Tverdokhlebova Tatyana Valerievna, Associate Professor, Head Department of Economics and International Business of the Mining and Metallurgical Complex of the Institute of Business Process Management and Economics of the Siberian Federal University; director of MIP LLC "SFU UBK", Russia
Danilova Lada Vladislavovna, Associate Professor, Department of Economics and International Business of the Mining and Metallurgical Complex, Institute of Business Process Management and Economics, Siberian Federal University; responsible executor MIP LLC "SFU UBK", Russia
Kuzmin Maxim Sergeevich, Assistant Professor, Department of Economics and International Business of the Mining and Metallurgical Complex, Institute of Business Process Management and Economics, Siberian Federal University; Leading Engineer at MIP OOO SFU UBK, Russia
Substantiation of approaches to calculating the required number of staff employed in maintenance at gold-mining plants
Publish your monograph in high quality for only 15 tr!
The base price includes proofreading of the text, ISBN, DOI, UDC, LBC, legal copies, uploading to the RSCI, 10 author's copies with delivery across Russia.
Moscow + 7 495 648 6241
Sources:
1. Zaitsev N.L. Economics of an industrial enterprise: educational and practical guide, 6th edition / - M .: INFRA-M, 2008. - 412 p.
2. Kuzmin M.S. Substantiation of the methodology for calculating the number of repair personnel // Collection of teaching materials of FGBOU VPO Tula State University. – S. 287–293.
3. Tverdokhlebova T.V., Danilova L.V., Kuzmin M.S. Innovative approaches to the organization of labor of auxiliary production at the enterprises of the mining and metallurgical complex // Periodical journal of the Higher Attestation Commission of the Siberian Federal University "Humanities & Social Sciences". - 2012. - No. 5. - S. 1336-1341.
4. Tverdokhlebova T.V., Vasina G.I., Danilova L.V. Improving the production efficiency of the repair service of the enterprise // Economic sciences. - 2011. - No. 3 (76). - S. 181-186.
5. Tverdokhlebova T.V., Vasina G.I., Danilova L.V. Industry specifics of the actual structure of the working day at the auxiliary production of gold mining enterprises // Economic Sciences. - 2013. - No. 2 (99). – P. 115–118.
6. Magazine and analytical center "Expert-Ural". – M.: Ros. state b-ka, 1997. - http://www.expert-ural.com/.
Rice. 15. Algorithm for planning the need for sales personnel
The main task of personnel planning is to ensure the implementation of enterprise plans in terms of the human factor of the workforce - its size, qualifications, productivity, and recruitment costs.
Another task of planning the number of labor resources of a trade enterprise is to ensure full and efficient employment of all categories of workers. In employment, there must be an appropriate balance between the number of jobs and the number of all workers. Under effective employment under market conditions labor relations understand the degree of use of labor at which the correspondence or excess of results over costs is achieved. At the same time, in order to restore the used labor force, the level of remuneration of each employee must not be lower than the actual living wage.
Since the trade enterprise is open social system, then the used labor needs arise under the influence of two groups of factors:
external;
Internal.
To external factors include market conditions, market structure, competition, socio-economic situation in the country, etc.
Internal factors include the level of technology, the level of work organization, downtime, changes in the volume of work, etc.
Enterprises should strive to establish the optimal number of employees in order to ensure the minimum cost of living labor.
When planning the number of employees of trade enterprises, the use of labor cost norms is of great importance. They are established by the administration of the enterprise in accordance with a certain level of technology, technical equipment and organization of production of this particular enterprise.
For trade enterprises Of the entire set of labor cost norms, the rationing of the number of employees is very important. The norm of the number of employees is the number of employees of a certain profession, qualifications for performing work in a given area (for example, the number of sellers for a given type of store, with a given area and a certain sales volume).
The normative number of managers, specialists and employees is established by functions and positions, depending on the factors affecting the complexity of the work.
The normative method for determining the states was used in Russia until 1992. It was based on the use of recommendations for determining the structure and states of various types of grocery stores and non-food items. The standard for the number of employees at these enterprises was determined taking into account:
Annual plan of goods turnover;
Specializations;
shifts;
An important role in planning the needs of personnel belonging to the category of working professions (salespeople, controllers, cashier controllers, etc.) is played by the balance of working hours. It is compiled for the enterprise as a whole, for structural units, sometimes for each group of workers. The purpose of determining the balance of working time is to establish an effective (useful) fund of time for one employee per year.
It is customary to distinguish between calendar, nominal and effective working time funds.
Calendar fund of working time - number calendar days in the planning period: 365 or 366 days a year (in 2008 - 366 days).
The nominal annual fund of working time is determined by multiplying the number of working days established in the planned year by the work schedule of the enterprise by the duration of the daily shift. In 2008, with a five-day working week with two days off, it was planned to distribute the general calendar fund for 250 working days, including 7 before public holidays with a duration reduced by 1 hour and 116 days off, taking into account three extra days rest due to the coincidence of public holidays with days off. The annual nominal fund of staff working time with a 40-hour working week is then 1,993 hours (). The average monthly number of working hours per worker in this mode of operation of the enterprise is 166.08 hours (1993/12 months).
The useful fund of working hours in days is the difference between the nominal fund of working hours and the number of absences in days. Absences with the permission of the administration and absenteeism are considered lost working hours.
An approximate calculation (and its sequence) of the balance of working time of one worker is presented in Table. 6.
1.6 Justification of the number of teams in the PPP and the number of workers in the team
where - the value of the criterion of sufficient power for the corresponding type of work in the houses of a given program;
The number of workers in the team of rational composition;
Accepted number of workers in the brigade;
Accepted number of brigades in the BCP.
Since the number of teams, as well as the number of workers in a team, can only be an integer, then with a fractional calculated value of "a", the decision on the number of teams should be made with rounding both up and down, so that the performance indicator production standards did not exceed 1.25. At the same time, it should be borne in mind that in the PPP, which is specialized in the construction of underground structures, as well as structures of the above-ground part of the house, due to the limited scope of work, the number of teams in the PPP cannot be more than two. The number of PPP in the organizational system corresponds to the OTM option. With the variant of an equal-rhythmic flow - one PPP for each technological cycle of work. With option 1-2-1-1 - two PPPs for the construction of structures of the above-ground part of the house and one for the rest of the work cycles.
