed for the normal functioning of the Russian economy. Only with this norm, small business will be reliably and organically integrated into the emerging market mechanism of the Russian economy.
For statistical study the scale and structure of entrepreneurship, statistical surveys are conducted of the entire array of business entities that are included in the general population (large and medium-sized ones are surveyed by a continuous method, and small and individual ones are surveyed by a sampling method).
The practice of such surveys in developed countries is limited to annual surveys based on questionnaires, the grouping of questions of which includes the main structural indicators: indicators on sales volume, volume of manufactured products, value added, volume of purchases of goods and services (including for resale), indicators by investments in tangible assets, by the number of employees, the amount wages and some other indicators.
A single set of indicators for all types of economic entities (defined normative document Council of the EU - Council Regulation No. 58/57, 20.12.1996) allows you to compare summary data for various groups of enterprises, analyze the structure of entrepreneurial activity.
Russian statistical practice is gradually approaching the European standard of statistical survey based on a structural approach, however, there are also significant differences. For example, in Russia, individual entrepreneurs are not surveyed on a regular basis and information about them is obtained using the imputed volume method, in which a composite indicator is calculated by multiplying the number of economic units by the average number of economic units of this type, by expert means or from one-time surveys.
Statistical groupings and classifications take into account the threshold value of the indicator for classifying an enterprise as a small enterprise.
Small businesses are those that have:
1) less than 50 employees;
2) an annual turnover not exceeding 7 million ECU or an annual balance sheet total not exceeding 5 million ECU;
3) have the status of an independent business entity, in the capital of which the share of participation of one or more enterprises that are not small does not exceed 25%.
According to Russian legislation (Law of the Russian Federation of June 14, 1995 No. 88-F3 "On state support small business in the Russian Federation”), an enterprise is considered small if it represents a legal entity and meets the following three conditions:
share of property of the Russian Federation and subjects of the Russian Federation, municipal property, property religious organizations, public, charitable and other funds in the authorized capital does not exceed 25%;
the share in the authorized capital of one or more legal entities that are not small businesses does not exceed 25%;
number of employees(person) does not exceed:
A special group of small enterprises under Russian law is made up of enterprises with up to 15 employees, for which a special legal and economic status is defined. The average number of employees of a small enterprise for a given period is determined taking into account all its employees, including those working under civil law contracts and part-time jobs, taking into account the time actually worked, as well as employees of representative offices, branches and other separate subdivisions this enterprise. Small businesses also include individuals engaged in entrepreneurship without forming a legal entity.
The above federal law simplified procedures and forms of statistical reporting are provided for small enterprises, in particular, a limited number of simplified questionnaires are used, while the sample of the survey of small enterprises does not exceed 15-20% of the entire population of small enterprises.
Among a wide range of summary indicators of entrepreneurial activity, special attention is paid to indicators of accounting reports of small enterprises. Decree of the State Committee of the Russian Federation on Statistics dated December 7, 1995 No. 195 approved the form of MP (small enterprises).
The MP form includes information on the main indicators of the financial and economic activities of small enterprises based on the results of their activities for the reporting year.
The MP form has the following indicators.
Section 1. Key indicators
| Line number | Name of indicator | unit of measurement | In fact, for the reporting period | For the corresponding period of the previous year |
| 010 | Average headcount employees (excluding part-time workers and non-roster employees) - total | human | ||
| 020 | Number of part-time workers (without internal ones) at the end of the period | « | ||
| 030 | Average number of employees who performed work under work contracts and other civil law contracts | « | ||
| 041 | Payroll fund for payroll and non-payroll employees (including part-time workers) | thousand roubles. (in whole) | ||
| 042 | From line 041 wages of payroll employees (including part-time workers) | « | ||
| 050 | Revenue (gross income) from the sale of products (works, services) | million rubles (in whole) | ||
| 060 | Balance sheet profit (+) or loss (-) - total | « | ||
| 070 | Fixed assets at original (replacement) cost at the end of the period | « | ||
| 071 | Capital investments | « |
Section 2. Products (works, services)
| Line number | Name of indicator | OKONH/OKP code | unit of measurement | SOEI unit code | In fact, for the reporting period | For the corresponding period of the previous year |
| The volume of products (works, services) in selling prices without VAT, special tax and excise duty for the main type of activity (specify which one) | ||||||
| For other activities | ||||||
| Products (works, services) in physical terms | ||||||
The reports should ensure comparability of data for the reporting period with indicators for the corresponding period of the previous year, based on structural changes and changes in the range of products (products) produced, work performed and services rendered.
When defining individual indicators, it is recommended to use the appropriate sample instructions(according to the statistics of the number and wages; on the composition of funds allocated for consumption; on the composition of the wage fund and social payments; on the procedure for compiling statistical reporting on industrial output, according to capital construction), which are located in the territorial bodies of statistics.
For example, you should determine on line 030 the average number of employees of a printing company from January to September, if it is known that: a) 11 people signed a contract for March; b) 10 people - for 15 days in April; c) 3 people - for 20 days in June; d) in January, February - May, July and August no contracts were concluded.
Decision: 1) the average number of employees in line 030 in March was 11 people; 2) the average number in April - (10 × 15): 30 = 5 people; 3) the average number in June - (3 × 20): 30 = 2 people. Therefore, the average number of employees in line 030 from January to September will be (11 + 5 + 2): 9 = 2 people.









Quality requirements
Peat resources Milling peat extraction
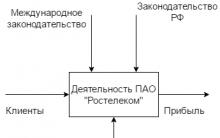
Closed Joint Stock Company Transtelecom
Setting up Wi-Fi equipment
Pasteurization drawer for the selection of "heads" during rectification