"right">Table 8
Substantiation of the structure of primary production units
|
Types of jobs |
Estimated values |
The decision was made |
|||||||||
|
Equivalent flow option (1-1-1-1) |
|||||||||||
|
underground part |
|||||||||||
|
Aboveground part |
|||||||||||
|
Multi-rhythmic flow option (1-2-1-1) |
|||||||||||
|
underground part |
|||||||||||
|
Aboveground part |
|||||||||||
Taking into account the decisions made on the number of teams, the planned indicator for the fulfillment of production time standards by workers is determined:
The number of workers in the PPP for each cycle of work cannot exceed the calculated value of the criterion of sufficient capacity.
An example of calculating the number of teams in the PPP and the number of workers in the team for the underground part according to the OTM option with an equal rhythm (house).
We accept the number of brigades in the PPP equal to 2.
We take the number of workers in the team equal to 15.
Calculation of the number of teams in the PPP and the number of workers in the team to perform a set of works on the above-ground part according to the OTM option with an equal rhythm (house).
We accept the number of brigades in the PPP equal to 4.
We take the number of workers in the team equal to 34.
After analyzing the number of threads and brigades in the thread, we conclude:
We accept a multi-rhythmic model with the allocation of launch complexes, i.e. one stream along the underground part with a team of 24 people and two streams along the above-ground part, two teams each with 33 people.
Quality, standardization and certification of products at the enterprise
Organization and planning of production for machining shops
The number of jobs required to fulfill the production program...
Organization of production and jobs in the cold shop of the cafe "Stary Dvorik" for 80 people in the hotel "Izmailovo"
Table No. 3 Name of groups of dishes Ratio of dishes,% Number of dishes, pcs Number of names of dishes ...
Enterprise planning
The required amount of equipment (Сj) is calculated according to formula 1, based on two-shift work. , (1) where Ttj - the norm of time for processing the i-th type of product on the j-th group of equipment, min.; Ni - annual program of the i-th product...
Market share and sales forecast
The amount of equipment required to fulfill the production program (output volumes) is determined for the first year, taking into account the production capacity reserve ...
The project of the vegetable shop of the canteen at the university for 130 seats
Taking into account the mode of operation of the enterprise, the number of visitors for each hour of work is calculated by the formula: Nh = (P* Rh * Khh) / 100...
The number of people for each hour of work is determined by the formula: p - the number of seats; c - the turnover of the place per day; x is the percentage of room loading per hour. Our cafe is open from 10:00 to 23:00, without a break. Table 1...
Development of a business plan for a cafe LLC "Breakfast at Tiffany's"
Calculation of the number of dishes Next, we calculate the number of sold dishes in trading floor, since we know the number of visitors. n = N *m, where n is the number of dishes of this assortment group, pcs N is the total number of consumers, people ...
Development of a project for the organization of a commercial Call-center
To solve the problems of calculating the parameters of call distribution systems, the theory of teletraffic and its methods are used, and it is supposed to carry out further calculation of the service of applications received by Call-centers. traffic model...
The number of consumers per day is determined by summing the number of consumers for each hour of operation of the enterprise. The basis of the calculation is the time norm established for the duration of a meal by one consumer ...
Development of the production program of the enterprise, organization of the work of the kitchen, workshops
The calculation of the number of dishes, n, pieces, is carried out according to the formula 2.2: n = N * m, (2.2) where N is the number of consumers per day; m is the food consumption coefficient. For a restaurant, the food consumption ratio is 3.5. The number of dishes in the restaurant will be: n = 2527 * 3...
Development management decisions site improvement current repair on the motor transport enterprise
The number of necessary repair workers is determined by the formula: - fund of working time per 1 worker, hours; people This calculation shows...
Calculation of technical and economic indicators of a structural unit
The calculation of the required quantity for the j-th group of equipment (Сj) is performed in tabular form based on two-shift work. , (1) where Tij is the norm of time for processing the i-th product on j-th group equipment, min; Ni - annual program of the i-th product...
Reconstruction service center LLC "Davpon" Ford Center Komi for servicing car owners in Syktyvkar
Production workers include working areas and sections that directly perform maintenance and repair work. There are technologically necessary (attendance) and full-time (list) number of workers ...
Improving the logistics system at the enterprise wholesale trade
Warehouse network through which distribution is carried out material flow, is an essential element of the logistics system, affecting the costs that arise in the process of bringing goods to consumers, and therefore ...
Determination of unified forms of primary documentation for the accounting of labor and its payment. Consideration of the features of personnel planning of personnel. Calculation of the number of main workers by labor intensity. The study of the essence of the typical nomenclature of positions.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
How is the average number of employees determined for the year, for the month, for each year. Basic unified forms primary documentation accounting for labor and its payment
Personnel planning is a component of the overall planning of activities and development of the enterprise, aimed at ensuring proportional and dynamic development of personnel. It provides for the determination of the total and additional needs in the next period, as well as the calculation of its qualification structure.
Personnel planning includes:
* forecasting the future needs of the enterprise in personnel (for its individual categories);
* study of the labor market (skilled labor market);
* analysis of the state of workplaces of the enterprise;
* development of programs and activities for the development of staff.
Personnel planning helps to maintain the competitiveness of the enterprise, the need for its further development and the optimal use of labor resources.
The practical basis for personnel planning at the enterprise is economic and social development teams.
All employees working at the enterprise are divided into the following categories: workers, managers, specialists, employees, security guards, students.
Workers, as already noted, are divided into the main ones directly involved in the performance of technological operations for the manufacture of products (for example, machine-building enterprise- casters, turners, welders, etc.), and auxiliary, who perform various auxiliary or auxiliary operations for repair, transportation, tool making, maintenance of energy facilities, etc. Workers are also differentiated by profession and qualification. Each profession is divided into specialties and categories depending on the level of qualification.
On the industrial enterprise workers, primarily the main ones, are the main core, since the volume, quality of products, and the level of labor productivity depend on them. From the work of managers and specialists, their level of qualification, responsibility, creativity, performance and labor discipline, attitude to their duties depends on the efficiency of the enterprise, the level technical progress and the level of organization of production.
AT modern conditions it is important to establish the minimum number required for production, improve the structure of personnel at each enterprise.
To determine the required number of workers, their professional and qualification composition, the initial data are the production program, production and time standards, the planned increase in labor productivity, and the structure of work. With enlarged calculations, the total need of the enterprise for personnel ( H) is determined by the ratio of the volume of production ( Ov) to the planned output per worker ( AT):
M = Ov / V .
Accurate calculations of the number must be done separately for certain categories of pieceworker personnel based on indicators of the labor intensity of products, the fund of working hours and the level of compliance with standards; time workers - taking into account the assigned zones and the labor intensity of maintenance, the norms for the number of personnel, labor intensity, normalized tasks, the fund of working hours; students - taking into account the need for the preparation of new working and planned terms of study.
Depending on the specifics of production, various methods are used to determine the number of key workers. Calculating the number of key workers according to the labor intensity of the work, first of all, it is necessary to determine the amount of working time required to carry out the production program. To do this, determine the number of standard hours required for the program, equal to the number of products multiplied by the current norm of time for one product. Considering that the established norms of time (production), as a rule, are overfulfilled, it is necessary to adjust the need for standard hours, calculated on the basis of the current norms of time, by the coefficient of overfulfillment of these norms.
To determine the number of basic workers, it is also necessary to determine the real fund of working time. To do this, they develop a balance of working time for one worker, in which three types of working time are calculated: calendar - the number of days during the planned year; nominal - the calendar number of days in the planned year, excluding weekends and holidays; the planned real or effective working time fund is obtained after the deduction from the nominal fund of all-day losses of working time associated with planned regular holidays, absenteeism due to illness, maternity leave, performance of official and public duties"connections. If we add the actual vacation with the permission of the administration, absenteeism and round-the-clock downtime to the planned real time fund of one worker, then we get the reporting balance of the working time of one worker.
The number of days of the next vacation is calculated based on the indicators of the number of employees by category and the duration of the vacation of individual groups.
Absences related to the implementation of state and public duties are planned at the level of their percentage in the total nominal fund of working time in the reporting year.
Maternity leave is planned based on the reporting data of the base period and the planned change in the proportion of women in the total number of all personnel.
Absenteeism due to illness in the planned balance is determined on the basis of reporting data, taking into account the improvement in sanitary and industrial hygiene and the reduction in diseases due to this.
The actual number of working days in the planned balance is calculated by subtracting absenteeism permitted by law from the nominal working time, namely:
1) regular and additional holidays;
2) maternity leave;
3) absenteeism for reasons of performance of state and public duties.
In the balance sheet, in order to establish the actual number of working days in a year, it is necessary to add to the listed deductions the loss of time due to illness, with the permission of the administration, round-the-clock absenteeism and round-the-clock downtime.
After the actual number of working days per year is established, the average nominal working hours are calculated. The basis for its calculation is data on the number or proportion of workers with different working hours established by law.
However, this duration does not remain unchanged, since there are still legally permitted loss of working time for breaks in feeding children. The size of these losses in the plan is determined on the basis of the reporting data of the previous year, adjusted for the coefficient of change in the proportion of women in the total number of personnel.
The balance sheet includes losses due to intra-shift downtime, determined by "idle" leaves. The duration of downtime in the balance sheet is calculated as follows: for simple leaves, the number of hours is summed up, the resulting amount is divided by the average number of workers.
Multiplying the actual length of the working day according to the report and according to the plan, we get the real (effective) working time per worker in hours.
To determine the number of main workers in terms of labor intensity, the calculation is performed according to the formula:
where Chpl - planned headcount basic workers, man;
thnor- planned scope of work, standard hour;
Kvn- the planned percentage of the fulfillment of time norms.
fpl- the real fund of working time of one average worker, hour.
In some areas, the number of individual groups of main workers employed in the same jobs can be determined by the production rates:
where R- the planned scope of work in natural units of measurement;
Hb- the planned rate of production in the same units for 1 hour.
At instrumentation and assembly work, the number of main workers involved in the control and supervision of units is determined according to service standards (in the chemical, oil refining, metallurgical industries, etc.):
where M- number of pieces of equipment;
FROM- number of shifts;
Cob- coefficient of reduction of attendance to payroll (in continuous production is determined by the ratio of nominal time to secret time, in continuous - by the ratio of calendar time to secret time);
But- service rate, i.e. the number of pieces of equipment that has to be serviced by one worker or a team of workers.
where F
Tno- service time.
The purpose of planning the number of auxiliary workers is to establish rational relationships between the main and auxiliary workers, to develop measures to reduce the number of auxiliary workers.
originality labor activity auxiliary workers determines the specifics in the methods of calculating their number. At work that can be rationed, as well as at work, the volume of which is set depending on the number of service machines, mechanisms and units, the number of auxiliary workers is calculated by the same methods as the number of main workers according to the labor intensity of work, production rates, service rates.
In cases where a production facility or equipment is serviced by a group of workers and their placement inside the facility is not determined, the calculation of the number is carried out according to the standards.
Number norms are determined through service norms or service time norms.
or
where R- scope of work;
But- the rate of service, expressed in the same units as the amount of work;
F- working time fund (shift, month);
Tno- the rate of service time for the corresponding period.
The number of auxiliary workers for whom it is impossible to establish the amount of work, service rates, is calculated by jobs. These include: crane operators, storekeepers, order pickers, etc.
The calculation can be made according to the formula:
where O- number of workplaces;
FROM- number of shifts;
Cob- the coefficient of reduction of the turnout number to the payroll.
Further improvement of rationing should contribute to a wider introduction of methods for planning the number of auxiliary workers according to the labor intensity of the work performed and service standards.
To calculate the number of specialists, the normative method is most often used, based on the application of load standards, maintenance, manageability and the number of specialists.
Load and service standards can be applied in non-production sectors (for example, in healthcare, education, consumer services, etc.). It is advisable to apply the standards for the number of specialists at enterprises in the material production sectors. They provide for the establishment of a relationship between the quantitative and qualitative indicators of the activities of specialists and the main technical and economic indicators of the enterprise, such as the range or range of products, labor productivity, the cost of basic production assets and etc.
where LF- the standard for the number of specialists with higher or secondary specialized education;
World Cup- number of specialists;
And- the value of the selected technical and economic indicator of the enterprise.
At enterprises, the use of the staff-nomenclature method, based on planned indicators for the development of production, is becoming more widespread. typical structures and states, as well as the nomenclature of positions to be filled by specialists with higher and secondary specialized education. Using this method, it is possible to determine both the quantitative need for specialists on the basis of staffing tables, and the qualitative one - on the basis of a typical nomenclature of positions, determines the level of classification and the profile of training of specialists.
A typical nomenclature of positions is developed at all levels of management - from an enterprise to a ministry, and is the initial base for the standards for the saturation of specialists and the need for them in the context of specialties.
The normative saturation coefficient in each planning period is calculated by the ratio of the normative number of specialists to the average payroll workers. The total need is determined by multiplying the standard coefficient of saturation with specialists (Kn) by the planned number of employees in this year(npp):
FM \u003d Kn * NPP
The enterprises analyze the implementation of the plan in terms of the number and composition of employees. The purpose of this analysis is:
* determination of the correspondence between the actual and planned number of employees in general and by certain categories;
* distribution of workers by the nature of production (main and auxiliary);
* determination of the composition of employees by sex, length of service, age and education;
* clarification of the reasons for the deviation of the actual number from the planned;
* establishment of qualitative changes in the composition of employees;
* identifying the size and causes of fluidity.
To determine the correspondence between the actual number of employees for each category and the planned one, it is necessary to determine the absolute and relative surpluses or shortages of employees. The absolute values of excess or shortage are equal to the difference between the actual and planned number. Relative surplus or relative shortage are determined taking into account the implementation of the output plan. personnel position
Example. The planned number of workers is 4,000 people, and the actual number is 4,200 people. At the same time, the production plan was fulfilled by 110%. The absolute surplus is 200 people (4200 - 4000). The same will be the relative shortage of 4200 - (4000 - 110/100) = - 200 people.
A detailed analysis of the headcount by the structure of the staff makes it possible to identify a trend in the change in the number of employees. As a result of the analysis of the composition of workers by profession and qualifications, the average qualification category is determined. For example, the average category of workers - 2.64, and works - 2.34; if the average category of work is lower than the average category of workers, then in this case it is necessary to load the enterprise with heavy and complex work, otherwise the enterprise must pay extra to those workers whose category is higher than the category of the work they perform. This will lead to fund overrun. wages and rising production costs. If the average category of work is higher than the average category of workers, then it is necessary to draw up a plan for the training and advanced training of workers at the enterprise by specialty and category.
Compliance of managers and specialists qualification category can be determined by the results of certification using an analytical indicator - the average certification score:
where Ab is the average attestation score of a given functional group of managers, specialists and employees;
B - a specific attestation score;
H - the number of managers, specialists and employees who have this attestation score (according to a three-point system - "excellent", "good", "satisfactory").
Separately, the additional need for skilled workers and specialists is determined. The method for calculating such a need is the development of balance calculations.
Balance sheet calculations at enterprises is an integral part of comprehensive plans for economic and social development. They are closely connected with the prospects for the development of production, with the introduction of organizational and technical measures.
The additional need of an enterprise for workers of certain vocational groups is defined as the difference between the actual number of workers, adjusted for the assumed in billing period reduction of workers, and the number calculated for the future. The quantitative value of the change in the number of workers in the planned period may be with a plus sign, which indicates an additional need for personnel for certain professional and qualification groups. On this basis, the need for training and advanced training of personnel is determined. In the case of a minus sign, the overall need for a given skill group is reduced. This causes the release of workers.
At enterprises, it is expedient to meet the additional need, primarily through the retraining and advanced training of their employees. To do this, it is necessary to analyze the actual vocational and qualification composition of workers, taking into account the decrease in the number of some workers who, in the planned period, remain at the enterprise or will be released according to certain vocational groups. At the stage of analysis, the need for advanced training and retraining of employees of the enterprise is determined. This creates the prerequisites for their successful professional advancement, identifying the contingent employed in unskilled, low-skilled and unattractive work. Based on this, a plan is being developed to improve the professional and qualification level of employees.
In the balance calculation, it is essential to determine the magnitude of the subsequent reduction of workers and the magnitude of the attraction of personnel in professional qualification groups.
The development of a balance planning method, taking into account the demand and supply of labor in the labor market, technical development, changes in the nature and essence of labor, in the professional and qualification composition of workers, makes it possible to ensure the necessary rates and proportions of expanded reproduction of the labor force.
In case of identifying the need for skilled workers, it is necessary to determine the circle of persons related to skilled workers. It is advisable to single out three groups of qualifications of workers depending on the categories: low-skilled (I-II categories), skilled (III-IV categories), highly skilled (V-VIII categories).
The qualification requirements of jobs and the qualifications of workers are characterized by a coefficient, which is determined by the ratio of the number of workers occupying jobs according to qualification requirements up to the required number of workers.
On the basis of data on the additional need for workers, the required number of students in vocational schools is determined.
The total need for specialists and employees is determined depending on the complexity of assigned functions, controllability standards, the level of management mechanization and taking into account typical staffing tables. The total need for specialists (Ns) is the sum of the number of specialists at the enterprise at the beginning of the planning period (Nsb) and the value of the additional need for specialists (where):
FM \u003d Chsb + Ds
When calculating the need for specialists, it is necessary to scientifically determine the necessary need for an increase (or decrease) in positions filled by specialists in connection with the expansion of the scope of work; to partial replacement of practitioners holding positions of specialists with higher and secondary specialized education, to cover the natural attrition of workers holding positions of specialists and managers.
The additional requirement for the growth of posts is the difference between the total need for specialists of the planned and base periods.
The issue of registration of primary accounting documents is extremely important for business entities. After all, documents drawn up in accordance with the law, in particular, confirm the expenses incurred by the taxpayer for the purposes of calculating income tax, and also prove the validity of applying VAT deductions. Therefore, the use of documents, the forms of which do not meet the established requirements, may lead to adverse consequences for business entities.
In accordance with Part 1 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ, each fact of economic life is drawn up as a primary accounting document. Note that until January 1, 2013, according to paragraph 1 of Art. 9 Federal Law No. 129-FZ of November 21, 1996 "On Accounting" (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 129-FZ), this document was drawn up for each business transaction. However, the concepts business transaction and "fact of economic life" are not identical.
The fact of economic life is a transaction, event, operation that has or is able to have an impact on financial position economic entity, financial results its activities and (or) cash flow ( paragraph 8 of Art. 3 Law N 402-FZ). AT law N 129-FZ, the concept of "business operations" was not defined, but from paragraph 2 of Art. one of this Law it followed that all operations carried out by organizations in the course of their activities were recognized as such.
Thus, contained in law N 402-FZ, the concept of "fact of economic life" is wider than the concept of "economic transaction", which was used in law N 129-FZ. And here the main question arises that worries specialists: what facts of economic life can be drawn up by primary accounting documents that are drawn up according to forms independently developed by the organization, and when does the use of unified forms remain mandatory? After all, the resolutions of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation, which approved the unified forms of primary accounting documentation, have not been canceled.
It should be noted that from January 1, 2014 in Part 1 Art. 9 of Law N 402-FZ clarified: it is not allowed to accept for accounting documents that document facts of economic life that did not take place, including those underlying imaginary and feigned transactions. Definitions of the concepts of imaginary and feigned objects accounting contained in Part 2 Art. ten Law N 402-FZ. In addition, from the said date in Part 3 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ comes into force clarification, according to which ensuring the timely transfer of primary accounting documents for entering the data contained in them into accounting registers and ensuring the reliability of such data is carried out by the person responsible for registration of the fact of economic life. At the same time, the person who is entrusted with the maintenance of accounting, and the person with whom the contract for the provision of accounting services has been concluded, shall not be liable for the compliance of primary accounting documents compiled by other persons with the accomplished facts of economic life.
According to Part 4 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ, the form of primary accounting documents used by an organization (with the exception of public sector organizations) must be determined by the head of the organization. At the same time, the specified Law does not require the mandatory use of unified forms. Recall that until January 1, 2013, apply independently developed forms primary documents it was possible only if the required form was not in the albums of unified forms of primary accounting documentation ( paragraph 2 of Art. 9 Law N 129-FZ). However, we note that even when compiling primary documents not according to unified forms, taxpayers managed to defend in court the legitimacy of recognizing expenses (for more details, see encyclopedias controversial situations for income tax).
When developing your own forms of primary accounting documents, you can take unified forms as a basis by adding or removing some of the details. Moreover, it is advisable to use GOST R 6.30-2003"Organizational and administrative documentation. Requirements for paperwork."
When developing, it should be borne in mind that the primary accounting document must contain the details listed in Part 2 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ:
- name and date of preparation of the document;
- the name of the economic entity that compiled the document;
- the value of the natural and (or) monetary measurement of the fact of economic life, indicating the units of measurement;
- signatures, surnames (with initials), as well as the positions of the persons who made the transaction, operation and those responsible for its registration, or the persons responsible for the registration of the event.
It must be borne in mind that the list of details for individual primary accounting documents can be expanded by others. regulations. For example, the requirements for the details of the waybill are contained in order Ministry of Transport of Russia dated September 18, 2008 N 152, adopted in pursuance Part 1 Art. 6 Federal Law No. 259-FZ of 08.11.2007 "Charter road transport and urban ground electric transport".
In addition to their own forms, business entities can use the recommended by the Federal Tax Service of Russia in Letter dated 21.10.2013 N ММВ-20-3/ [email protected] the form of a universal transfer document. This the form developed on the basis of the current forms invoice, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 N 1137. In addition to the mandatory invoice details listed in p. p. 5, 6 art. 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the universal transfer document contains the mandatory details of the primary accounting document established Part 2 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ. In this regard, such a document can be used both to reflect the fact of economic life for accounting purposes, and for the purpose of taxing VAT and income tax. The procedure for filling in individual details, as well as a list of operations for which a universal transfer document can be used, are contained in the annexes to the specified Letter. In addition, as the Federal Tax Service of Russia explained, additional columns can be included in the form and (or) Additional information necessary for the participants of the transaction being processed (Letter dated 01.24.2014 N ED-4-15 / [email protected]).
As already mentioned, the head of the organization needs to determine the applicable forms of primary accounting documents ( Part 4 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ).
It should also be noted that the primary accounting document can be drawn up in in electronic format (Part 5 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ). And as you know, for the exchange electronic documents it is necessary that the participants electronic document management document formats were compatible. Accordingly, when developing your own forms of documents and their formats, it will be difficult to implement electronic document management. Note that on the basis of unified forms, the Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 21, 2012 N MMV-7-6 / [email protected] recommended formats of widely used documents have been approved: consignment note(TORG-12) and act acceptance and delivery of works (services). In electronic form, these documents can be submitted to the tax authority (to confirm expenses for the purpose of calculating income tax and for other purposes at the request of the inspection) and counterparties.
From January 1, 2013, the requirement to use unified forms when compiling primary accounting documents in law N 402-FZ is absent, but their use is customary for many business entities. In addition, independent development of forms of documents other than unified ones requires time, special knowledge and additional costs for setting software under new forms, and the use of such forms can cause difficulties in working both within the organization and with counterparties.
The ban on the use of unified forms in law N 402-FZ is not contained, therefore, they can still be applied by approving such a decision in the accounting policy or by a separate order of the head.
In addition, it is quite risky to refuse to use all unified forms.
AT Information N PZ-10/2012 The Ministry of Finance of Russia noted that the forms of primary accounting documents established by the authorized bodies in accordance with other federal laws and on their basis (for example, forms of cash documents).
Really, Regulation on the order of conduct cash transactions with banknotes and coins of the Bank of Russia on the territory Russian Federation(approved by the Bank of Russia on October 12, 2011 N 373-P) provides for the use of the following unified forms:
- income and expenses cash orders (form N KO-1 and KO-2);
- cash book (Form N KO-4);
- accounting book of cash received and issued by the cashier (Form N KO-5);
- payroll and pay slips ( form N T-49 and T-53).
These forms are approved by the Decrees of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated 18.08.1998 No. 88, from 05.01.2004 N 1.
Note that these are not all unified forms, which have been mandatory since 2013, despite the freedom to develop their own forms.
In addition, the non-use of unified forms of documents when accounting for labor and its payment may lead to undesirable consequences for organizations. The next section of this special issue is devoted to the application of these forms.
There are other mandatory forms of primary documents. However, the requirement in Part 4 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ, general: the form must be determined by the head of the economic entity. Therefore, in order to avoid disagreements with regulatory authorities, it is better to approve the use of unified forms by order of the head or provide for in the accounting policy.
Special attention should be paid to the issue of the use of unified forms for registration of events that occur in the field of labor relations (hiring, dismissal of an employee, granting him leave, etc.).
According to Rostrud, after the entry into force law N 402-FZ, that is, from January 1, 2013, non-governmental organizations have the right to use the forms of primary accounting documents developed by them independently (Letters of 01/09/2013 N 2-TK, from 23.01.2013 N PG/10659-6-1, from 02/14/2013 N PG/1487-6-1).
As an example, Rostrud mentions an employee's personal card (Form N T-2) and notes that the primary accounting document must contain all the required details established by Part 2 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ. Similar clarifications were given to non-governmental organizations regarding forms N T-3 "staffing" (Letter Rostrud dated January 23, 2013 N PG / 409-6-1).
Employee personal card form (Form N T-2), as well as other unified forms of primary accounting documents for accounting for labor and its payment, approved by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation of 01/05/2004 N 1 (hereinafter - Decree N 1).
At the same time, it must be taken into account that the requirements for the application of this unified forms to maintain military registration installed item 27 Regulations on military registration (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 27, 2006 N 719 in accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. eight Federal Law of March 28, 1998 N 53-FZ "On military duty and military service").
Considering the issue of processing primary documents when sending an employee on a business trip, the Ministry of Labor of Russia in Letter dated 14.02.2013 N 14-2-291 noted that the relevant documents (in particular, travel certificate) must be drawn up in the forms approved by Decree N 1. Rostrud in the Letter of 03/04/2013 N 164-6-1 also explained that when issuing a travel certificate, you should use the unified form N T-10 and be guided by the instructions for filling it out, approved by this Decree.
When clarifying the issue of accounting for working time in the case of employees working on shift schedule Ministry of Labor of Russia ( item 3 Letters dated 05/24/2013 N 14-1-1061) noted that Part 4 Art. 91 The Labor Code of the Russian Federation establishes the obligation of the employer to keep records of the time worked by employees. For this, unified forms of the time sheet are provided. N N T-12 and T-13 approved by Decree No. 1.
As the Ministry of Finance of Russia pointed out in Information N PZ-10/2012 from January 1, 2013, the forms of primary accounting documents established by the authorized bodies in accordance with other federal laws and on the basis of such laws remain mandatory for use.
In addition, it should be noted that the requirements for primary accounting documents contained in Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ can only be partially applied to documents used to process events in the field of labor relations. Yes, in Part 5 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ provides for the possibility of compiling a primary accounting document in electronic form. At the same time, labor code Russian Federation and other regulatory legal acts containing norms labor law, this possibility is not allowed. For example, in par. 3 p. 26 Regulations on the specifics of sending employees to business trips, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 N 749, it is expressly established that the employee's report on the work performed on a business trip is submitted to the employer in writing. Unified forms of assignment, report on its implementation and travel certificate are also contained in Decree N 1.
In view of the foregoing, it can be concluded that the execution of documents using independently developed forms for recording labor and its payment may cause claims from the inspection authorities, since the new form may not take into account (not fully take into account) the requirements of labor legislation for a specific document.
For example, an employee's personal card should contain columns in which it is necessary to enter information about the work performed, transfer to another permanent job and dismissal ( item 12 Rules for maintaining and storing work books, making forms work book and providing employers with them, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of April 16, 2003 N 225). At the same time, this information is not included in the list given in Part 2 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ.
Thus, with regard to the preparation of documents on accounting for labor and its payment, it is currently more expedient for organizations to use unified forms approved by Decree N 1. And, as already noted, the use of these unified forms in accordance with Part 4 Art. 9 Law N 402-FZ must be approved either by a separate order of the head of the organization, or by an annex to the accounting policy.
Technology of substantiation (planning) of the number of personnel "
On the example of a specific organization (enterprises, institutions)
Information about the enterprise where the methodology for planning a labor indicator (personnel work) is being studied
- Name
- location
-actual types of economic activity carried out
- present the following indicators in the analytical table (Table 1)
The figures are produced for the last reporting year (2012-13)
Table No. 1 Implementation of the plan for the main social economic indicators enterprises
Indicate whether it will be studied in the organization of headcount planning as a whole for the enterprise or for a separate structural unit
Schematically (in the figure) display the functional interaction structural divisions(positions) assigned to workforce planning.
Reveal the planning methodology
- stages (terms) of planning
- periodicity
-information base of the plan's employees (on the basis of what documents, information the plan is being developed)
- formulas for calculating the target indicator
- plan form (photocopy)
Give a specific example of headcount planning with calculations of the category of personnel.
Table 2. Balance of working time per employee
|
Balance indicator |
Calculation procedure |
|||
|
Calendar fund of time, days |
||||
|
Number of weekends and holidays |
According to working mode |
10 (holiday only) |
||
|
Number of calendar working days |
||||
|
Number of days away from work |
In accordance with planned absenteeism estimates |
|||
|
Number of actual business days |
||||
|
Changes in working hours due to a reduction or increase in the working day, h |
In accordance with planned calculations |
|||
|
Average working day, h |
Normal duration subject to change |
|||
|
Normative (useful) fund of working time F t, h |
p. 7 x p. 5 + p. 6 |
10 x 350 + 8 = 3508 |
Table 3 - calculation of the number of personnel in the repair shop of the LHF based on data on the labor intensity of the work process
|
Index |
Diagnostics repair |
||||
|
brake automatic. |
brake automatic. |
hitch system |
hitch system |
||
|
Labor intensity of the product, h |
|||||
|
Production program, units |
|||||
|
Total, the complexity of the program, h |
|||||
|
Time to change the balance of work in progress, h |
|||||
|
Total labor intensity of work under the program for both types of diagnostics and repair, h |
|||||
|
Planned percentage of compliance with the norms,% |
|||||
|
Time required to complete the program, h |
|||||
|
Normative (useful) time fund of one employee, H |
|||||
|
Estimated number of personnel, h |
|||||
|
Accepted number of personnel, persons |
Thus, according to the calculations made, the planned number of workers in the repair shop of the LHF in 2011 will be 60 people.
The results obtained will make it possible to make informed decisions on providing the enterprise with personnel.
Solution
A variation of the method under consideration is the method for determining the number of administrative and managerial personnel H and using the Rosencrantz formula in general view:
,
where n-- the number of types of organizational and managerial work that determines the load of this category of specialists;
m i-- the average number of certain actions (settlements, order processing, negotiations, etc.) within the i-th organizational and managerial type of work for a specified period of time (for example, for a year);
t i-- the time it takes to complete the unit m within i th organizational and managerial type of work;
T- working hours of a specialist according to employment contract(contract) for the corresponding period of calendar time taken in the calculations;
t R- time for various works that cannot be taken into account in preliminary (scheduled) calculations;
To n.r.v -- the coefficient of the necessary distribution of time;
To f.r.v -- the coefficient of the actual distribution of time.
The coefficient of necessary distribution of time Kn.r.v is calculated as follows:
K n.r.v \u003d K d.r x K o x K p,
where K d.r is a coefficient that takes into account the costs of additional work, not taken into account in advance in the time required for a particular process? m it i(as a rule, it is in the range of 1.2 ... 1.4);
To about -- the coefficient taking into account the time spent on the rest of employees during the working day (set at 1.12);
K n -- the coefficient of conversion of the attendance to the payroll.
The coefficient of the actual distribution of time K f.r.v is determined by the ratio of the total fund of working time of any unit to the time calculated as? m it i.
It should be noted that, in general terms, the Rosencrantz formula serves to check whether the actual number of personnel (for example, of any unit) is necessary, which depends on the load of this unit.
To use the Rosencrantz formula in planned calculations, it should be given the following form:
,
since the quantities t p and K d.f.w are unknown in this case.
Let us give an example of calculating the number of administrative and managerial personnel using the Rosencrantz formula based on the following initial data.
Number of actions to perform work:
A -- 500
B -- 3000
V -- 300
Time required to perform actions for each job, h:
A - 1
B - 0.5
· AT 3
Monthly (normative) fund of time of one employee according to the contract, h -- 170
The coefficient of time spent on additional work -- 1.3
The coefficient of time spent on rest of employees -- 1.12
Coefficient of conversion of attendance to payroll -- 1.1
The time allocated for various work not included in the planned calculations, h - 200
The actual number of units, people. -- thirty
The total time for the implementation of organizational and managerial work:
(500 x 1) + (3000 x 0.5) + (300 x 3) = 2900.
Required time allocation factor:
K n.r.v \u003d 1.3 x 1.12 x 1.1 \u003d 1.6.
Actual Time Allocation Coefficient:
The required number of units is calculated using the full Rosenkranz formula:
As indicated in the initial data, the actual number of units is 30 people. Thus, the calculation of the required number showed a surplus (1 person) of the actual number of employees.
Service rate calculation method
The number of workers Ch p according to service standards is calculated by the formula:
Service rates are determined by the formula:
Where F t -- normative (useful) fund of the employee's working time per day (shift);
n-- the number of types of works on maintenance of the facility;
t units i -- time required to complete a unit of volume i-th type of work;
n R і -- number of volume units i-th type of work per unit of equipment or other calculation object (for example, per unit of production area);
T e - the time required for the employee to perform additional functions that are not included in t units i.
You can calculate the number of workers using service rates based on the following data:
Operation execution time for such works, h:
loading of the unit - 0.02
workflow control -- 0.08
unit unloading - 0.03
Number of operations per shift:
unit loading -- 60
workflow control -- 120
unit unloading -- 60
Number of units -- 8
Load factor -- 1.5
Normative (useful) fund of time of one worker per shift, h - 7.0
Time for additional maintenance operations of the unit, h -- 1.4
First, the service standards are defined:
Hence the number of workers:
Calculation method for jobs and headcount standards
This method is used in the case of using the method of calculation according to service standards, since both the required number of employees in terms of the number of jobs and the headcount standards are set based on service standards. The number of employees by jobs is determined by the formula:
.
The population standards are calculated as follows:
As you can see, it is quite simple to calculate the required number of employees, and the results obtained will make it possible to make informed decisions on providing the enterprise with personnel.
Bibliography
1. Rich, I. N. Accounting. Series " Tutorials» / I. N. Bogataya, N. N. Khakhonova. Rostov n / a: Phoenix, 2012. - 608 p.
2. Egorshin, A. P. Personnel management: Textbook for universities. 3rd ed. / A. P. Egorshin. - N. Novgorod: NIMB, 2011. - 720 p.
3. Information base http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_144025/
Hosted on Allbest.ru
...Similar Documents
Exploring the Essence personnel planning- the activities of the organization to provide jobs at the right time and in the required quantity in accordance with the abilities, inclinations of employees. Calculation of the number of production personnel.
abstract, added 05/27/2010
The study of the essence, goals and objectives of personnel planning. Consideration of the main types and stages of personnel planning. a brief description of enterprises LLC "Dream". Evaluation of the personnel planning process at a given enterprise, personnel management.
term paper, added 04/21/2015
Material-technical and socio-economic conditions of production. Analysis of the dynamics of the number of personnel and the labor intensity of coal mining processes. Planning the number of industrial and production personnel and labor productivity indicators.
term paper, added 02/14/2010
Conceptual basis of search and recruitment. Instrumental methods of personnel selection. Empirical bases of personnel selection. Definition of the subject of the personnel planning process. The problem of integrating personnel planning into the plans of the organization.
term paper, added 10/15/2007
The main stages of headcount planning manufacturing enterprise. Peculiarities of planning the need for personnel in "Sakartvelo" LLC. Linear structure restaurant management. Planned staffing. Analysis of economic indicators.
term paper, added 06/16/2014
The concept of the number and structure of personnel. Personnel planning. Personnel planning. Methods for forecasting staffing needs. Determination of the number of personnel. Professional staff planning.
term paper, added 04/04/2006
Consideration of functions (stimulating, status), forms and systems (piecework, time-based, tariff-free) remuneration at the enterprise. Characteristics of payroll planning methods. The study international experience contractual regulation of wages.
thesis, added 03/27/2010
Headcount planning: concept, essence, determination of future needs. Line managers in the field of personnel planning. Brief organizational description of LLC "Mirage", features of the personnel section. Restaurant schedule.
test, added 12/02/2014
The essence of labor rationing as a function rational organization labor. Optimization of the division of labor and the number of personnel. Professional staff planning. Standards for the number of specialists and employees. Division and cooperation of labor.
term paper, added 12/02/2007
The essence, types and significance of modern forms of organization of personnel work. Methodology for calculating the number of raters, the percentage of compliance with the standards by the brigade and the normative labor intensity. Analysis and assessment of the state of labor rationing in teams, ways to improve it.
The calculation of the staffing is made taking into account the peculiarities of the structure of the organization, functions and levels of management. Learn how to determine the staffing, what formulas to apply.
From the article you will learn:
What is headcount: definition
The calculation of the number of employees should be carried out in order to optimize the number of employees. To ensure that personnel costs do not exceed the norm, and the organization is able to receive a stable profit, it is rational to apply industry standards calculated by research institute specialists.
Based on the calculation of the staffing, such indicators are determined as:
the amount of time required by employees of the relevant specialty and qualifications to perform work of a certain complexity;
the number of employees who should be involved in a particular division of the company.
Total cost per year/h
Normative fund of working time of each employee for one year in hours
The coefficient of absenteeism during the next vacation, illness, etc.
The normative working time fund is conditionally taken as two thousand hours. These calculation recommendations are given for budgetary organizations. But the standard for calculating the nominal value can also be applied commercial organizations. The relevant laws and regulations have approved the standards for employees:
- legal services;
- financial services;
- accounting;
- labor protection services;
- military accounting tables;
- laundries;
- boiler houses;
- health-improving complexes, etc.
How is the headcount calculated
The number of employees is the number of personnel of the relevant specialty and qualifications sufficient to perform the tasks. When determining the standard value, it is necessary to use a simple formula:
- V is the planned scope of work, the figures are requested from the heads of the department;
- Frv refers to the fund of working time for the corresponding planning period. On average, the annual fund of time with a 40-hour week is 2004 hours, the monthly one is 176 hours;
- Vpl indicates the planned output per employee. You can request indicators from the heads of departments;
- Kvn takes into account the planned coefficient for the implementation of standards. The indicators are determined in the ratio of the planned output of a certain period in the current year and the actual output of the same period of the previous year. The indicators are requested from the heads of structural divisions.
Example
15 people worked in the sales department. The general director of the enterprise considered that this is a lot for small company, and asked the HR director to calculate and determine whether it is possible to reduce the staff of the relevant unit. The HR director used the standard formula: H = V: (Frv × Vpl × Kvn). The sales volume planned for the period from January to November 2017 was used as the basis for the planned volume of indicator V. The figure was 1,264,710,000 rubles. The working time fund in terms of FW from January to November 2017 amounted to 1803 hours. The planned output per one specialist in terms of GPL for the accounting period amounted to 66,699 rubles. At the same time, the actual output for the accounting and comparable similar period of the previous 2016 is 60,305 rubles. The planned coefficient for fulfilling the norms of Kvn indicators was calculated as follows: 66,699: 60,305 = 1.11. These indicators were substituted into the standard formula and the corresponding result was obtained: 1,264,710,000: (1803 × 66,699 × 1.11) = 9 people. The figure directly showed that the number of staff was exceeded, and the staff needed to be reduced.
Read also:
Accounting staffing standard
The calculation of the staffing of the accounting department is carried out taking into account the relevant industry norms. When determining the number of accountants, the standard number of employees of the enterprise and all structural divisions is taken into account. For each measurement range, different calculated dependencies are used and specially developed formulas are used. The specifics of the work of each enterprise and such indicators as:
- number of serviced structural divisions;
- odds specific gravity on accounting.
The regular and actual size of employees are two different units. In each range, different dependences of the calculated data are applied. If the company conducts specific species accounting, the results of the number of accountants will differ significantly than with typical types of work.
How to determine the number of staff members of the organization and departments
The calculation of the staff value is carried out taking into account the fact that the standard number of employees is an idealistic state of affairs. The regulations do not take into account that employees periodically get sick, go on vacation, etc. the employer needs to determine how many people will be required to replace temporarily absent staff. To answer this question, it is necessary to define a list value. The indicators are determined by the formula:
H is the standard number of employees;
Kn reflects the planned absenteeism rate. The indicator is calculated according to the following formula: Кн = 1 + Дн. At the same time, Dn is the determining share of non-working time in the total fund of all working time, calculated according to the production calendar. The indicators are defined as total amount hours of absenteeism divided by the estimated total of all work hours in the corresponding specified period.
Example
The HR director calculated the standard size of the sales department. The result was the number 9. To calculate the headcount, the planned absenteeism rate was determined - Kn, starting from January to November 2017. The following data were taken into account: the number of non-working days during the year is 49, of which 28 days are planned holidays, plus 7 days without pay in accordance with Labor Code and plus 14 days standard sick leave, that's 392 hours based on an 8-hour week. The share of all non-working hours according to the Days formula was: 392 hours (absenteeism): 1,803 hours (taking into account the total number of working days). The result was 0.22. Absenteeism coefficient in January-November: 1 + 0.22 = 1.22. The required staffing is 9 × 1.22 = 11 employees.
Note! The concept of staffing is closer to reality than the normative, which always turns out to be much lower in calculations. When saving the budget for wages, it is rational to choose the average.
On what indicators does the structure and staff size depend
Structure and staff size are two comparable concepts. When calculating the regular number of employees, it is always worth considering the structural features of the organization. It is necessary to identify disproportions between the number of managers and ordinary employees:
see how many staff each accountant, economist, lawyer serves;
quantify production departments, serving units;
the number of subordinates for each leader.
The nominal value, based on the effectiveness of management, is:
for top-level managers - from three to five;
for the middle link - from seven to nine.
These norms have been used for a long time at enterprises of all forms of ownership. They were developed by the French scientist Graikūnas and are recognized worldwide as classics. If the number of subordinates exceeds the specified standards, the level of staff management drops sharply.
The maximum staffing of an institution is calculated according to formulas, taking into account profitability and economic feasibility. It is important to normative and staffing indicators corresponded to the optimal number necessary for the successful completion of the tasks.
Recommendations for substantiating the staffing of the organization
Alina Malysheva, HR Director at Solta-Invest, recommends:
When the company summed up the results for the year, CEO requested from financial director data on how much money each unit spent. The head of the organization noticed that the HR department, which does not produce or sell anything, over the past year cost the company a little less than the marketing department. The general director had a question: what are the costs of the personnel service. The HR director promised to budget for his service, but ran into a problem. There are a lot of publications in magazines and on the Internet about the budget for personnel in general, but there is almost nothing about the budget of the HR service. I decided to give advice to a colleague so that the proposed costs would not raise objections from the budget committee.
Check with the CEO about company development plans and expectations from the HR service. With this in mind, develop a budget
Find out what the company plans to change the number of employees. If the company is going to expand, then you will need to hire new recruiters and development managers, train department heads in interviewing skills, establish cooperation with universities, and expand the company's presence on job search sites. Put these costs into your HR budget.
Then specify which priority tasks the head of the company puts before your division on next year. What makes the CEO happy or unhappy with HR? Does he have any suggestions for changing the social package or motivation system, or information about the experience of other companies, which, in his opinion, should be adopted? Answering these questions will help you create an HR budget that fits your business needs. So, such a budget will be easier to protect.
Important Findings
- Budgeting for HR next year, ask the director if he plans to expand the company. If yes, then budget for the cost of increasing the staff of the HR service and training managers.
- In the item of expenses for training, first of all, provide for the costs of training a labor protection specialist and a C&B manager, if they are in the staff of the HR service.
- For protection, prepare three versions of the budget: optimistic, pessimistic and optimal. And keep in mind the “minimum plan” - expenses that cannot be abandoned under any circumstances.
Download form










Quality requirements
Peat resources Milling peat extraction
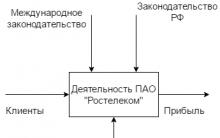
Closed Joint Stock Company Transtelecom
Setting up Wi-Fi equipment
Pasteurization drawer for the selection of "heads" during rectification